As a system asymptotically approaches absolute zero of
... “The direction of spontaneous change as a result of a random influence is from order toward disorder.” “high-grade energy is dissipated irreversibly to a lowgrade form in every energy transformation.” Book on energy needs of the world, no religious slant. Energy, Science and the pursuit of susta ...
... “The direction of spontaneous change as a result of a random influence is from order toward disorder.” “high-grade energy is dissipated irreversibly to a lowgrade form in every energy transformation.” Book on energy needs of the world, no religious slant. Energy, Science and the pursuit of susta ...
WRL1738.tmp - Symposium on Chemical Physics
... can use either classical or quantum mechanics. In either case the system as a whole evolves in time and it satisfies the law of conservation of energy. This is true only for conservative systems, but this suffices as the associated Hamiltonians describe the fundamental laws of nature. 2. There exist ...
... can use either classical or quantum mechanics. In either case the system as a whole evolves in time and it satisfies the law of conservation of energy. This is true only for conservative systems, but this suffices as the associated Hamiltonians describe the fundamental laws of nature. 2. There exist ...
Thermodynamics
... result, entropy generally increases when liquids or solutions are formed from solids, gases are formed from either solids or liquids, or the number of molecules of gas increases during a chemical reaction. The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a pure crystalline solid at 0 K is ...
... result, entropy generally increases when liquids or solutions are formed from solids, gases are formed from either solids or liquids, or the number of molecules of gas increases during a chemical reaction. The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a pure crystalline solid at 0 K is ...
WRL1834.tmp - Symposium on Chemical Physics
... would involve an increase in entropy, and hence cannot be reversed under adiabatic conditions. To obtain the energy difference it suffices if the process can be carried out one way or the other. 4. It is possible to transform state A to B (or conversely) by other processes. The mechanical work wAB ...
... would involve an increase in entropy, and hence cannot be reversed under adiabatic conditions. To obtain the energy difference it suffices if the process can be carried out one way or the other. 4. It is possible to transform state A to B (or conversely) by other processes. The mechanical work wAB ...
WRL0638.tmp - Symposium on Chemical Physics
... would involve an increase in entropy, and hence cannot be reversed under adiabatic conditions. To obtain the energy difference it suffices if the process can be carried out one way or the other. 4. It is possible to transform state A to B (or conversely) by other processes. The mechanical work wAB ...
... would involve an increase in entropy, and hence cannot be reversed under adiabatic conditions. To obtain the energy difference it suffices if the process can be carried out one way or the other. 4. It is possible to transform state A to B (or conversely) by other processes. The mechanical work wAB ...
Fundamentals of Equilibrium Thermodynamics
... would involve an increase in entropy, and hence cannot be reversed under adiabatic conditions. To obtain the energy difference it suffices if the process can be carried out one way or the other. 4. It is possible to transform state A to B (or conversely) by other processes. The mechanical work wAB ...
... would involve an increase in entropy, and hence cannot be reversed under adiabatic conditions. To obtain the energy difference it suffices if the process can be carried out one way or the other. 4. It is possible to transform state A to B (or conversely) by other processes. The mechanical work wAB ...
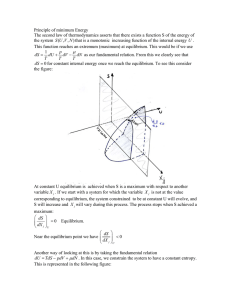
Principle of minimum Energy The second law of thermodynamics
... TdStotal = − dFsystem + δ Wsystem (rev) = 0 (Isothermal, reversible) TdStotal = − dFsystem + δ Wsystem (irrev) ≥ 0 or if δ Wsystem = 0 then dFsystem ≤ 0 dFsystem = d (U − TS ) = dU − TdS ≤ 0 Therefore F reaches a minimum at equilibrium A system that is isothermal with a bath, and that can only excha ...
... TdStotal = − dFsystem + δ Wsystem (rev) = 0 (Isothermal, reversible) TdStotal = − dFsystem + δ Wsystem (irrev) ≥ 0 or if δ Wsystem = 0 then dFsystem ≤ 0 dFsystem = d (U − TS ) = dU − TdS ≤ 0 Therefore F reaches a minimum at equilibrium A system that is isothermal with a bath, and that can only excha ...
Unit 1.3 Key Terms Active Solar Energy Collection A type of system
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
Chapter 15: Thermodynamics
... An ideal gas is in contact with a heat reservoir so that it remains at constant temperature of 300.0 K. The gas is compressed from a volume of 24.0 L to a volume of 14.0 L. During the process, the mechanical device pushing the piston to compress the gas is found to expend 5.00 kJ of energy. ...
... An ideal gas is in contact with a heat reservoir so that it remains at constant temperature of 300.0 K. The gas is compressed from a volume of 24.0 L to a volume of 14.0 L. During the process, the mechanical device pushing the piston to compress the gas is found to expend 5.00 kJ of energy. ...
Thermodynamics - Christian Hill
... intended to provide a background to some of the basic concepts and principles of the subject. In particular, the course concentrates on the important but deeply unfashionable subject of chemical thermodynamics. Thermodynamics is one of the most powerful techniques that scientists have developed to u ...
... intended to provide a background to some of the basic concepts and principles of the subject. In particular, the course concentrates on the important but deeply unfashionable subject of chemical thermodynamics. Thermodynamics is one of the most powerful techniques that scientists have developed to u ...
Is there a negative absolute temperature?
... with two other bodies B and C, then B and C are in thermal equilibrium with one another.” Two bodies in thermal equilibrium means: if the two bodies are to be brought into thermal contact, there would be no net flow of energy between them. Basis for thermometer and definition of isotherms ...
... with two other bodies B and C, then B and C are in thermal equilibrium with one another.” Two bodies in thermal equilibrium means: if the two bodies are to be brought into thermal contact, there would be no net flow of energy between them. Basis for thermometer and definition of isotherms ...
File
... – Note: these macroscopic properties of matter are capable of being measured and are often capable of being perceived by our senses. – Note: macroscopic properties of matter contrasts markedly with the microscopic properties of matter such as masses, speeds, energies , etc of the constituent atoms / ...
... – Note: these macroscopic properties of matter are capable of being measured and are often capable of being perceived by our senses. – Note: macroscopic properties of matter contrasts markedly with the microscopic properties of matter such as masses, speeds, energies , etc of the constituent atoms / ...
The Four Laws of Thermodynamics
... ”The laws of thermodynamics drive everything that happens in the universe. From the sudden expansion of a cloud of gas to the cooling of hot metal, and from the unfurling of a leaf to the course of life itself–everything is moved or restrained by four simple laws. They establish fundamental concepts ...
... ”The laws of thermodynamics drive everything that happens in the universe. From the sudden expansion of a cloud of gas to the cooling of hot metal, and from the unfurling of a leaf to the course of life itself–everything is moved or restrained by four simple laws. They establish fundamental concepts ...
Eötvös Loránd Science University Faculty of Sciences Department of
... Historical evolution of thermodynamics within the context of 19th century science. Basic quantities and notions of thermodynamics. The nature of thermodynamic systems. Describing equilibria within a variety of constraints. Thermodynamic potential functions and their interrelations. Fundamental equat ...
... Historical evolution of thermodynamics within the context of 19th century science. Basic quantities and notions of thermodynamics. The nature of thermodynamic systems. Describing equilibria within a variety of constraints. Thermodynamic potential functions and their interrelations. Fundamental equat ...
New Microsoft Office Word Document
... State of the system:- the existence of system with its respective microscopic and macroscopic properties Surrounding:- Part of universe apart from system Universe:- System along with all the surroundings Boundary:- Walls that separate System from Surroundings Equilibrium:- A state of dynamics wherei ...
... State of the system:- the existence of system with its respective microscopic and macroscopic properties Surrounding:- Part of universe apart from system Universe:- System along with all the surroundings Boundary:- Walls that separate System from Surroundings Equilibrium:- A state of dynamics wherei ...
Laws of Thermodynamics
... in which entropy is associated with disorder. As absolute zero is approached, all thermal motions cease, and any system must approach an ordered state in which the particles do not move. Hence, the entropy of a system is defined only to within an arbitrary constant, and only changes in entropy have ...
... in which entropy is associated with disorder. As absolute zero is approached, all thermal motions cease, and any system must approach an ordered state in which the particles do not move. Hence, the entropy of a system is defined only to within an arbitrary constant, and only changes in entropy have ...
1. (a) Consider that an entropy S is as function of temperature T and
... temperature Ti,1 , whereas box 2 starts with Ti,2 . (The subscript “i” means “initial,” and “f ” will mean “final.”) Assume that both gases are ideal so that the internal energy is given by Ei (T ) = Ci T . Note that the boxes are neither permeable nor deformable. Now we put the boxes into thermal c ...
... temperature Ti,1 , whereas box 2 starts with Ti,2 . (The subscript “i” means “initial,” and “f ” will mean “final.”) Assume that both gases are ideal so that the internal energy is given by Ei (T ) = Ci T . Note that the boxes are neither permeable nor deformable. Now we put the boxes into thermal c ...
Nonextensivity-Nonintensivity
... systems. For determining some experimental data or reliable calculations on the relevant properties of the small system under consideration need to be carried out. Any extensive thermodynamic property is a summation of the same property of the particles of the system, which are related to the ener ...
... systems. For determining some experimental data or reliable calculations on the relevant properties of the small system under consideration need to be carried out. Any extensive thermodynamic property is a summation of the same property of the particles of the system, which are related to the ener ...
2. Local equilibrium thermodynamics.
... occurring or can be triggered; within the system, every microscopic process is balanced by its opposite; this is called the principle of detailed balance. A central aim in equilibrium thermodynamics is: given a system in a well-defined initial state, subject to specified constraints, to calculate wh ...
... occurring or can be triggered; within the system, every microscopic process is balanced by its opposite; this is called the principle of detailed balance. A central aim in equilibrium thermodynamics is: given a system in a well-defined initial state, subject to specified constraints, to calculate wh ...