SUPPORT MATERIAL FOR XI CLASS PHYSICS
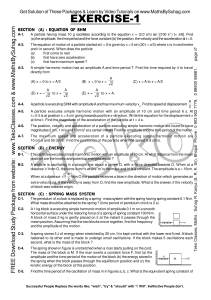
... Acceleration. The acceleration of an object is defined as the ratio of change of velocity of the object, and time taken i.e., Acceleration = change in velocity/time taken. Acceleration is a vector quantity. Acceleration is positive, if the velocity is increasing and is negative if velocity is decrea ...
... Acceleration. The acceleration of an object is defined as the ratio of change of velocity of the object, and time taken i.e., Acceleration = change in velocity/time taken. Acceleration is a vector quantity. Acceleration is positive, if the velocity is increasing and is negative if velocity is decrea ...
Chapter 12 - FIA Science
... 12.3 Newton’s Third Law of Motion and Momentum Newton’s Third Law A force cannot exist alone. Forces always exist in pairs. According to Newton’s third law of motion, whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object. ...
... 12.3 Newton’s Third Law of Motion and Momentum Newton’s Third Law A force cannot exist alone. Forces always exist in pairs. According to Newton’s third law of motion, whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object. ...
006 Friction
... • A frictional force can exist when two substances contact each other. • The molecules of each surface interact according to Newton’s Laws of Motion. • Friction always opposes motion, i.e., it is opposite to the direction of velocity. • If there is no motion, then friction opposes the sum of all the ...
... • A frictional force can exist when two substances contact each other. • The molecules of each surface interact according to Newton’s Laws of Motion. • Friction always opposes motion, i.e., it is opposite to the direction of velocity. • If there is no motion, then friction opposes the sum of all the ...
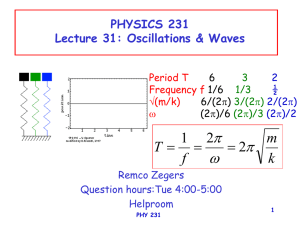
Simple Harmonic Motion Type 2 PART 2 OF 3 ENG
... suspnsion as it goes through its mean position, (c) the acceleration of this particle as it goes through its mean position and (d) the acceleration of this particle when it is at an exetreme position. Take g = π2 m/s2. ...
... suspnsion as it goes through its mean position, (c) the acceleration of this particle as it goes through its mean position and (d) the acceleration of this particle when it is at an exetreme position. Take g = π2 m/s2. ...
Springs ppt
... store potential energy that can be transformed into kinetic energy. The spring force is not constant as an object is pushed or pulled. The motion of the mass is not constant-acceleration motion, and therefore we cannot use our old kinematics equations. One way to analyze motion when spring for ...
... store potential energy that can be transformed into kinetic energy. The spring force is not constant as an object is pushed or pulled. The motion of the mass is not constant-acceleration motion, and therefore we cannot use our old kinematics equations. One way to analyze motion when spring for ...
gravitation - Physics Unit
... a) An Astronaut orbiting the earth An astronaut orbiting the earth in a space vehicle with its rocket motors off is said to be weightless. The astronaut is moving with a constant speed along the orbit but since he is travelling in a circle he has a centripetal acceleration of the same value as that ...
... a) An Astronaut orbiting the earth An astronaut orbiting the earth in a space vehicle with its rocket motors off is said to be weightless. The astronaut is moving with a constant speed along the orbit but since he is travelling in a circle he has a centripetal acceleration of the same value as that ...
Work - mrbernabo
... The FORCE on a spring goes up with a linearly when it is stretched. This is why the scale on a spring scale is not logarithmic. The Energy required to stretch a spring is exponential, because the force increases as it is stretched or compressed. ...
... The FORCE on a spring goes up with a linearly when it is stretched. This is why the scale on a spring scale is not logarithmic. The Energy required to stretch a spring is exponential, because the force increases as it is stretched or compressed. ...
Newton`s 2nd Law, friction
... Specifically, kinematics is the descriptive branch of mechanics, and dynamics is the causal. Newton's second law relates the net sum of vector forces that are dynamical to the acceleration of an object. In this lab, we verify Newton's second law on an air track. Equipment: air track, masses, photoga ...
... Specifically, kinematics is the descriptive branch of mechanics, and dynamics is the causal. Newton's second law relates the net sum of vector forces that are dynamical to the acceleration of an object. In this lab, we verify Newton's second law on an air track. Equipment: air track, masses, photoga ...
Impulse and Momentum
... 2. Each team shall have a thrower, a catcher, and a courier 3. The thrower is in charge of throwing the balloon to the catcher. The thrower must keep his/her throws within the team's throwing lane (as specified by the referee). Throwing outside the lane disqualifies the team. The thrower must throw ...
... 2. Each team shall have a thrower, a catcher, and a courier 3. The thrower is in charge of throwing the balloon to the catcher. The thrower must keep his/her throws within the team's throwing lane (as specified by the referee). Throwing outside the lane disqualifies the team. The thrower must throw ...
Slide 1 - Mr Lundy`s Room
... A simple pendulum consists of a mass at the end of a lightweight cord. We assume that the cord does not stretch, and that its mass is negligible. ...
... A simple pendulum consists of a mass at the end of a lightweight cord. We assume that the cord does not stretch, and that its mass is negligible. ...
Lecture 15
... released. The restoring force becomes k(s + x). So that the resultant of weight and the restoring force acting on the body is given by Resultant= k s x mg. nd By Newton’s 2 Law of motion, we can written d 2x m 2 k s x mg dt d 2x or m 2 kx ks mg dt mg ks 0 Since Therefore ...
... released. The restoring force becomes k(s + x). So that the resultant of weight and the restoring force acting on the body is given by Resultant= k s x mg. nd By Newton’s 2 Law of motion, we can written d 2x m 2 k s x mg dt d 2x or m 2 kx ks mg dt mg ks 0 Since Therefore ...
Unit 4 - State of New Jersey
... Students then investigate Newton’s first and second laws of motion through hands-on activities in which they observe the result of balanced and unbalanced forces on an object’s motion. Some examples may include using a seesaw or kicking a ball. In addition, students will observe how an object’s moti ...
... Students then investigate Newton’s first and second laws of motion through hands-on activities in which they observe the result of balanced and unbalanced forces on an object’s motion. Some examples may include using a seesaw or kicking a ball. In addition, students will observe how an object’s moti ...
Molecular dynamics simulation
... molecular mechanics force field – Move the atoms a little bit: update position and velocity of each atom using Newton’s laws of motion ...
... molecular mechanics force field – Move the atoms a little bit: update position and velocity of each atom using Newton’s laws of motion ...
Center of Mass and Momentum
... •If the net external force on a system of particles is zero, then (even if the velocity of individual objects changes), there is a point associated with the distribution of objects that moves with zero acceleration (constant velocity). •This point is called the “center of mass” of the system. It is ...
... •If the net external force on a system of particles is zero, then (even if the velocity of individual objects changes), there is a point associated with the distribution of objects that moves with zero acceleration (constant velocity). •This point is called the “center of mass” of the system. It is ...
No Slide Title
... An anchored fishing boat is going up and down with the waves. It reaches a maximum height every 5 seconds and a person on the boat sees that while reaching a maximum, the previous wave has moved about 40 m away from the boat. What is the speed of the traveling waves? ...
... An anchored fishing boat is going up and down with the waves. It reaches a maximum height every 5 seconds and a person on the boat sees that while reaching a maximum, the previous wave has moved about 40 m away from the boat. What is the speed of the traveling waves? ...