electromagnetic induction. - GTU e
... and the area through which the magnetic field passes. Electromagnetic induction is the principle behind the electric generator. The direction of the induced current due to the induced emf is governed by Lenz’s Law. ...
... and the area through which the magnetic field passes. Electromagnetic induction is the principle behind the electric generator. The direction of the induced current due to the induced emf is governed by Lenz’s Law. ...
Assignment 9.
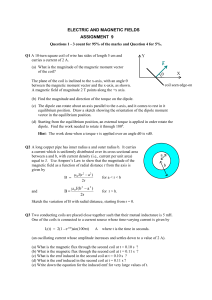
... (d) Starting from the equilibrium position, an external torque is applied in order rotate the dipole. Find the work needed to rotate it through 1800. Hint: The work done when a torque is applied over an angle d is d. ...
... (d) Starting from the equilibrium position, an external torque is applied in order rotate the dipole. Find the work needed to rotate it through 1800. Hint: The work done when a torque is applied over an angle d is d. ...
Magnetic Fields, Forces, and EM Induction
... force on a current carrying wire in a uniform magnetic field can be found by F=BILsin. Find the force on the wire if it makes an angle with the magnetic field lines of a. 90. b. 45. c. 0. ...
... force on a current carrying wire in a uniform magnetic field can be found by F=BILsin. Find the force on the wire if it makes an angle with the magnetic field lines of a. 90. b. 45. c. 0. ...
Electromagnetic Units
... A relation like (A.1.5) is of course no surprise. Electric and magnetic fields are related to each other through Lorentz transformations, so the proportionality constants ε0 and µ0 should be related through c. In Gaussian units, there are no analogues of ε0 or µ0 , but c appears explicitly instead. ...
... A relation like (A.1.5) is of course no surprise. Electric and magnetic fields are related to each other through Lorentz transformations, so the proportionality constants ε0 and µ0 should be related through c. In Gaussian units, there are no analogues of ε0 or µ0 , but c appears explicitly instead. ...
How To Calculate Net Force
... How to Calculate Net Forces Continued • When two unequal forces act in opposite directions on an object, the net force is the difference of the two forces ...
... How to Calculate Net Forces Continued • When two unequal forces act in opposite directions on an object, the net force is the difference of the two forces ...
Physics 272: Electricity and Magnetism
... • Charged atoms are called ions • Electrons can be pulled from the nucleus, but it requires work – Must remove an integer number of electrons ...
... • Charged atoms are called ions • Electrons can be pulled from the nucleus, but it requires work – Must remove an integer number of electrons ...
Define and Explain Electromagnetic Induction
... just the rate of the motion of charges; therefore, Ohm's law and other relationships for currents in wires are still valid. Lenz's law The direction of the induced current can be found from Lenz's law, which states that the magnetic field generated by the induced emf produces a current whose magneti ...
... just the rate of the motion of charges; therefore, Ohm's law and other relationships for currents in wires are still valid. Lenz's law The direction of the induced current can be found from Lenz's law, which states that the magnetic field generated by the induced emf produces a current whose magneti ...
4.8 Integrals using grad, div, and curl
... Calculating the vector product of the nabla operator and a function with several components f~(~x) we get the curl ~ × f~. curlf~ = rotf~ = ∇ Note that the curl is applied to a vector and the result is a vector. One essential aspect of the curl is the solution of area integrals (Stokes integral equa ...
... Calculating the vector product of the nabla operator and a function with several components f~(~x) we get the curl ~ × f~. curlf~ = rotf~ = ∇ Note that the curl is applied to a vector and the result is a vector. One essential aspect of the curl is the solution of area integrals (Stokes integral equa ...