final-96s
... rC/E = - 4 i + 3.37 j + 2.25 k ft eC/E = rC/E / | rC/E | = (-4 i + 3.37 j + 2.25 k ft)/((-4)2 + (3.37)2 + (2.25)2) eC/E = -0.703 i + 0.592 j + 0.395 k T = T eC/E = -0.703T i + 0.592T j + 0.395T k F = 20 i - 60 j lb Note: Since you don’t want any hinge reactions, easiest method to find the tension, ...
... rC/E = - 4 i + 3.37 j + 2.25 k ft eC/E = rC/E / | rC/E | = (-4 i + 3.37 j + 2.25 k ft)/((-4)2 + (3.37)2 + (2.25)2) eC/E = -0.703 i + 0.592 j + 0.395 k T = T eC/E = -0.703T i + 0.592T j + 0.395T k F = 20 i - 60 j lb Note: Since you don’t want any hinge reactions, easiest method to find the tension, ...
SolnsCh6
... 65. Find the “new” Earth radius by setting the acceleration due to gravity at the Sun’s surface equal to the acceleration due to gravity at the “new” Earth’s surface. g Earth gSun new ...
... 65. Find the “new” Earth radius by setting the acceleration due to gravity at the Sun’s surface equal to the acceleration due to gravity at the “new” Earth’s surface. g Earth gSun new ...
Name
... If an object has a net force of zero, what is its acceleration? What is the net force on an object with balanced forces? What two things can you say about an object’s motion if the net forces on the object are zero? Which of these objects are accelerating? a. A ball that is falling. b. A rocket flyi ...
... If an object has a net force of zero, what is its acceleration? What is the net force on an object with balanced forces? What two things can you say about an object’s motion if the net forces on the object are zero? Which of these objects are accelerating? a. A ball that is falling. b. A rocket flyi ...
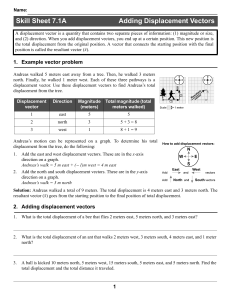
Skill Sheet 7.1A Adding Displacement Vectors
... 3. Sample projectile motion problem A ball is kicked with an initial total velocity (v0) of 10 m/sec at an angle of 60 degrees off the ground. The time that it takes for the ball to reach the ground again is twice the time it takes for the ball to reach its maximum height. Using this information, es ...
... 3. Sample projectile motion problem A ball is kicked with an initial total velocity (v0) of 10 m/sec at an angle of 60 degrees off the ground. The time that it takes for the ball to reach the ground again is twice the time it takes for the ball to reach its maximum height. Using this information, es ...
Class Notes
... newton (N) - the amount of force required to accelerate a one kilogram mass at a rate of one meter per second squared. Forces and the accelerations they cause are vector quantities, so we can use the techniques of adding and resolving vectors to analyze the acceleration of objects that have any nu ...
... newton (N) - the amount of force required to accelerate a one kilogram mass at a rate of one meter per second squared. Forces and the accelerations they cause are vector quantities, so we can use the techniques of adding and resolving vectors to analyze the acceleration of objects that have any nu ...
1 - CSUN.edu
... you will be using for table B. 2.Decide on three NET forces you will be testing. For example you can test the net forces of 2N, 4N, and 6N. Write these net forces in time table B. 3. Draw the three free body diagrams in table B that depict what you will test. See the free body diagram in table B for ...
... you will be using for table B. 2.Decide on three NET forces you will be testing. For example you can test the net forces of 2N, 4N, and 6N. Write these net forces in time table B. 3. Draw the three free body diagrams in table B that depict what you will test. See the free body diagram in table B for ...
• What is work done by a force • What is kinetic energy • work
... • What is work done by a force • What is kinetic energy • work-energy theorem • How to calculate work done by a varying force along a curved path • The meaning and calculation of power in a ...
... • What is work done by a force • What is kinetic energy • work-energy theorem • How to calculate work done by a varying force along a curved path • The meaning and calculation of power in a ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - Tamalpais Union High School District
... • A space probe may be carried by a rocket into outer space. What keeps the probe going after the rocket no longer pushes it? • Your friend says that inertia is a force that keeps things in their place, either at rest or in motion. Do you agree? Why or why not? • In terms of inertia, how does a car ...
... • A space probe may be carried by a rocket into outer space. What keeps the probe going after the rocket no longer pushes it? • Your friend says that inertia is a force that keeps things in their place, either at rest or in motion. Do you agree? Why or why not? • In terms of inertia, how does a car ...
HW7
... which yields two positive roots: 98 s and 572 s. Since the question makes sense only if t1 < t2 we conclude the correct result is t1 = 98 s. 10.30. (a) The tangential acceleration, using Eq. 10-22, is ...
... which yields two positive roots: 98 s and 572 s. Since the question makes sense only if t1 < t2 we conclude the correct result is t1 = 98 s. 10.30. (a) The tangential acceleration, using Eq. 10-22, is ...
Physics, Mr - TeacherWeb
... 17.Billy swings his 35 kg brother Mark in a circle around his body. The distance between Billy and Mark's center of gravity is 0.7 m. Describe the axis of rotation: ______________________________________________ Fc = ________________ Direction of Fc = ___________________________________ Is Fc a push ...
... 17.Billy swings his 35 kg brother Mark in a circle around his body. The distance between Billy and Mark's center of gravity is 0.7 m. Describe the axis of rotation: ______________________________________________ Fc = ________________ Direction of Fc = ___________________________________ Is Fc a push ...
determination of the acceleration of an elevator.
... DETERMINATION OF THE ACCELERATION OF AN ELEVATOR. INTRODUCTION: In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. We know that the direction of the acceleration will be in the same direction as the direction of the net force. The equation for Newton’s 2nd law is F = ma o ...
... DETERMINATION OF THE ACCELERATION OF AN ELEVATOR. INTRODUCTION: In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. We know that the direction of the acceleration will be in the same direction as the direction of the net force. The equation for Newton’s 2nd law is F = ma o ...
Chapter 3
... • If the reaction force, R, is larger than your weight, you feel heavier and the net force acts upward, resulting in an upward acceleration (e.g. speeding up in the upward direction) • If the reaction force, R, is equal to your weight, you feel neither heavier nor lighter, and the net force is zero, ...
... • If the reaction force, R, is larger than your weight, you feel heavier and the net force acts upward, resulting in an upward acceleration (e.g. speeding up in the upward direction) • If the reaction force, R, is equal to your weight, you feel neither heavier nor lighter, and the net force is zero, ...
13. Hookes Law and SHM
... However there are many instances when a moving object is subject to a changing force – can we still calculate future position and velocity? Well, we can if we can quantify the force, i.e. if we know how the force is changing. One example of an object experiencing a changing force is a stretched spri ...
... However there are many instances when a moving object is subject to a changing force – can we still calculate future position and velocity? Well, we can if we can quantify the force, i.e. if we know how the force is changing. One example of an object experiencing a changing force is a stretched spri ...
Unit 5 Review Packet
... When an unbalanced force acts on an object, there is a change only in the _______________________________ or ___________________________ of the object. a. Mass; speed b. Speed; direction c. Position; mass d. Direction; mass What force is needed for this box to reach equilibrium? ...
... When an unbalanced force acts on an object, there is a change only in the _______________________________ or ___________________________ of the object. a. Mass; speed b. Speed; direction c. Position; mass d. Direction; mass What force is needed for this box to reach equilibrium? ...
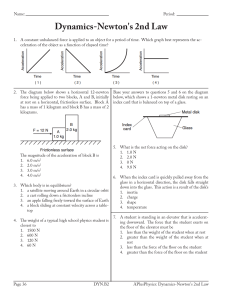
Dynamics-Newton`s 2nd Law
... Dynamics-Newton's 2nd Law 51. A woman is standing on a bathroom scale in an elevator car. If the scale reads a value greater than the weight of the woman at rest, the elevator car could be moving 1. downward at constant speed 2. upward at constant speed 3. downward at increasing speed 4. upward ...
... Dynamics-Newton's 2nd Law 51. A woman is standing on a bathroom scale in an elevator car. If the scale reads a value greater than the weight of the woman at rest, the elevator car could be moving 1. downward at constant speed 2. upward at constant speed 3. downward at increasing speed 4. upward ...