Unit 7 Vocabulary
... Friction- a force that opposes motion between objects that are touching Line graph- graph used to represent the relationship between two variables. Constant speed- to travel at a steady pace not changing the speed of an object. Relative motion- the motion of an object as compared to another object D ...
... Friction- a force that opposes motion between objects that are touching Line graph- graph used to represent the relationship between two variables. Constant speed- to travel at a steady pace not changing the speed of an object. Relative motion- the motion of an object as compared to another object D ...
First
... Question: An object is being pushed along at constant velocity by a force of 5 N [left]. What is the force of friction acting on the object? If the velocity is constant, there is no net force, so the force of friction must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the applied force: Ff = 5 ...
... Question: An object is being pushed along at constant velocity by a force of 5 N [left]. What is the force of friction acting on the object? If the velocity is constant, there is no net force, so the force of friction must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the applied force: Ff = 5 ...
GSCI 101A - Section 006
... 35. In a hydrogen atom, an electron drops from the n = 5 orbital to the n = 3 orbital. What is the wavelength of light emitted by this change? a) 6.84 x 10-7 m b) 7.81 x 10-5 m c) 1.28 x 10-6 m d) 1.46 x 10-6 m c. 36. In exerting a 105-N force on a 20.5-kg crate as you push it across a frictionless ...
... 35. In a hydrogen atom, an electron drops from the n = 5 orbital to the n = 3 orbital. What is the wavelength of light emitted by this change? a) 6.84 x 10-7 m b) 7.81 x 10-5 m c) 1.28 x 10-6 m d) 1.46 x 10-6 m c. 36. In exerting a 105-N force on a 20.5-kg crate as you push it across a frictionless ...
Applications of Integration handout
... to speak. You recognize a potential application of integration by seeing that you can approximate the thing you’re interested in as a sum of small pieces, and get a better approximation by using a larger number of smaller pieces. Then, some computation like this is needed to tell you exactly what in ...
... to speak. You recognize a potential application of integration by seeing that you can approximate the thing you’re interested in as a sum of small pieces, and get a better approximation by using a larger number of smaller pieces. Then, some computation like this is needed to tell you exactly what in ...
Review for Final Exam - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... a) the distance that Jocelyn drove {41 km} b) her displacement {28 km[W28oN]} c) her average speed {46 km/h} d) her average velocity {31 km/h[W28oN]} 59. A pilot wants to fly due north. However, a strong wind is blowing from the west. Therefore the pilot maintains a heading of a few degrees west of ...
... a) the distance that Jocelyn drove {41 km} b) her displacement {28 km[W28oN]} c) her average speed {46 km/h} d) her average velocity {31 km/h[W28oN]} 59. A pilot wants to fly due north. However, a strong wind is blowing from the west. Therefore the pilot maintains a heading of a few degrees west of ...
Planetary Properties - University of Dayton
... Note: the speed can easily be determined from knowledge of the radius of the orbit and the period. In one period, the object must travel a distance equal to the circumference of the orbit: ...
... Note: the speed can easily be determined from knowledge of the radius of the orbit and the period. In one period, the object must travel a distance equal to the circumference of the orbit: ...
chapter 4 - forces and newton`s laws of motion
... are considering are called Static(friction when the two surfaces involved are not moving) and Kinetic(they are moving) Friction exists because rough surfaces interlock and reduce or stop motion. Even if surfaces are polished as smooth as possible, other factors play a role. These forces are the dipo ...
... are considering are called Static(friction when the two surfaces involved are not moving) and Kinetic(they are moving) Friction exists because rough surfaces interlock and reduce or stop motion. Even if surfaces are polished as smooth as possible, other factors play a role. These forces are the dipo ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. Obtain the equations of motion of a simple pendulum by using Lagrangian method and hence deduce the formula for its time period for small amplitude oscillations. 12. Derive an expression for the rotational kinetic energy of a rigid body. 13. Show that the shortest distance between two points in ...
... 11. Obtain the equations of motion of a simple pendulum by using Lagrangian method and hence deduce the formula for its time period for small amplitude oscillations. 12. Derive an expression for the rotational kinetic energy of a rigid body. 13. Show that the shortest distance between two points in ...
GRADE 10F: Physics 2
... Get pairs or small groups of students to use a forces board to measure forces acting on an object and draw the corresponding vector diagram. The diagram will probably show a (small) non-zero resultant force. Discuss the reasons for this (e.g. frictional forces, uncertainty in measurement of forces a ...
... Get pairs or small groups of students to use a forces board to measure forces acting on an object and draw the corresponding vector diagram. The diagram will probably show a (small) non-zero resultant force. Discuss the reasons for this (e.g. frictional forces, uncertainty in measurement of forces a ...
(null): 033.NL1
... keeps penny in place ??? (Inertia = stay-puttedness) c. Stack of coins “trick” 1) Stack of 5 or so pennies 2) How can you remove the bottom one without touching the others? 3) Use card to knock bottom penny out sideways while inertia of rest of stack keeps them in place d. What keeps upper pennies i ...
... keeps penny in place ??? (Inertia = stay-puttedness) c. Stack of coins “trick” 1) Stack of 5 or so pennies 2) How can you remove the bottom one without touching the others? 3) Use card to knock bottom penny out sideways while inertia of rest of stack keeps them in place d. What keeps upper pennies i ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... future. They only know what forces act on them right now. Newton’s First Law of Motion Every object continues in a state of rest or a state of motion with a constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion When a force, F, acts on an object with a ...
... future. They only know what forces act on them right now. Newton’s First Law of Motion Every object continues in a state of rest or a state of motion with a constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion When a force, F, acts on an object with a ...
Mechanical Energy
... When a force acts in a direction that is not in line with the displacement, only part of the force does work. The component of F that is parallel to the displacement does work, but the perpendicular component of F does zero work. So, a more general formula for work is ...
... When a force acts in a direction that is not in line with the displacement, only part of the force does work. The component of F that is parallel to the displacement does work, but the perpendicular component of F does zero work. So, a more general formula for work is ...
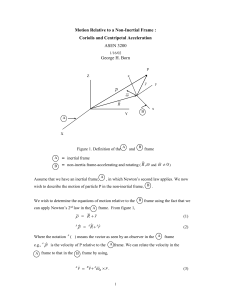
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
Wksht Momentum and Collisions
... 4. A car of mass 700 kg is travelling at 20 m/s [N] toward an intersection. If it collides with a stationary truck of mass 1300 kg, and they lock bumpers as a result of the collision. What is the final velocity of the truck? 5. A bullet of mass 50 g strikes a stationary wooden block of mass 5 kg. Th ...
... 4. A car of mass 700 kg is travelling at 20 m/s [N] toward an intersection. If it collides with a stationary truck of mass 1300 kg, and they lock bumpers as a result of the collision. What is the final velocity of the truck? 5. A bullet of mass 50 g strikes a stationary wooden block of mass 5 kg. Th ...
Slide 1 - Phy 2048-0002
... 5. There are two forces on the 2 kg box in the overhead view of the figure below but only one is shown. The figure also shows the acceleration of the box. Find the second force (a) in unit-vector notation and as (b) magnitude and (c) direction. ...
... 5. There are two forces on the 2 kg box in the overhead view of the figure below but only one is shown. The figure also shows the acceleration of the box. Find the second force (a) in unit-vector notation and as (b) magnitude and (c) direction. ...
Physics 6A - UCSB C.L.A.S.
... the spring and block are pulled forward at constant speed, the spring stretches by 25 cm. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table. The key phrase here is “constant speed”. Since the block is moving at constant speed (and direction) we know that its acceleration is 0. ...
... the spring and block are pulled forward at constant speed, the spring stretches by 25 cm. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table. The key phrase here is “constant speed”. Since the block is moving at constant speed (and direction) we know that its acceleration is 0. ...