C4_SecondLaw
... Newtons of force. If the friction force is 100 Newtons, does the crate accelerate? ...
... Newtons of force. If the friction force is 100 Newtons, does the crate accelerate? ...
Forces
... any change in its motion. An unbalanced force must act upon the object in order for its motion to change. ...
... any change in its motion. An unbalanced force must act upon the object in order for its motion to change. ...
Forces and Friction Worksheet (Key)
... • The amount of friction depends on two things: how smooth the objects are and how hard they push together. • There are four kinds of friction: 1. Static friction is between two things that are not moving. 2. Sliding friction happens when two objects slide past each other. 3. Rolling friction occurs ...
... • The amount of friction depends on two things: how smooth the objects are and how hard they push together. • There are four kinds of friction: 1. Static friction is between two things that are not moving. 2. Sliding friction happens when two objects slide past each other. 3. Rolling friction occurs ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... you push on a cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or, is the force related to something else? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter o ...
... you push on a cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or, is the force related to something else? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter o ...
newton`s lesson 6 homework
... 3. In a physics lab, Kate and Rob use a hanging mass and pulley system to exert a 2.45 N rightward force on a 0.500-kg cart to accelerate it across a low-friction track. If the total resistance force to the motion of the cart is 0.720 N, then what is the cart's acceleration? Answer: Fgrav = 4.90 N; ...
... 3. In a physics lab, Kate and Rob use a hanging mass and pulley system to exert a 2.45 N rightward force on a 0.500-kg cart to accelerate it across a low-friction track. If the total resistance force to the motion of the cart is 0.720 N, then what is the cart's acceleration? Answer: Fgrav = 4.90 N; ...
Holt Physics Chapter 8
... object’s mass and the distribution of mass around the axis of rotation. The farther the center of mass from the axis of rotation, the more difficult it is to rotate the object, and therefore, the higher the moment of inertia. Use Table 8-1, page 285 ...
... object’s mass and the distribution of mass around the axis of rotation. The farther the center of mass from the axis of rotation, the more difficult it is to rotate the object, and therefore, the higher the moment of inertia. Use Table 8-1, page 285 ...
Forces and Motion
... An object will remain at rest or in motion in a straight line at constant velocity (not accelerating) unless an UNBALANCED FORCE acts on the object. ...
... An object will remain at rest or in motion in a straight line at constant velocity (not accelerating) unless an UNBALANCED FORCE acts on the object. ...
Chapter 6 Motion
... • The object that appears to _______________ • _________ is commonly used as reference, buildings, trees • Reference point can also be _________ (Earth) • ____________ depends on Reference Point Distance ...
... • The object that appears to _______________ • _________ is commonly used as reference, buildings, trees • Reference point can also be _________ (Earth) • ____________ depends on Reference Point Distance ...
Lecture 03: Rotational Dynamics II: 2nd Law
... The force F1 will tend to cause a counterclockwise rotation about O The force F2 will tend to cause a clockwise rotation about O S 1 2 F1d1 – F2d2 If S 0, starts rotating Rate of rotation of an If S 0, rotation rate object does not change, does not change unless the object i ...
... The force F1 will tend to cause a counterclockwise rotation about O The force F2 will tend to cause a clockwise rotation about O S 1 2 F1d1 – F2d2 If S 0, starts rotating Rate of rotation of an If S 0, rotation rate object does not change, does not change unless the object i ...
Chapter 10 PowerPoint
... The Nature of Force Unbalanced Forces - acting on an object will change the object’s motion Unbalanced forces acting on an object result in a net force and cause a change in the object’s motion. Equal forces acting on one object in opposite directions are called balanced forces. Balanced Force ...
... The Nature of Force Unbalanced Forces - acting on an object will change the object’s motion Unbalanced forces acting on an object result in a net force and cause a change in the object’s motion. Equal forces acting on one object in opposite directions are called balanced forces. Balanced Force ...
Circular Motion Chapter
... around a circle. Period is a measure of time so the standard units for period are seconds and the symbol for period is “T” (easily confused with the symbol for Tension). If an object completes a certain number of rotations, n, in a given amount of time, t, then it follows that T = t/n, since that is ...
... around a circle. Period is a measure of time so the standard units for period are seconds and the symbol for period is “T” (easily confused with the symbol for Tension). If an object completes a certain number of rotations, n, in a given amount of time, t, then it follows that T = t/n, since that is ...
kx F = The Spring
... ❑ One way to understand SHM is to consider the circular motion of a particle and rotational kinematics (The Reference Circle) ❑ The particle travels on a circle of radius r=A with the line from the center to the particle making an angle θ with respect to the x-axis at some instant in time • Now, pr ...
... ❑ One way to understand SHM is to consider the circular motion of a particle and rotational kinematics (The Reference Circle) ❑ The particle travels on a circle of radius r=A with the line from the center to the particle making an angle θ with respect to the x-axis at some instant in time • Now, pr ...
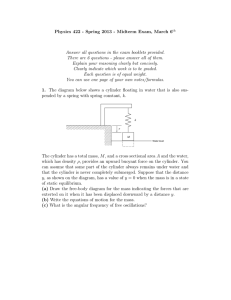
Physics 422 - Spring 2013 - Midterm Exam, March 6
... (a) If the pin on the wheel is at a radius r and the mass oscillates in the vertical direction with a maximum amplitude of 10r when the motor is driven at a frequency ω0 , what is the value of Q for this oscillating system? (b) When driven at the angular frequency ω0 , the mass has a peak kinetic en ...
... (a) If the pin on the wheel is at a radius r and the mass oscillates in the vertical direction with a maximum amplitude of 10r when the motor is driven at a frequency ω0 , what is the value of Q for this oscillating system? (b) When driven at the angular frequency ω0 , the mass has a peak kinetic en ...
Rotational Motion
... axis, will change its rotational motion when an external force exerts a torque on the object. • The magnitude of the torque due to a given force is the product of the perpendicular distance from the axis to the line of application of the force (the lever arm) and the magnitude of the force. • The ra ...
... axis, will change its rotational motion when an external force exerts a torque on the object. • The magnitude of the torque due to a given force is the product of the perpendicular distance from the axis to the line of application of the force (the lever arm) and the magnitude of the force. • The ra ...