CPphysics review 2-10
... 3) A person pushes a 10 kg box at a constant velocity over a distance of 4 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the floor is 0.3. How much work does the person do in pushing the box? (the applied force is horizontal). a) 12.0 J b) 29.4 J c) 118 J d) 392 J ...
... 3) A person pushes a 10 kg box at a constant velocity over a distance of 4 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the floor is 0.3. How much work does the person do in pushing the box? (the applied force is horizontal). a) 12.0 J b) 29.4 J c) 118 J d) 392 J ...
Physics 11 Dynamics - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. Why does a child in a wagon seem to fall backward when you give the wagon a sharp pull? 3. If the acceleration of a body is zero, are no forces acting on it? 4. Why do you push harder on the pedals of a bicycle when first starting out than when moving at a constant speed? 5. Only one force acts o ...
... 2. Why does a child in a wagon seem to fall backward when you give the wagon a sharp pull? 3. If the acceleration of a body is zero, are no forces acting on it? 4. Why do you push harder on the pedals of a bicycle when first starting out than when moving at a constant speed? 5. Only one force acts o ...
2 - ScienceScene
... of- war. Realcontexts: Changing the direction--changing the direction of a billiard ball, bus turning a corner; changing the speed--car speeding up, a rolling ball slowing down, magnets changing the motion of objects, walking, swimming, jumping, rocket motion, objects resting on a table, tug- of- wa ...
... of- war. Realcontexts: Changing the direction--changing the direction of a billiard ball, bus turning a corner; changing the speed--car speeding up, a rolling ball slowing down, magnets changing the motion of objects, walking, swimming, jumping, rocket motion, objects resting on a table, tug- of- wa ...
Work PRobs - New Haven Science
... **14. Determine the work done on a sled that is pulled 20.0 m by a 105 N force applied at an angle of 50° to the horizontal. 15. A 34.5 kg box with an initial velocity of 10.0 m/s slides to a stop along a level road. If the displacement of the box is 17.5 m, determine the force of friction on the bo ...
... **14. Determine the work done on a sled that is pulled 20.0 m by a 105 N force applied at an angle of 50° to the horizontal. 15. A 34.5 kg box with an initial velocity of 10.0 m/s slides to a stop along a level road. If the displacement of the box is 17.5 m, determine the force of friction on the bo ...
Document
... 41. Acceleration that always points towards the center of a circle is called ____________ acceleration. 42. A sprinter runs at a speed of 3.00 m/s on a circular track that has a radius of 40.00 m. Find the centripetal acceleration of the sprinter. 43. A car moving at 12.67 m/s rounds a bend in the r ...
... 41. Acceleration that always points towards the center of a circle is called ____________ acceleration. 42. A sprinter runs at a speed of 3.00 m/s on a circular track that has a radius of 40.00 m. Find the centripetal acceleration of the sprinter. 43. A car moving at 12.67 m/s rounds a bend in the r ...
Exam 1 F11
... 5) A sheet of paper can be withdrawn from under a container of milk without toppling it if the paper is jerked quickly. This best demonstrates that A) the milk carton has inertia. B) gravity tends to hold the milk carton secure. C) there is an action‐reaction pair of forces. D) the milk carton has n ...
... 5) A sheet of paper can be withdrawn from under a container of milk without toppling it if the paper is jerked quickly. This best demonstrates that A) the milk carton has inertia. B) gravity tends to hold the milk carton secure. C) there is an action‐reaction pair of forces. D) the milk carton has n ...
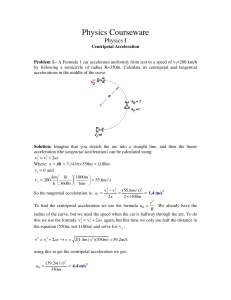
AP centripetal accelerations
... Problem 8.- The radius of a curve in the highway is 220m. What is the maximum possible speed of a vehicle rounding the curve if the centripetal acceleration should not exceed 3.5 m/s2? Give your answer in miles per hour. [1 mile=1609m]. Solution: The maximum velocity will happen when the car has ma ...
... Problem 8.- The radius of a curve in the highway is 220m. What is the maximum possible speed of a vehicle rounding the curve if the centripetal acceleration should not exceed 3.5 m/s2? Give your answer in miles per hour. [1 mile=1609m]. Solution: The maximum velocity will happen when the car has ma ...
Chapter 3 lecture notes pdf
... slides down at constant velocity. What is the friction force that acts on the bear? 2. How does the force of gravity on a raindrop compare with the air drag it encounters when it falls at constant velocity? 3. Upon which will air resistance be greater; a sheet of falling paper or the same paper wadd ...
... slides down at constant velocity. What is the friction force that acts on the bear? 2. How does the force of gravity on a raindrop compare with the air drag it encounters when it falls at constant velocity? 3. Upon which will air resistance be greater; a sheet of falling paper or the same paper wadd ...
If you put your cursor over a text box, it will be an arrow and WILL
... example of acceleration? a) A runner moving at a constant speed of 2 m/s in a straight line. b) A car going at a constant speed around a circular track. c) An airplane taxiing at a constant speed in a straight line. d) All of the above. ...
... example of acceleration? a) A runner moving at a constant speed of 2 m/s in a straight line. b) A car going at a constant speed around a circular track. c) An airplane taxiing at a constant speed in a straight line. d) All of the above. ...
Physics Laboratory #1: Simple Harmonic Motion
... Tension – A rope exerts a pull at each end that is equal to the tension force in the rope. Normal Force – The force pushing two surfaces together (FN). Frictional Force – The force that opposes motion between two surfaces in contact. The force is parallel to the surfaces. Static friction is th ...
... Tension – A rope exerts a pull at each end that is equal to the tension force in the rope. Normal Force – The force pushing two surfaces together (FN). Frictional Force – The force that opposes motion between two surfaces in contact. The force is parallel to the surfaces. Static friction is th ...