Form B
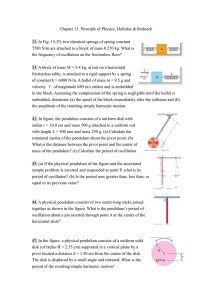
... 1. Suppose the force of wind resistance (friction) is proportional to the speed of an object and in the direction opposite to the object's velocity. From a platform 10 m above the ground an object is thrown upward and it eventually falls into a hole in the ground 10 m deep. By drawing free-body diag ...
... 1. Suppose the force of wind resistance (friction) is proportional to the speed of an object and in the direction opposite to the object's velocity. From a platform 10 m above the ground an object is thrown upward and it eventually falls into a hole in the ground 10 m deep. By drawing free-body diag ...
Name - MIT
... formed by hydrogen appears at a wavelength of 486.1 nm. The spectrum of a particular star shows the same hydrogen line appearing at a wavelength of 486.3 nm. What can we conclude from this observation? A) The star is getting hotter. B) The star must be very distant. C) The star is getting colder. D) ...
... formed by hydrogen appears at a wavelength of 486.1 nm. The spectrum of a particular star shows the same hydrogen line appearing at a wavelength of 486.3 nm. What can we conclude from this observation? A) The star is getting hotter. B) The star must be very distant. C) The star is getting colder. D) ...
Name
... 39) Galileo supposedly dropped balls of different masses from the leaning tower of Pisa. If he dropped a steel ball with a mass of 5 kg and wooden ball with a mass of 1 kg, which of the following would describe what happens? A) The force on the steel ball is greater so the steel ball would hit the g ...
... 39) Galileo supposedly dropped balls of different masses from the leaning tower of Pisa. If he dropped a steel ball with a mass of 5 kg and wooden ball with a mass of 1 kg, which of the following would describe what happens? A) The force on the steel ball is greater so the steel ball would hit the g ...
Summary of the unit on force, motion, and energy
... because moving in a straight line at constant speed is what things are supposed to do. Only when we want the velocity to change do we have to do something. The relevant and interesting part of motion is the acceleration, which is the rate of change of velocity: Acceleration = (final velocity – initi ...
... because moving in a straight line at constant speed is what things are supposed to do. Only when we want the velocity to change do we have to do something. The relevant and interesting part of motion is the acceleration, which is the rate of change of velocity: Acceleration = (final velocity – initi ...
Name
... 39) Galileo supposedly dropped balls of different masses from the leaning tower of Pisa. If he dropped a steel ball with a mass of 5 kg and wooden ball with a mass of 1 kg, which of the following would describe what happens? A) The force on the steel ball is greater so the steel ball would hit the g ...
... 39) Galileo supposedly dropped balls of different masses from the leaning tower of Pisa. If he dropped a steel ball with a mass of 5 kg and wooden ball with a mass of 1 kg, which of the following would describe what happens? A) The force on the steel ball is greater so the steel ball would hit the g ...
CIE IGCSE Forces
... when they are placed into a fluid (liquid or gas). An object will float on a liquid if the upthrust force ...
... when they are placed into a fluid (liquid or gas). An object will float on a liquid if the upthrust force ...
SPW Chapter 4 PPT
... direction of the net force on the ball also must be toward the center of the curved path. • The net force exerted toward the center of a curved path is called a centripetal force. ...
... direction of the net force on the ball also must be toward the center of the curved path. • The net force exerted toward the center of a curved path is called a centripetal force. ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... A specific type of interaction between 2 objects. The basic assumptions of a collision: 1. Interaction is short lived compared to the time of observation 2. A relatively large force acts on each colliding object 3. The motion of one or both objects changes abruptly following ...
... A specific type of interaction between 2 objects. The basic assumptions of a collision: 1. Interaction is short lived compared to the time of observation 2. A relatively large force acts on each colliding object 3. The motion of one or both objects changes abruptly following ...
Motion and Forces
... 4. You push a friend on a sled. Your friend and the sled together has a mass of 70 kg. If the net force on the sled is 35 N, what is it’s acceleration? ...
... 4. You push a friend on a sled. Your friend and the sled together has a mass of 70 kg. If the net force on the sled is 35 N, what is it’s acceleration? ...
Physics 235 Chapter 10 Motion in a Non-Inertial Reference Frame
... easy to express the motion of interest in an inertial reference frame. Consider for example the motion of a book laying on top of a table. In a reference frame that is fixed with respect to the Earth, the motion is simple: if the book is at rest, it will remain at rest (here we assume that the surfa ...
... easy to express the motion of interest in an inertial reference frame. Consider for example the motion of a book laying on top of a table. In a reference frame that is fixed with respect to the Earth, the motion is simple: if the book is at rest, it will remain at rest (here we assume that the surfa ...
universalgravitation
... Apparent Weight is the normal support force. In an inertial (non-accelerating) frame of reference • FN = FG What is the weight of a 70 kg astronaut in a satellite with an orbital radius of 1.3 x 107 m? Weight = GMm/r2 Using: G = 6.67 x 10-11 N-m2/kg2 and M = 5.98 x 1024 kg Weight = 165 N What is the ...
... Apparent Weight is the normal support force. In an inertial (non-accelerating) frame of reference • FN = FG What is the weight of a 70 kg astronaut in a satellite with an orbital radius of 1.3 x 107 m? Weight = GMm/r2 Using: G = 6.67 x 10-11 N-m2/kg2 and M = 5.98 x 1024 kg Weight = 165 N What is the ...
Chapter 4
... Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not apply ...
... Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not apply ...