2000 - Year 11
... (a) Is the collision between the car and the wall elastic or inelasdc? Explain. [1] (b) If the mass of the dummy is 80 kg and the initial velocity of the car was 22 m/s, calculate the change in momentum of the dummy as it comes to rest. [1] (c) If the collision takes place in 0.3 seconds, calculate ...
... (a) Is the collision between the car and the wall elastic or inelasdc? Explain. [1] (b) If the mass of the dummy is 80 kg and the initial velocity of the car was 22 m/s, calculate the change in momentum of the dummy as it comes to rest. [1] (c) If the collision takes place in 0.3 seconds, calculate ...
18 Center of gravity.
... likewise for object B. Conditions: B must be outside of A A and B must be ‘homogeneous’ PHY 231 ...
... likewise for object B. Conditions: B must be outside of A A and B must be ‘homogeneous’ PHY 231 ...
Powerpoint
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 3 ...
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 3 ...
Recitation #3 Solutions
... To calculate the electric field from many charges, we use SUPERPOSITION: If we have a discrete collection of point charges, figure out the electric field vector from each charge using Coulomb's Law and then add all the vectors. If we have a continuous distribution of charge, we divide up the d ...
... To calculate the electric field from many charges, we use SUPERPOSITION: If we have a discrete collection of point charges, figure out the electric field vector from each charge using Coulomb's Law and then add all the vectors. If we have a continuous distribution of charge, we divide up the d ...
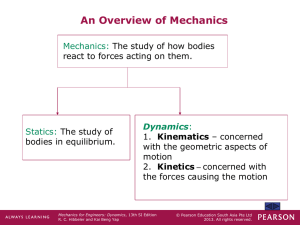
Dynamics
... If a force acts of a body, the body will accelerate. The ratio of the applied force to the resulting acceleration is the inertia (or mass) of the body. If a torque acts on a body that can rotate freely about some axis, the body will undergo an angular acceleration. The ratio of the applied torque to ...
... If a force acts of a body, the body will accelerate. The ratio of the applied force to the resulting acceleration is the inertia (or mass) of the body. If a torque acts on a body that can rotate freely about some axis, the body will undergo an angular acceleration. The ratio of the applied torque to ...
Physics - CSUN.edu
... causes the object to change direction but not speed (for example, the Earth’s gravitational force causes a satellite in a circular orbit to change direction but not speed). g. circular motion requires application of a constant force directed toward the center of the circle. h.* ...
... causes the object to change direction but not speed (for example, the Earth’s gravitational force causes a satellite in a circular orbit to change direction but not speed). g. circular motion requires application of a constant force directed toward the center of the circle. h.* ...
Motion & Force
... (a) speeds close to the speed of light – requires relativistic mechanics. (b) very small bodies (atoms and smaller) – requires quantum mechanics ...
... (a) speeds close to the speed of light – requires relativistic mechanics. (b) very small bodies (atoms and smaller) – requires quantum mechanics ...
Document
... On which basis was decided that one term was the radiation and the other an electrostatic type of field? It was decided on the basis of the dependence from the distance “r”: this is 1/r in one case and 1/r2 in the other. Note moreover that B being equal to the vector product of ε’ and E must be orth ...
... On which basis was decided that one term was the radiation and the other an electrostatic type of field? It was decided on the basis of the dependence from the distance “r”: this is 1/r in one case and 1/r2 in the other. Note moreover that B being equal to the vector product of ε’ and E must be orth ...
t - leonkag
... The English physicist Michael Faraday wrote, “Nowhere is there a pure creation or production of power without a corresponding exhaustion of something to supply it.” This statement represents one of the first formulation of one of the most important laws of physics—the Law of Conservation of Energy. ...
... The English physicist Michael Faraday wrote, “Nowhere is there a pure creation or production of power without a corresponding exhaustion of something to supply it.” This statement represents one of the first formulation of one of the most important laws of physics—the Law of Conservation of Energy. ...
Physics 241 – Exam #2
... 8. A proton (charge = +e = +1.6 × 10−19 C) travels in the x − y plane as shown below with a speed of 250 m/s. There is a magnetic field of magnitude 2.5 T along the +x direction. What is the direction and magnitude of the magnetic force on the proton? Note that the +z direction is out of the plane o ...
... 8. A proton (charge = +e = +1.6 × 10−19 C) travels in the x − y plane as shown below with a speed of 250 m/s. There is a magnetic field of magnitude 2.5 T along the +x direction. What is the direction and magnitude of the magnetic force on the proton? Note that the +z direction is out of the plane o ...
ISNS4371_011807_bw
... - opposes gravity and prevents us falling to the center of the Earth - what is measured by a weighing scale. For a body supported in a stationary position, normal force exactly balances earth's gravitational force - apparent weight has the same magnitude as actual weight. If no contact with any surf ...
... - opposes gravity and prevents us falling to the center of the Earth - what is measured by a weighing scale. For a body supported in a stationary position, normal force exactly balances earth's gravitational force - apparent weight has the same magnitude as actual weight. If no contact with any surf ...
Exam Review Answer Key 1) Force of Friction = 50N
... forces, by definition, are those which result from the physical contact of two forces. h. True (mostly) - A field force is a force which can acts between two objects even when they are separated by a distance. Field forces have magnitudes which are dependent upon the distance of separation between t ...
... forces, by definition, are those which result from the physical contact of two forces. h. True (mostly) - A field force is a force which can acts between two objects even when they are separated by a distance. Field forces have magnitudes which are dependent upon the distance of separation between t ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Assume the pulleys are massless and frictionless. T1 Assume the rope is massless. T3 T2 The action of a massless frictionless pulley is to change the direction of a T5 F tension. M Here F = T1 = T2 = T3 Equilibrium means S F = 0 for x, y & z For example: y-dir ma = 0 = T2 + T3 – T5 and ma = 0 = ...
... Assume the pulleys are massless and frictionless. T1 Assume the rope is massless. T3 T2 The action of a massless frictionless pulley is to change the direction of a T5 F tension. M Here F = T1 = T2 = T3 Equilibrium means S F = 0 for x, y & z For example: y-dir ma = 0 = T2 + T3 – T5 and ma = 0 = ...
Lecture14-10
... • calculate the rotational kinetic energy at the beginning and at the end of a second, by taking the moment of inertia to be 1.2x1038 kg-m2 and the initial angular speed to be 190 s-1. Δω over one second is given by the angular acceleration. ...
... • calculate the rotational kinetic energy at the beginning and at the end of a second, by taking the moment of inertia to be 1.2x1038 kg-m2 and the initial angular speed to be 190 s-1. Δω over one second is given by the angular acceleration. ...