Center of Mass and Momentum
... •If the net external force on a system of particles is zero, then (even if the velocity of individual objects changes), there is a point associated with the distribution of objects that moves with zero acceleration (constant velocity). •This point is called the “center of mass” of the system. It is ...
... •If the net external force on a system of particles is zero, then (even if the velocity of individual objects changes), there is a point associated with the distribution of objects that moves with zero acceleration (constant velocity). •This point is called the “center of mass” of the system. It is ...
Forces - Lemon Bay High School
... motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s acceleration (or the change in the object’s velocity) is zero. ...
... motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s acceleration (or the change in the object’s velocity) is zero. ...
Kinetic Friction Experiment
... Kinetic friction forces are the forces that sliding surfaces exert on each other parallel to their surfaces. Kinetic friction forces are cumulative effects of the forces between all the microscopic contact points of the sliding surfaces. As a result, friction forces vary with the types of surfaces i ...
... Kinetic friction forces are the forces that sliding surfaces exert on each other parallel to their surfaces. Kinetic friction forces are cumulative effects of the forces between all the microscopic contact points of the sliding surfaces. As a result, friction forces vary with the types of surfaces i ...
Lecture8
... Planets move in an ellipse with the sun at one focus Planet–Sun line sweeps out equal areas in equal time (moves faster when closer!) Period and distance (semi-major axis) are related: P2=A3 ...
... Planets move in an ellipse with the sun at one focus Planet–Sun line sweeps out equal areas in equal time (moves faster when closer!) Period and distance (semi-major axis) are related: P2=A3 ...
Dynamics and Space
... 37. How long will it take a car to increase its speed from 8 ms-1 to 20 ms-1 if it accelerates at 3 ms-2? 38. A cyclist can accelerate at 0.5 m/s2 when cycling at 4 ms-1. How long will she take to reach 5.5 ms-1? 39. The maximum deceleration a car’s brakes can safely produce is 8 ms-2. What will be ...
... 37. How long will it take a car to increase its speed from 8 ms-1 to 20 ms-1 if it accelerates at 3 ms-2? 38. A cyclist can accelerate at 0.5 m/s2 when cycling at 4 ms-1. How long will she take to reach 5.5 ms-1? 39. The maximum deceleration a car’s brakes can safely produce is 8 ms-2. What will be ...
... What happens to the work done on a system? Energy is transferred into the system, but in what form? Does it remain in the system or move on? The answers depend on the situation. For example, if the lawn mower in Figure 7.2(a) is pushed just hard enough to keep it going at a constant speed, then ener ...
View PDF
... ____ 18. Which of the following would exert the most pressure on the ground? a. A woman standing in running shoes b. A woman standing on skis c. A woman standing in high-heel shoes ____ 19. A tennis ball and a solid steel ball with the same diameter are dropped at the same time. In the absence of ai ...
... ____ 18. Which of the following would exert the most pressure on the ground? a. A woman standing in running shoes b. A woman standing on skis c. A woman standing in high-heel shoes ____ 19. A tennis ball and a solid steel ball with the same diameter are dropped at the same time. In the absence of ai ...
Measuring Changes in Motion
... S.IP.05.11 Generate scientific questions about motion based on observations, investigations, and research. S.IP.05.12 Design and conduct scientific investigations on motion and changes in motion. S.IP.05.13 Use tools and equipment (stop watches, meter sticks and tapes, models, balances) appropriate ...
... S.IP.05.11 Generate scientific questions about motion based on observations, investigations, and research. S.IP.05.12 Design and conduct scientific investigations on motion and changes in motion. S.IP.05.13 Use tools and equipment (stop watches, meter sticks and tapes, models, balances) appropriate ...
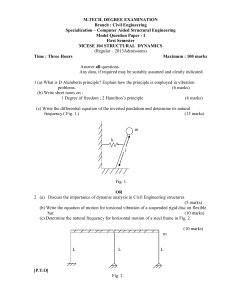
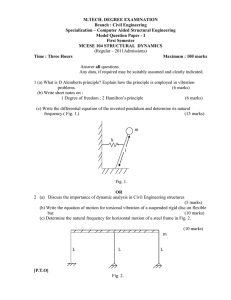
mcese 104 structural dynamics
... 4. (a) Derive an expression for the force transmitted to the foundation and phase angle for a damped oscillator idealized as a SDOF system subjected to harmonic force. (8 marks) (b) Compare the decay curves for various types of damping. ...
... 4. (a) Derive an expression for the force transmitted to the foundation and phase angle for a damped oscillator idealized as a SDOF system subjected to harmonic force. (8 marks) (b) Compare the decay curves for various types of damping. ...
CCC HOH FUK TONG COLLEGE
... A. All molecules move with the same speed at a certain temperature. B. All molecules are point particles that have no physical size. C. All collisions are perfectly elastic. D. All molecules do not exert force on one another except during collisions. 21. An external work W is done on an ideal gas, w ...
... A. All molecules move with the same speed at a certain temperature. B. All molecules are point particles that have no physical size. C. All collisions are perfectly elastic. D. All molecules do not exert force on one another except during collisions. 21. An external work W is done on an ideal gas, w ...
Physics Applet review - Futur-E
... A rock thrown from a tall building sails in a modest orbit that soon intersects the earth not far from its point of launch. If the ball were fired more swiftly to start with, it would travel further. Futher increasing the speed would result in ever larger, rounder elliptical paths and more distant i ...
... A rock thrown from a tall building sails in a modest orbit that soon intersects the earth not far from its point of launch. If the ball were fired more swiftly to start with, it would travel further. Futher increasing the speed would result in ever larger, rounder elliptical paths and more distant i ...
s - Nuffield Foundation
... find the frictional force acting on each can. 4 A sledge has mass 15 kg. A horizontal pull of 25 N will just move the sledge when it is on a horizontal surface of compacted snow. a Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the sledge, modelled as a particle, when it is just on the point of sliding ...
... find the frictional force acting on each can. 4 A sledge has mass 15 kg. A horizontal pull of 25 N will just move the sledge when it is on a horizontal surface of compacted snow. a Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the sledge, modelled as a particle, when it is just on the point of sliding ...
PHYSICS 151 – Notes for Online Lecture #15
... horizontally, but now let’s consider a frictional force of magnitude 43 N. Find a) the work done by the frictional force on the object b) the net force acting in the direction of the displacement and c) the net work done by forces acting in the direction of the displacement. ...
... horizontally, but now let’s consider a frictional force of magnitude 43 N. Find a) the work done by the frictional force on the object b) the net force acting in the direction of the displacement and c) the net work done by forces acting in the direction of the displacement. ...