Chapter 1 What is Psychology? Philosophical Developments
... • Placebo control group—exposed to a fake IV (placebo), the effects of which are compared to group receiving the actual IV. • Double-blind study—technique in which neither experimenter nor participant is aware of the group to which participant is ...
... • Placebo control group—exposed to a fake IV (placebo), the effects of which are compared to group receiving the actual IV. • Double-blind study—technique in which neither experimenter nor participant is aware of the group to which participant is ...
Chapter 1
... remembered, and used to guide behavior? • Influences include – Piaget – studied intellectual development – Chomsky – studied language – Cybernetics – science of information processing ...
... remembered, and used to guide behavior? • Influences include – Piaget – studied intellectual development – Chomsky – studied language – Cybernetics – science of information processing ...
High School Psychology
... guide for instruction. It is not intended to be a state-mandated curriculum for how and when content is taught. The outline is not a list of required items, and so, was developed with the understanding that content often overlaps. Because of this overlap, it may seem as if important ideas, people, p ...
... guide for instruction. It is not intended to be a state-mandated curriculum for how and when content is taught. The outline is not a list of required items, and so, was developed with the understanding that content often overlaps. Because of this overlap, it may seem as if important ideas, people, p ...
AP Psychology Course Information
... AP Psychology Course Information – 2006/2007 Course Specific Standards Upon completion of this course students will be able to: ! Comprehend, articulate, and disseminate psychology as a science. ! Integrate natural and social sciences as they apply to psychology. ! Identify and define the principles ...
... AP Psychology Course Information – 2006/2007 Course Specific Standards Upon completion of this course students will be able to: ! Comprehend, articulate, and disseminate psychology as a science. ! Integrate natural and social sciences as they apply to psychology. ! Identify and define the principles ...
Document
... children was measured before and after a noisy airport was built within earshot of their elementary school near Munich, Germany. They found that children who were exposed to chronic noise (the IV) showed increased psychological and physical stress (the DV). The control-group children showed little c ...
... children was measured before and after a noisy airport was built within earshot of their elementary school near Munich, Germany. They found that children who were exposed to chronic noise (the IV) showed increased psychological and physical stress (the DV). The control-group children showed little c ...
Exam 1 - Weber State University
... 6. Which of the following theoretical perspectives in psychology is a physical explanation? A. Behaviorism B. Biological Psychology C. Cognitive Psychology D. Psychoanalytic Psychology E. Social-Cultural Psychology 7. Most of the theoretical perspectives in scientific psychology are __________expla ...
... 6. Which of the following theoretical perspectives in psychology is a physical explanation? A. Behaviorism B. Biological Psychology C. Cognitive Psychology D. Psychoanalytic Psychology E. Social-Cultural Psychology 7. Most of the theoretical perspectives in scientific psychology are __________expla ...
Key Influences in the Development of Behaviorism
... Samples and Sampling • Population—large (potentially infinite) group represented by the sample. Findings are generalized to this group. • Sample—selected segment of the population • Representative sample—closely parallels the population on relevant characteristics • Random selection—every member of ...
... Samples and Sampling • Population—large (potentially infinite) group represented by the sample. Findings are generalized to this group. • Sample—selected segment of the population • Representative sample—closely parallels the population on relevant characteristics • Random selection—every member of ...
Chapter 14, Modules 32
... 12. Define aggression and explain how the following factors contribute to its expression: a) genetic and neural influences; b) biochemistry; c) learning. 13. Explain how the following can reduce prejudice and discrimination: a) superordinate goals; b) cooperative contact (refer to Sherif’s experime ...
... 12. Define aggression and explain how the following factors contribute to its expression: a) genetic and neural influences; b) biochemistry; c) learning. 13. Explain how the following can reduce prejudice and discrimination: a) superordinate goals; b) cooperative contact (refer to Sherif’s experime ...
SYSTEMS OR SCHOOLS OF PSYCHOLOGY AND THEIR BEARING
... intelligent behavior rather than a simple stimulus-response mechanism. An individual perceives the situation as a whole and after seeing and evaluating the different relationships in relation to the available environment, takes the proper decision in an intelligent way although quite often he does s ...
... intelligent behavior rather than a simple stimulus-response mechanism. An individual perceives the situation as a whole and after seeing and evaluating the different relationships in relation to the available environment, takes the proper decision in an intelligent way although quite often he does s ...
Introduction to Psychology
... examples of assessment tools What students need to do: describe how personality can explain individual differences and individual consistencies explain the influence of variables such as culture, family, and genetics on personality development identify important contributions to the understa ...
... examples of assessment tools What students need to do: describe how personality can explain individual differences and individual consistencies explain the influence of variables such as culture, family, and genetics on personality development identify important contributions to the understa ...
Prologue: Psych`s Roots
... between brain/mind & the body..the physical body 2. Developmental psychologists study changing abilities from womb to tomb..how aging affects us 3. Cognitive psychologists study how we perceive, think, use language, & solve problems 4. Personality psychologists investigate our persistent personality ...
... between brain/mind & the body..the physical body 2. Developmental psychologists study changing abilities from womb to tomb..how aging affects us 3. Cognitive psychologists study how we perceive, think, use language, & solve problems 4. Personality psychologists investigate our persistent personality ...
Lecture 11: Functionalism, the US brand of
... He earned his doctorate in psychology under William James at Harvard, after which he spent time at Wundt's lab. In 1882 (until 1888) he is appointed Prof. of Psychology and Pedagogics at Johns Hopkins where he organized the first psychology laboratory Founded the American Journal of ...
... He earned his doctorate in psychology under William James at Harvard, after which he spent time at Wundt's lab. In 1882 (until 1888) he is appointed Prof. of Psychology and Pedagogics at Johns Hopkins where he organized the first psychology laboratory Founded the American Journal of ...
AP Psychology - Cloudfront.net
... Summarizes a set of data. A single score that represents a whole set of scores. the typical score or value in a set of data ...
... Summarizes a set of data. A single score that represents a whole set of scores. the typical score or value in a set of data ...
AP Psychology Topics and Learning Objectives
... Exam, as well as the approximate percentages of the multiple-choice section devoted to each area. This listing is not intended to be an exhaustive list of topics. ...
... Exam, as well as the approximate percentages of the multiple-choice section devoted to each area. This listing is not intended to be an exhaustive list of topics. ...
AP Psychology Summer Assignments
... Welcome to Advanced Placement Psychology at North County School! During the 2015-2016 school-year we will be exploring the world of psychology, improving our research/writing skills and preparing for the AP Examination in the spring. Successful completion of this course will yield a greater understa ...
... Welcome to Advanced Placement Psychology at North County School! During the 2015-2016 school-year we will be exploring the world of psychology, improving our research/writing skills and preparing for the AP Examination in the spring. Successful completion of this course will yield a greater understa ...
LESSONS 1+2 presentations
... Sigmund Freud- the foundations (at the turn of 20st century) the main idea is the concept of unconsciousness unconscious mind is a reservoir of feelings, thoughts, urges, and memories that outside of our conscious awareness. Most of the contents of the unconscious are unacceptable or unpleasant, suc ...
... Sigmund Freud- the foundations (at the turn of 20st century) the main idea is the concept of unconsciousness unconscious mind is a reservoir of feelings, thoughts, urges, and memories that outside of our conscious awareness. Most of the contents of the unconscious are unacceptable or unpleasant, suc ...
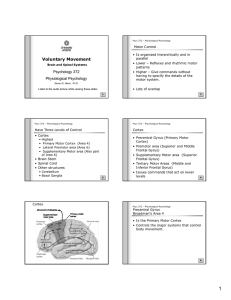
Voluntary Movement
... • Destruction: loss of muscle strength, reduced dexterity of hands and fingers • No effect of corticospinal lesions on posture or use of limbs for reaching • Uses different brain structures (BG, Cerebellum) ...
... • Destruction: loss of muscle strength, reduced dexterity of hands and fingers • No effect of corticospinal lesions on posture or use of limbs for reaching • Uses different brain structures (BG, Cerebellum) ...
The Introductory Concepts, Principles and History
... manifest themselves through what people do- their behaviour. Thus, it is through behaviour that we can actually study and come to understand internal mental processes that would otherwise be hidden from us. When we define psychology as “ the science of behaviour,” we are not exluding mind; we are sa ...
... manifest themselves through what people do- their behaviour. Thus, it is through behaviour that we can actually study and come to understand internal mental processes that would otherwise be hidden from us. When we define psychology as “ the science of behaviour,” we are not exluding mind; we are sa ...
Punctuation Power - Centre for Writers
... Big four comma rules: 1. Insert a comma between an introductory element and the rest of the sentence. An introductory element can be a single word, a phrase, or an entire clause. ...
... Big four comma rules: 1. Insert a comma between an introductory element and the rest of the sentence. An introductory element can be a single word, a phrase, or an entire clause. ...
Chapter 1: Introduction and Research Methods I. Introduction: The
... 1. A theory, or model, is a tentative explanation that tries to integrate and account for diverse findings on the same topic. 2. Theories are tools for explaining behavior and mental processes; they evolve and change as new evidence emerges, reflecting the selfcorrecting nature of the scientific ent ...
... 1. A theory, or model, is a tentative explanation that tries to integrate and account for diverse findings on the same topic. 2. Theories are tools for explaining behavior and mental processes; they evolve and change as new evidence emerges, reflecting the selfcorrecting nature of the scientific ent ...
Main PowerPoint for class
... specifically that we are the result of what we have learned from our environment. Behaviorism is concerned with how environmental factors (called stimuli) affect observable behavior (called the ...
... specifically that we are the result of what we have learned from our environment. Behaviorism is concerned with how environmental factors (called stimuli) affect observable behavior (called the ...
Psychology - Pearson School
... 6. Distinguish the purposes of descriptive pp. 22–28, 34–42 statistics and inferential statistics. 7. Apply basic descriptive statistical pp. 34–38 concepts, including interpreting and constructing graphs and calculating simple descriptive statistics (e.g., measures of central tendency, standard dev ...
... 6. Distinguish the purposes of descriptive pp. 22–28, 34–42 statistics and inferential statistics. 7. Apply basic descriptive statistical pp. 34–38 concepts, including interpreting and constructing graphs and calculating simple descriptive statistics (e.g., measures of central tendency, standard dev ...
aproaches-revision-book
... Main assumptions All psychology is pre-determined The unconscious plays a very important role in motivating our behaviour Childhood plays an important role in determining adult behaviour Psychological determinism- all behaviour is motivated, and the reasons we behave in certain ways are unconsc ...
... Main assumptions All psychology is pre-determined The unconscious plays a very important role in motivating our behaviour Childhood plays an important role in determining adult behaviour Psychological determinism- all behaviour is motivated, and the reasons we behave in certain ways are unconsc ...
Lesson 7 J.B. Watson (1878-1958) B.Watson J.B. Watson is
... knowledge, therefore, psychology focused merely on factual evidences and observable phenomena after the advent of this school. A measure of how seriously his appeal was taken by his professional colleagues is that he was elected as the President of American Psychological Association. In one of his b ...
... knowledge, therefore, psychology focused merely on factual evidences and observable phenomena after the advent of this school. A measure of how seriously his appeal was taken by his professional colleagues is that he was elected as the President of American Psychological Association. In one of his b ...
Seven Major Perspectives in Psychology
... human behavior across different cultures. • By looking at these differences, we can learn more about how our culture influences our thinking and behavior. – For example: how social behaviors differ in individualistic and collectivistic cultures. • In individualistic cultures, such as the U.S., peopl ...
... human behavior across different cultures. • By looking at these differences, we can learn more about how our culture influences our thinking and behavior. – For example: how social behaviors differ in individualistic and collectivistic cultures. • In individualistic cultures, such as the U.S., peopl ...