Chapter 4
... Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not apply ...
... Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not apply ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... lasts for 0.150 seconds, what would be the impulse caused by the collision and the average force exerted on the automobile? Let’s assume that the force involved in the collision is a lot larger than any other forces in the system during the collision. From the problem, the initial and final momentum ...
... lasts for 0.150 seconds, what would be the impulse caused by the collision and the average force exerted on the automobile? Let’s assume that the force involved in the collision is a lot larger than any other forces in the system during the collision. From the problem, the initial and final momentum ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... The rotational kinetic energy of a rigid rotating object is ...
... The rotational kinetic energy of a rigid rotating object is ...
FORCE What is force?
... Relation between Mass and Weight • Mass and Weight are not the same quantity ! • Mass is a quantitative measure of inertia • Mass is an intrinsic property • Weight varies depending on the location ...
... Relation between Mass and Weight • Mass and Weight are not the same quantity ! • Mass is a quantitative measure of inertia • Mass is an intrinsic property • Weight varies depending on the location ...
Chapter 2 Motion Along a Line In order to specify a position, it is
... “In straight line motion, the acceleration is always in the same direction as the velocity, in the direction opposite to the velocity, or zero.” p. 34 Our first set of formulas: The equations of uniformly accelerated motion. I will follow the derivation in the book and then do it a different way. If ...
... “In straight line motion, the acceleration is always in the same direction as the velocity, in the direction opposite to the velocity, or zero.” p. 34 Our first set of formulas: The equations of uniformly accelerated motion. I will follow the derivation in the book and then do it a different way. If ...
Newton
... • Forces always occur in ________. doesn’t matter which is Therefore, it ________ the action and the reaction, as long as you can identify both. ...
... • Forces always occur in ________. doesn’t matter which is Therefore, it ________ the action and the reaction, as long as you can identify both. ...
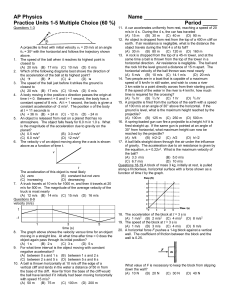
AP Physics
... m/s in 4 s. During the 4 s, the car has traveled (A) 15 m (B) 30 m (C) 40 m (D) 90 m 12. An object is dropped from rest from the top of a 400 m cliff on earth. If air resistance is negligible, what is the distance the object travels during the first 4 s of its fall? (A) 30 m (B) 80 m (C) 120 m (D) 1 ...
... m/s in 4 s. During the 4 s, the car has traveled (A) 15 m (B) 30 m (C) 40 m (D) 90 m 12. An object is dropped from rest from the top of a 400 m cliff on earth. If air resistance is negligible, what is the distance the object travels during the first 4 s of its fall? (A) 30 m (B) 80 m (C) 120 m (D) 1 ...
Unit IIIB Worksheet 1
... What you should know when all is said and done By the time you finish all labs, worksheets and related activities, you should be able to: 1. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe the relationship between m and a, F and a, m and F. (e.g., if you double the mass, the acceleration will…) 2. De ...
... What you should know when all is said and done By the time you finish all labs, worksheets and related activities, you should be able to: 1. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe the relationship between m and a, F and a, m and F. (e.g., if you double the mass, the acceleration will…) 2. De ...
midterm study guide answer key
... Describe constant acceleration due ONLY to a change in direction_______BALL ROLLING ON CIRCULAR TRACK_______________________ The rate at which velocity changes is called_________ACCELERATION_____________________ The gravitational force between two objects increases as mass_____INCREASES OR DISTANCE ...
... Describe constant acceleration due ONLY to a change in direction_______BALL ROLLING ON CIRCULAR TRACK_______________________ The rate at which velocity changes is called_________ACCELERATION_____________________ The gravitational force between two objects increases as mass_____INCREASES OR DISTANCE ...