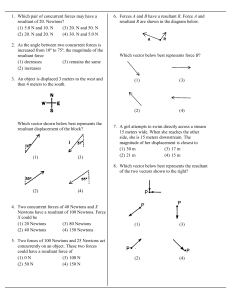
Forces Review Game
... Andy pushes 65 kg crate with a horizontal force of 250 N across the physics portable at a constant velocity of 3.0 m/s. Trying to be helpful and knowing a bit of physics, Betty uses a rope to pull directly up on the box. The coefficient of static friction is 0.70 and the coefficient of kinetic frict ...
... Andy pushes 65 kg crate with a horizontal force of 250 N across the physics portable at a constant velocity of 3.0 m/s. Trying to be helpful and knowing a bit of physics, Betty uses a rope to pull directly up on the box. The coefficient of static friction is 0.70 and the coefficient of kinetic frict ...
Laws of Motion - auroraclasses.org
... Laws of Motion Newton’s three Laws of motion are as given below: 1. Every body continues in its state of rest or of uniform motion unless it is compelled by some external force to change that state. 2. The rate of change of momentum is proportional to the impressed force and takes place in the direc ...
... Laws of Motion Newton’s three Laws of motion are as given below: 1. Every body continues in its state of rest or of uniform motion unless it is compelled by some external force to change that state. 2. The rate of change of momentum is proportional to the impressed force and takes place in the direc ...
Physics Final Review Sheet Name
... 21. If a force of 10 N is applied to an object with a mass of 1 kg, the object will accelerate at ...
... 21. If a force of 10 N is applied to an object with a mass of 1 kg, the object will accelerate at ...
PHYSICAL SCI E06 11
... 9. TSW explain how action and reaction forces are related according to Newton’s third law of motion and calculate the momentum of an object using the law of conservation of momentum. (p. 372 – 377) 10. TSW design or choose from a selection of investigations provided by the instructor and implement i ...
... 9. TSW explain how action and reaction forces are related according to Newton’s third law of motion and calculate the momentum of an object using the law of conservation of momentum. (p. 372 – 377) 10. TSW design or choose from a selection of investigations provided by the instructor and implement i ...
ce-phy ii
... Pisa. He found that the two balls reached the ground at almost the same time. Which of the following is/are correct deduction(s) from this experiment ? (1) The two balls fell with the same acceleration. (2) A body will maintain uniform motion if there is no external force acting on it. (3) The gravi ...
... Pisa. He found that the two balls reached the ground at almost the same time. Which of the following is/are correct deduction(s) from this experiment ? (1) The two balls fell with the same acceleration. (2) A body will maintain uniform motion if there is no external force acting on it. (3) The gravi ...
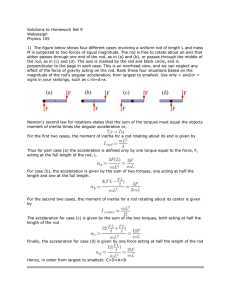
Solutions to Homework Set 9
... perpendicular to the page in each case. This is an overhead view, and we can neglect any effect of the force of gravity acting on the rod. Rank these four situations based on the magnitude of the rod's angular acceleration, from largest to smallest. Use only > and/or = signs in your rankings, such a ...
... perpendicular to the page in each case. This is an overhead view, and we can neglect any effect of the force of gravity acting on the rod. Rank these four situations based on the magnitude of the rod's angular acceleration, from largest to smallest. Use only > and/or = signs in your rankings, such a ...
Mass and Weight
... The force of gravity on any object is actually the weight of the object! So this means that because weight is a force it is measured in NEWTONS! The thing we usually call ‘weight’ and is measured in kilograms and grams is really called the MASS! ...
... The force of gravity on any object is actually the weight of the object! So this means that because weight is a force it is measured in NEWTONS! The thing we usually call ‘weight’ and is measured in kilograms and grams is really called the MASS! ...
Ph211_CH5_worksheet-f06
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
Sections 1 - Columbia Physics
... 3. A mass m can slide without friction in two dimensions on a horizontal surface. It is attached by a massless rope of length L to a second mass M through a hole in the surface. The mass M hangs vertically in a uniform vertical gravitational field g. (a) If the mass m moves in a circle of radius r0 ...
... 3. A mass m can slide without friction in two dimensions on a horizontal surface. It is attached by a massless rope of length L to a second mass M through a hole in the surface. The mass M hangs vertically in a uniform vertical gravitational field g. (a) If the mass m moves in a circle of radius r0 ...