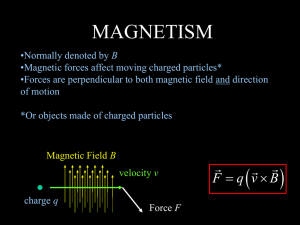
Magnetic Force Exerted on a Current Carrying Wire Magnetic force
... Magnetic force exerted on a current: The magnitude of the magnetic force FB on W that a magnetic field B exerts on a current I passing through a wire of length L is F B on W = ILBsinθ where θ is the angle between the directions of the B-field and the direction the Length of the wire points(which is ...
... Magnetic force exerted on a current: The magnitude of the magnetic force FB on W that a magnetic field B exerts on a current I passing through a wire of length L is F B on W = ILBsinθ where θ is the angle between the directions of the B-field and the direction the Length of the wire points(which is ...
Homework 7
... of B = 0.390 T. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force on the wire assuming that the angle between the magnetic field and the current is (a) θa = 60.0◦ , (b) θb = 90.0◦ , and (c) θc = 120◦ . Using our formula for the force on a wire due to a uniform field we have F = Il × B ...
... of B = 0.390 T. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force on the wire assuming that the angle between the magnetic field and the current is (a) θa = 60.0◦ , (b) θb = 90.0◦ , and (c) θc = 120◦ . Using our formula for the force on a wire due to a uniform field we have F = Il × B ...
solutions
... magnitude of B = 0.390 T. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force on the wire assuming that the angle between the magnetic field and the current is (a) θa = 60.0◦ , (b) θb = 90.0◦ , and (c) θc = 120◦ . Using our formula for the force on a wire due to a uniform field we have F = Il × B ...
... magnitude of B = 0.390 T. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force on the wire assuming that the angle between the magnetic field and the current is (a) θa = 60.0◦ , (b) θb = 90.0◦ , and (c) θc = 120◦ . Using our formula for the force on a wire due to a uniform field we have F = Il × B ...
Ch33 The Magnetic Field
... Compass needle : a probe of Magnetic field (承)Moving charge is the source of magnetic field ...
... Compass needle : a probe of Magnetic field (承)Moving charge is the source of magnetic field ...
Formulas and constants Mass of electron m = 9.1. 10 kg
... Formulas and constants Mass of electron me = 9.1. 10 -31 kg Charge on electron = 1.6.10-19 C Planck’s Constant h= 6.626. 10-34 J.s =4.136. 10-15 eV.s h = h / 2! = 1.055.10 "34 J.s = 6.582.10 "16 eV.s ...
... Formulas and constants Mass of electron me = 9.1. 10 -31 kg Charge on electron = 1.6.10-19 C Planck’s Constant h= 6.626. 10-34 J.s =4.136. 10-15 eV.s h = h / 2! = 1.055.10 "34 J.s = 6.582.10 "16 eV.s ...
Course Outline - Madeeha Owais
... The first course in time varying electromagnetic fields which is designed for the undergraduate students to make them understand the thorough working knowledge of the rich and varied phenomena of electricity and magnetism before moving on to more advance subjects of their interest e.g. antennas and ...
... The first course in time varying electromagnetic fields which is designed for the undergraduate students to make them understand the thorough working knowledge of the rich and varied phenomena of electricity and magnetism before moving on to more advance subjects of their interest e.g. antennas and ...
Gas Laws
... In the last section, we learned that if a charged particle is moving and then placed in an EXTERNAL magnetic field, it will be acted upon by a magnetic force. The same is true for a current carrying wire. The reason the wire and/or particle was moved was because there was an INTERNAL magnetic field ...
... In the last section, we learned that if a charged particle is moving and then placed in an EXTERNAL magnetic field, it will be acted upon by a magnetic force. The same is true for a current carrying wire. The reason the wire and/or particle was moved was because there was an INTERNAL magnetic field ...
cp19
... 8.0A running anti-parallel to each other. They are both parallel to the z-axis, and are located on the xaxis at x=3.0m and x=0.0m respectively. Find the magnetic field at the following points on the x-y plane: (a) (5,0,0) (b) (1,0,0) (c) (3,1,0) ...
... 8.0A running anti-parallel to each other. They are both parallel to the z-axis, and are located on the xaxis at x=3.0m and x=0.0m respectively. Find the magnetic field at the following points on the x-y plane: (a) (5,0,0) (b) (1,0,0) (c) (3,1,0) ...
Lecture Notes Y F Chapter 29
... Direction of the Induced EMF’s and Currents In the previous problem, we found the direction of the induced current by noting that the force resulting from the induced current had to oppose the applied force. This observation can be generalized into: Lenz’s Law The direction of any magnetic induct ...
... Direction of the Induced EMF’s and Currents In the previous problem, we found the direction of the induced current by noting that the force resulting from the induced current had to oppose the applied force. This observation can be generalized into: Lenz’s Law The direction of any magnetic induct ...