23.4 The Electric Field
... Because the electric field at P, the position of the test charge, is defined by E=Fe/q0, we find that at P, the electric field created by q is ...
... Because the electric field at P, the position of the test charge, is defined by E=Fe/q0, we find that at P, the electric field created by q is ...
Lecture 16
... A magnetic field is a collection of measurements across a region of space that indicates the relative strength of the magnetic force and the direction of the force on a north pole of a magnet placed there. The symbol for the magnetic field is B. The unit is the Tesla or Gauss. ...
... A magnetic field is a collection of measurements across a region of space that indicates the relative strength of the magnetic force and the direction of the force on a north pole of a magnet placed there. The symbol for the magnetic field is B. The unit is the Tesla or Gauss. ...
ELECTRIC MOTOR
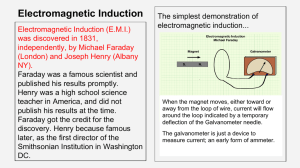
... A change in magnetic field associated with a conductor will induce a electric current in the conductor. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. The direction of induced current can be found using Fleming’s right-hand rule. Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of right hand ...
... A change in magnetic field associated with a conductor will induce a electric current in the conductor. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. The direction of induced current can be found using Fleming’s right-hand rule. Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of right hand ...
Fundamental nuclear symmetries meet classical electrodynamic
... – Ampère’s law H(J), Potential A(B), Faraday’s law E(dB/dt) – Calculation of Resistance, Inductance, Reluctance ...
... – Ampère’s law H(J), Potential A(B), Faraday’s law E(dB/dt) – Calculation of Resistance, Inductance, Reluctance ...
Cross Product
... If a particle with linear momentum p is at a position r with respect to some point, then its angular momentum L is the cross product of r and p L=rxp ...
... If a particle with linear momentum p is at a position r with respect to some point, then its angular momentum L is the cross product of r and p L=rxp ...
Magnetic Fields and Forces
... Particle 1, with a charge q1 = 3.60 μC and a speed of v1 = 382 m/s, travels at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. The magnetic force it experiences is 4.25 x 10-3 N. Particle 2, with a charge of q2 = 5.30 μC and a speed of v2 = 1.30 x 103 m/s, moves at an angle of 55.0º relative to the same m ...
... Particle 1, with a charge q1 = 3.60 μC and a speed of v1 = 382 m/s, travels at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. The magnetic force it experiences is 4.25 x 10-3 N. Particle 2, with a charge of q2 = 5.30 μC and a speed of v2 = 1.30 x 103 m/s, moves at an angle of 55.0º relative to the same m ...
Tuesday, October 23 rd
... Electric currents - line charge Current is charge per unit time passing a given point. Convention: positive current points in the direction the positive charges are flowing. Currents only relate to the moving charges. It is measured in Ampere: 1 A=1 C/s. A line charge traveling in a wire with speed ...
... Electric currents - line charge Current is charge per unit time passing a given point. Convention: positive current points in the direction the positive charges are flowing. Currents only relate to the moving charges. It is measured in Ampere: 1 A=1 C/s. A line charge traveling in a wire with speed ...