newton`s laws webquest - Trimble County Schools
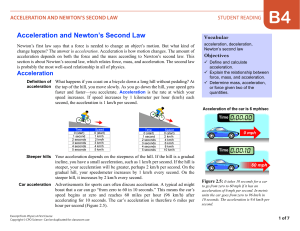
... the motion of all bodies is governed by the same basic rules. In the elementary years of conceptual development, students need multiple opportunities to experience, observe and describe (in words and pictures) motion, including factors (pushing and pulling) that affect motion. At the middle level, q ...
... the motion of all bodies is governed by the same basic rules. In the elementary years of conceptual development, students need multiple opportunities to experience, observe and describe (in words and pictures) motion, including factors (pushing and pulling) that affect motion. At the middle level, q ...
Phy 201: General Physics I
... the product of the rotational inertia and the angular acceleration: n ...
... the product of the rotational inertia and the angular acceleration: n ...
Physics 111 Fall 2007 Electrostatic Forces and the Electric Field
... Electrostatic Forces and the Electric Field - Solutions 1. Two point charges, 5 µC and -8 µC are 1.2 m apart. Where should a third charge, equal to 5 µC, be placed to make the electric field at the mid-point between the first two charges equal to zero? From the diagram below we see that the charge h ...
... Electrostatic Forces and the Electric Field - Solutions 1. Two point charges, 5 µC and -8 µC are 1.2 m apart. Where should a third charge, equal to 5 µC, be placed to make the electric field at the mid-point between the first two charges equal to zero? From the diagram below we see that the charge h ...
Electro-statics - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2 neutrons). (a) What is the force between the two alpha particles when they are 5.00 x 10–15 m apart, and (b) what will be the magnitude of the acceleration of the alpha particles due to this force? Note that the mass of an alpha particle is 4.0026 u. Solution: Since the charges have opposite signs ...
... 2 neutrons). (a) What is the force between the two alpha particles when they are 5.00 x 10–15 m apart, and (b) what will be the magnitude of the acceleration of the alpha particles due to this force? Note that the mass of an alpha particle is 4.0026 u. Solution: Since the charges have opposite signs ...
Document
... (a) (i). derive an expression centripetal acceleration of a body moving in a circular path of radius r. (3mks) (ii). Explain why it is necessary for a bicycle rider moving a round a circular path to lean towards the center of the path (3mks) (iii). Derive the expression for the angle inclination to ...
... (a) (i). derive an expression centripetal acceleration of a body moving in a circular path of radius r. (3mks) (ii). Explain why it is necessary for a bicycle rider moving a round a circular path to lean towards the center of the path (3mks) (iii). Derive the expression for the angle inclination to ...
On the Russell Hall case Andrei Galiautdinov
... with an ideal fluid approaches zero, thus violating the impulse-momentum theorem. JUSTIFICATION: Should follow from A → ∞ when used in (6) due to splattering down to a single atomic ...
... with an ideal fluid approaches zero, thus violating the impulse-momentum theorem. JUSTIFICATION: Should follow from A → ∞ when used in (6) due to splattering down to a single atomic ...
The Mathematics of Star Trek
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation: The gravitational force between two masses M and m is proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them, i.e. F = GMm/r2, where G is a constant. Newton’s Second Law: The net external force on an obje ...
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation: The gravitational force between two masses M and m is proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them, i.e. F = GMm/r2, where G is a constant. Newton’s Second Law: The net external force on an obje ...
ppt
... along the axis of a thick conducting shell of inner radius a = 2.7 cm and outer radius b = 5.0 cm and infinite length. The conducting shell is uniformly charged with a linear charge density λ 2 = +2.0 μC/m. ...
... along the axis of a thick conducting shell of inner radius a = 2.7 cm and outer radius b = 5.0 cm and infinite length. The conducting shell is uniformly charged with a linear charge density λ 2 = +2.0 μC/m. ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... Example 9 The Moment of Inertial Depends on Where the Axis Is. Two particles each have mass and are fixed at the ends of a thin rigid rod. The length of the rod is L. Find the moment of inertia when this object rotates relative to an axis that is perpendicular to the rod at (a) one end and (b) the c ...
... Example 9 The Moment of Inertial Depends on Where the Axis Is. Two particles each have mass and are fixed at the ends of a thin rigid rod. The length of the rod is L. Find the moment of inertia when this object rotates relative to an axis that is perpendicular to the rod at (a) one end and (b) the c ...
AP Physics Test – Magnetism and EM Induction Name: Each of the
... 8) Which of the following will NOT induce an electric current in the loop? (A) increase the magnitude of the field (B) crush the loop, decreasing its area (C) move the loop parallel to the field (D) remove the loop from the field (E) rotate the loop 45° about a diameter 9) If the magnetic field is d ...
... 8) Which of the following will NOT induce an electric current in the loop? (A) increase the magnitude of the field (B) crush the loop, decreasing its area (C) move the loop parallel to the field (D) remove the loop from the field (E) rotate the loop 45° about a diameter 9) If the magnetic field is d ...
F - Civil Engineering Department
... Multiplication and Division of a Vector by a Scalar - Product of vector A and scalar a = aA - Magnitude = aA - If a is positive (+), sense of aA is the same as sense of A - If a is negative (-), sense of aA, it is opposite to the sense of A ...
... Multiplication and Division of a Vector by a Scalar - Product of vector A and scalar a = aA - Magnitude = aA - If a is positive (+), sense of aA is the same as sense of A - If a is negative (-), sense of aA, it is opposite to the sense of A ...
Section 3 Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion Chapter 19
... • The Size of Earth’s Gravitational Force Compared with all objects around you, Earth has a huge mass. Therefore, Earth’s gravitational force is very large. • You must apply forces to overcome the Earth’s gravitational force any time you lift objects or even parts of your body. ...
... • The Size of Earth’s Gravitational Force Compared with all objects around you, Earth has a huge mass. Therefore, Earth’s gravitational force is very large. • You must apply forces to overcome the Earth’s gravitational force any time you lift objects or even parts of your body. ...