conceptual physics c#39AC39
... What is rotational inertia, and how does it compare to inertia as studied in previous chapters? Ans. Rotational inertia, often called moment of inertia, is the sum of the products of an object’s mass multiplied by their distance to the center of rotation squared. Inertia is the resistance an object ...
... What is rotational inertia, and how does it compare to inertia as studied in previous chapters? Ans. Rotational inertia, often called moment of inertia, is the sum of the products of an object’s mass multiplied by their distance to the center of rotation squared. Inertia is the resistance an object ...
Experiment 5 - Atwood`s Machine
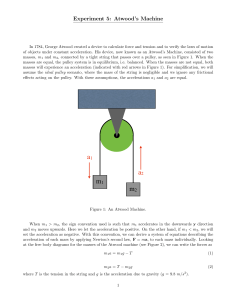
... When m1 > m2 , the sign convention used is such that m1 accelerates in the downwards y direction and m2 moves upwards. Here we let the acceleration be positive. On the other hand, if m1 < m2 , we will set the acceleration as negative. With this convention, we can derive a system of equations describ ...
... When m1 > m2 , the sign convention used is such that m1 accelerates in the downwards y direction and m2 moves upwards. Here we let the acceleration be positive. On the other hand, if m1 < m2 , we will set the acceleration as negative. With this convention, we can derive a system of equations describ ...
1, 3, 6, 10, 11, 17, 21 / 1, 4, 12, 15, 20, 24, 28, 36, 38
... 11. REASONING AND SOLUTION The weight of the ball always acts downward. The force of air resistance will always act in the direction that is opposite to the direction of motion of the ball. The net force on the ball is the resultant of the weight and the force of air resistance. a. As the ball moves ...
... 11. REASONING AND SOLUTION The weight of the ball always acts downward. The force of air resistance will always act in the direction that is opposite to the direction of motion of the ball. The net force on the ball is the resultant of the weight and the force of air resistance. a. As the ball moves ...
PS02H - willisworldbio
... • ________ is the rate of change of velocity. When the _______ of an object changes, the object is accelerating. • A change in velocity can be either a change in how _____ something is moving, or a change in the ______ it is moving. • Acceleration occurs when an object changes its _____, it's _____ ...
... • ________ is the rate of change of velocity. When the _______ of an object changes, the object is accelerating. • A change in velocity can be either a change in how _____ something is moving, or a change in the ______ it is moving. • Acceleration occurs when an object changes its _____, it's _____ ...
Review- some Forces, CF, Friction
... unless the curve is banked. • A curve that is banked changes the direction of the normal force. • The normal force, which is perpendicular to the surface of the road, can provide the force required for circular motion. • In this way, you can round the curve even when there is no friction ……. but onl ...
... unless the curve is banked. • A curve that is banked changes the direction of the normal force. • The normal force, which is perpendicular to the surface of the road, can provide the force required for circular motion. • In this way, you can round the curve even when there is no friction ……. but onl ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... with the cart’s acceleration. The total mass of the cart is easy to vary by adding masses. Using these tools, you can determine how the net force on the cart, its mass, and its acceleration are related. This relationship is Newton’s second law of motion. ...
... with the cart’s acceleration. The total mass of the cart is easy to vary by adding masses. Using these tools, you can determine how the net force on the cart, its mass, and its acceleration are related. This relationship is Newton’s second law of motion. ...
Science TAKS Objective 5
... The ideal mechanical advantage of a machine (IMA) of a machine is the number of times the output force is larger than the input force IMA=Fout/Fin A machine can only make this happen by moving the input force through a farther distance than the output force ...
... The ideal mechanical advantage of a machine (IMA) of a machine is the number of times the output force is larger than the input force IMA=Fout/Fin A machine can only make this happen by moving the input force through a farther distance than the output force ...
Spring Forces and Simple Harmonic Motion
... Simple Harmonic Motion x Acost displacement vs. t ...
... Simple Harmonic Motion x Acost displacement vs. t ...