SECTION 5 Magnetostatics The Lorentz Force Law
... The magnetic field circles a wire, in the direction given by the right hand rule (right thumb along wire, fingers show direction of magnetic field) ...
... The magnetic field circles a wire, in the direction given by the right hand rule (right thumb along wire, fingers show direction of magnetic field) ...
Motion and Forces
... A force is a push or pull which may: ◦ A) Change the shape of an object ◦ B) Change the velocity of an object ...
... A force is a push or pull which may: ◦ A) Change the shape of an object ◦ B) Change the velocity of an object ...
extra example - FIU Faculty Websites
... For a given charge distribution, the total electric field at a point is the vector sum of the fields at this point due to each point charge in the charge distribution. If the charges are continuously distributed along a line, over a surface, or through a volume, i.e. the charges cannot be considered ...
... For a given charge distribution, the total electric field at a point is the vector sum of the fields at this point due to each point charge in the charge distribution. If the charges are continuously distributed along a line, over a surface, or through a volume, i.e. the charges cannot be considered ...
win2Tues2
... E field due to charge distributions Superposition: add the E fields to to each charge For more complex charge distributions, find the Electric FLUX through a surface enclosing the charges Gauss: E fields diverge from charges ...
... E field due to charge distributions Superposition: add the E fields to to each charge For more complex charge distributions, find the Electric FLUX through a surface enclosing the charges Gauss: E fields diverge from charges ...
HERE. - Lnk2Lrn
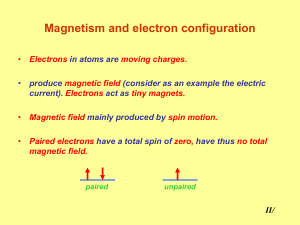
... The name probably comes from Magnesia, but there is a fable of Magnes, a Greek shepherd, who discovered magnetite when the nails in his shoes stuck to the ground! ...
... The name probably comes from Magnesia, but there is a fable of Magnes, a Greek shepherd, who discovered magnetite when the nails in his shoes stuck to the ground! ...
Lecture 06
... accelerating an external force F must be applied which is exactly equal and opposite to the electrical force. If this external force moves the charge a short distance dl along the path from A to B then an element of work will have been done equal to F.dl. To find the total work done we have to integ ...
... accelerating an external force F must be applied which is exactly equal and opposite to the electrical force. If this external force moves the charge a short distance dl along the path from A to B then an element of work will have been done equal to F.dl. To find the total work done we have to integ ...
Waves, Fields & Nuclear Energy
... Electric Field Strength: is inversely proportional to the square of the radius ...
... Electric Field Strength: is inversely proportional to the square of the radius ...
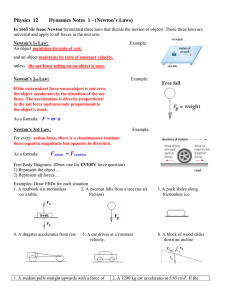
Newton`s Laws of Motion 1) An object with no net force acting on it
... 3) For every force acting on an object, there is an equal but opposite force acting from the object. ...
... 3) For every force acting on an object, there is an equal but opposite force acting from the object. ...
Inclined Planes
... This is a trick question because a constant velocity means that there is no acceleration! The piano is being pulled at the same speed the entire time. ...
... This is a trick question because a constant velocity means that there is no acceleration! The piano is being pulled at the same speed the entire time. ...