Classical Thermodynamics Written by Jussi Eloranta
... where N is the number of molecules. Use SI-units in all calculations. Convert to other units at the final stage. At equilibrium a system is described by its thermodynamic variables. Thermodynamic equation of state introduces dependencies between the variables. An example of thermodynamic equation of ...
... where N is the number of molecules. Use SI-units in all calculations. Convert to other units at the final stage. At equilibrium a system is described by its thermodynamic variables. Thermodynamic equation of state introduces dependencies between the variables. An example of thermodynamic equation of ...
Classical Thermodynamics Written by Jussi Eloranta () (Updated: October 31, 2014)
... where N is the number of molecules. Use SI-units in all calculations. Convert to other units at the final stage. At equilibrium a system is described by its thermodynamic variables. Thermodynamic equation of state introduces dependencies between the variables. An example of thermodynamic equation of ...
... where N is the number of molecules. Use SI-units in all calculations. Convert to other units at the final stage. At equilibrium a system is described by its thermodynamic variables. Thermodynamic equation of state introduces dependencies between the variables. An example of thermodynamic equation of ...
Chapter One :- Concepts and Definitions
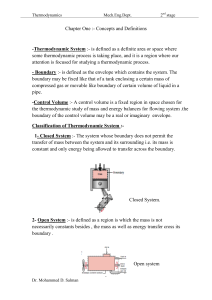
... entire system is not equal to the sum of their values for the individual parts of the system .These properties does not depend on the mass of the system.(like pressure ,Temperature ,Specific volume and density ). -Steady State :- is that circumstance in which there is no accumulation of mass or ener ...
... entire system is not equal to the sum of their values for the individual parts of the system .These properties does not depend on the mass of the system.(like pressure ,Temperature ,Specific volume and density ). -Steady State :- is that circumstance in which there is no accumulation of mass or ener ...
Prediction of the Steady Rate of Flame Spread Over
... The mathematical statement defined by Eqs.(l)-(6) provides six equations for six variables which are ui , T, Y, , p, p, T,.Therefore, two additional equations are necessary to obtain the other unknown parameters: pyrolysis rate v, and steady flame spread rate uf.The nature of the first of these equa ...
... The mathematical statement defined by Eqs.(l)-(6) provides six equations for six variables which are ui , T, Y, , p, p, T,.Therefore, two additional equations are necessary to obtain the other unknown parameters: pyrolysis rate v, and steady flame spread rate uf.The nature of the first of these equa ...
ABSTRACT Trinity: A Unified Treatment of Turbulence, Transport, and Heating in Magnetized Plasmas
... To faithfully simulate ITER and other modern fusion devices, one must resolve electron and ion fluctuation scales in a five-dimensional phase space and time. Simultaneously, one must account for the interaction of this turbulence with the slow evolution of the large-scale plasma profiles. Because of ...
... To faithfully simulate ITER and other modern fusion devices, one must resolve electron and ion fluctuation scales in a five-dimensional phase space and time. Simultaneously, one must account for the interaction of this turbulence with the slow evolution of the large-scale plasma profiles. Because of ...
Module P7.4 Specific heat, latent heat and entropy
... To begin the study of this module you will need to be familiar with the following terms: energy, kelvin, mole, power, pressure, ☞temperature, volume and work. It would also be helpful if you have some understanding of the following terms equation of state (of an ideal gas), first law of thermodynami ...
... To begin the study of this module you will need to be familiar with the following terms: energy, kelvin, mole, power, pressure, ☞temperature, volume and work. It would also be helpful if you have some understanding of the following terms equation of state (of an ideal gas), first law of thermodynami ...
Exergy: the quality of energy
... Thermodynamics are based on experience, experience with nature that shows which conversions from one kind of energy into the other are possible and which are not. In the following several kinds of energy will play a role like: kinetic energy, potential energy, internal energy, heat, work, electrical ...
... Thermodynamics are based on experience, experience with nature that shows which conversions from one kind of energy into the other are possible and which are not. In the following several kinds of energy will play a role like: kinetic energy, potential energy, internal energy, heat, work, electrical ...
Ch 15) The Laws of Thermodynamics
... where Q is the net heat added to the system and W is the net work done by the system. We must be careful and consistent in following the sign conventions for Q and W. Because W in Eq. 15–1 is the work done by the system, then if work is done on the system, W will be negative and U will increase. Sim ...
... where Q is the net heat added to the system and W is the net work done by the system. We must be careful and consistent in following the sign conventions for Q and W. Because W in Eq. 15–1 is the work done by the system, then if work is done on the system, W will be negative and U will increase. Sim ...
longitudinal plasma oscillations in an electric field
... to expect a similar behaviour in the case n? # M and also for other choices of f,,but we have not explicitly demonstrated this. ...
... to expect a similar behaviour in the case n? # M and also for other choices of f,,but we have not explicitly demonstrated this. ...
Summary Sheets in a single PDF file
... • Inter-Stellar Medium (ISM): The gas in between the stars in a galaxy. The ISM is typically extremely complicated, and roughly has a three-phase structure: it consists of a dense, cold (∼ 10K) molecular phase, a warm (∼ 104 K) phase, and a dilute, hot (∼ 106 K) phase. Stars form out of the dense mo ...
... • Inter-Stellar Medium (ISM): The gas in between the stars in a galaxy. The ISM is typically extremely complicated, and roughly has a three-phase structure: it consists of a dense, cold (∼ 10K) molecular phase, a warm (∼ 104 K) phase, and a dilute, hot (∼ 106 K) phase. Stars form out of the dense mo ...
Modern Thermodynamics
... Fundamental Notions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Fundamental Notions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Basic Thermodynamics - Alpha College of Engineering
... constant pressure p=1.4 bar, V1=0.028m3, W12=10.5kJ; ii) process 2-3: compression with PV=constant, U3=U2 and iii) process3-1: constant volume, U1-U3=-26.4kJ. There are no significance change in KE and PE. i) Calculate the net work for the cycle; ii) Calculate the heat transfer for the process 1-2; ...
... constant pressure p=1.4 bar, V1=0.028m3, W12=10.5kJ; ii) process 2-3: compression with PV=constant, U3=U2 and iii) process3-1: constant volume, U1-U3=-26.4kJ. There are no significance change in KE and PE. i) Calculate the net work for the cycle; ii) Calculate the heat transfer for the process 1-2; ...
H-theorem

In classical statistical mechanics, the H-theorem, introduced by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872, describes the tendency to increase in the quantity H (defined below) in a nearly-ideal gas of molecules. As this quantity H was meant to represent the entropy of thermodynamics, the H-theorem was an early demonstration of the power of statistical mechanics as it claimed to derive the second law of thermodynamics—a statement about fundamentally irreversible processes—from reversible microscopic mechanics.The H-theorem is a natural consequence of the kinetic equation derived by Boltzmann that has come to be known as Boltzmann's equation. The H-theorem has led to considerable discussion about its actual implications, with major themes being: What is entropy? In what sense does Boltzmann's quantity H correspond to the thermodynamic entropy? Are the assumptions (such as the Stosszahlansatz described below) behind Boltzmann's equation too strong? When are these assumptions violated?↑