Document
... the total momentum remains constant. Or: The total momentum of an isolated system of bodies remains constant. ...
... the total momentum remains constant. Or: The total momentum of an isolated system of bodies remains constant. ...
More en the Work-Energy Theorem Mechanical Energy Alternate
... as shown. What component of the net force does no work on.the object? is perpendicular to net 90° A d . It does no work on the object. Depending on 6 , net I along A d can only Ad apeed up or slow down the net I object. Therefore, work done We can write ... ..by the net force only changes ...
... as shown. What component of the net force does no work on.the object? is perpendicular to net 90° A d . It does no work on the object. Depending on 6 , net I along A d can only Ad apeed up or slow down the net I object. Therefore, work done We can write ... ..by the net force only changes ...
Exam 2 Solutions
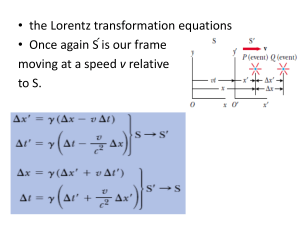
... perpendicular to the direction of motion. However, the electric charge in some region (let’s say a square in the rest frame of the sheet), must remain invariant between different reference frames. So if the square area on the sheet gets contracted along the direction of motion (becoming a rectangle ...
... perpendicular to the direction of motion. However, the electric charge in some region (let’s say a square in the rest frame of the sheet), must remain invariant between different reference frames. So if the square area on the sheet gets contracted along the direction of motion (becoming a rectangle ...
File - Mr. Graham`s AP Physics 1 & AP Physics C
... The clay is now removed from the pan and the pan is returned to equilibrium at the end of the spring. A rubber ball, also of mass M, is dropped from the same height H onto the pan, and after the collision is caught in midair before hitting anything else. e) Indicate below whether the period of the ...
... The clay is now removed from the pan and the pan is returned to equilibrium at the end of the spring. A rubber ball, also of mass M, is dropped from the same height H onto the pan, and after the collision is caught in midair before hitting anything else. e) Indicate below whether the period of the ...
Name
... f) If the elevator is traveling upwards at a velocity of 2 m/s, what are the magnitudes of the forces on it? ...
... f) If the elevator is traveling upwards at a velocity of 2 m/s, what are the magnitudes of the forces on it? ...
Harmonic notes
... The drawing above gives you an idea of the sequential motion of the system. Initially the spring is compressed. This is shown in the first drawing. The ball is released and the spring pushes it outward. In the second drawing, the spring has reached its normal displacement and is no longer exerting a ...
... The drawing above gives you an idea of the sequential motion of the system. Initially the spring is compressed. This is shown in the first drawing. The ball is released and the spring pushes it outward. In the second drawing, the spring has reached its normal displacement and is no longer exerting a ...
Transport Homework Package
... 5. Look at the pairs of forces acting on the objects below. In each case, state the resultant force and the direction in which it is acting. (a) ...
... 5. Look at the pairs of forces acting on the objects below. In each case, state the resultant force and the direction in which it is acting. (a) ...
10-12 Circular Rotational Motion
... To simulate an acceleration due to gravity, g, which is 10 m/s2, a space station must • have a radius of about 1 km (i.e. diameter of 2 km). • rotate at a speed of about 1 revolution per minute. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... To simulate an acceleration due to gravity, g, which is 10 m/s2, a space station must • have a radius of about 1 km (i.e. diameter of 2 km). • rotate at a speed of about 1 revolution per minute. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Universal Gravitation
... Apparent Weight is the normal support force. In an inertial (non-accelerating) frame of reference • FN = FG What is the weight of a 70 kg astronaut in a satellite with an orbital radius of 1.3 x 107 m? Weight = GMm/r2 Using: G = 6.67 x 10-11 N-m2/kg2 and M = 5.98 x 1023 kg Weight = 16 N What is the ...
... Apparent Weight is the normal support force. In an inertial (non-accelerating) frame of reference • FN = FG What is the weight of a 70 kg astronaut in a satellite with an orbital radius of 1.3 x 107 m? Weight = GMm/r2 Using: G = 6.67 x 10-11 N-m2/kg2 and M = 5.98 x 1023 kg Weight = 16 N What is the ...
Name
... Which of the following is true? Weight and mass are proportional but not equal. Weight is the gravitational force an object experiences due to its mass. The weight of an object on Earth is greater than the weight of the same object on the surface of the moon, but the object’s mass stays the same. Al ...
... Which of the following is true? Weight and mass are proportional but not equal. Weight is the gravitational force an object experiences due to its mass. The weight of an object on Earth is greater than the weight of the same object on the surface of the moon, but the object’s mass stays the same. Al ...
Newton`s Laws - Mayfield City Schools
... Newton’s 1st Law: The Law of Inertia Newton’s First Law – Simple English: Objects that are not moving will not move unless pushed by a not-0 Net Force. Objects that are moving will keep moving at the same velocity (a = 0) unless a not-0 Net Force pushes on them. If the Net Force on an object is ...
... Newton’s 1st Law: The Law of Inertia Newton’s First Law – Simple English: Objects that are not moving will not move unless pushed by a not-0 Net Force. Objects that are moving will keep moving at the same velocity (a = 0) unless a not-0 Net Force pushes on them. If the Net Force on an object is ...
Homework No. 07 (2014 Fall) PHYS 320: Electricity and Magnetism I
... (b) The electric field of a point dipole d at distance r from the dipole is given by Eq. (4). The force on a point charge in the presence of an electric field is F = qE. ...
... (b) The electric field of a point dipole d at distance r from the dipole is given by Eq. (4). The force on a point charge in the presence of an electric field is F = qE. ...
A box is sliding up an incline that makes an angle of 20 degrees with
... horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the surface of the incline is 0.2. The initial speed of the box at the bottom of the incline is 2 m/s. How far does the box travel along the incline before coming to rest? Solution: The first part in the problem is to find an accele ...
... horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the surface of the incline is 0.2. The initial speed of the box at the bottom of the incline is 2 m/s. How far does the box travel along the incline before coming to rest? Solution: The first part in the problem is to find an accele ...
File - Thomas Tallis Science
... Objects moving in free space with no forces acting on them will continue to move in a straight line at a constant velocity until a force causes them to change speed or direction. This is Newton’s first law, also known as the law of inertia. For instance, a space shuttle requires large forces from it ...
... Objects moving in free space with no forces acting on them will continue to move in a straight line at a constant velocity until a force causes them to change speed or direction. This is Newton’s first law, also known as the law of inertia. For instance, a space shuttle requires large forces from it ...