Integrals - San Diego Unified School District
... Antiderivative (Integral) – F(x): A function x of y such that x’ = y. (Think opposite of derivative.) [Don’t write this.] Question…What is the difference between dy of 2x3 + 5 and dy of 2x3 + 99? dx dx Does the 5 or 99 matter? But the functions are totally different. Here we introduce C or the const ...
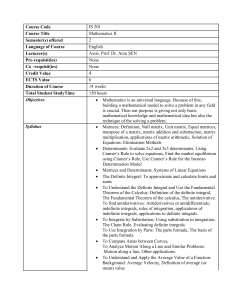
... Antiderivative (Integral) – F(x): A function x of y such that x’ = y. (Think opposite of derivative.) [Don’t write this.] Question…What is the difference between dy of 2x3 + 5 and dy of 2x3 + 99? dx dx Does the 5 or 99 matter? But the functions are totally different. Here we introduce C or the const ...
Study guide for the third exam
... The third exam is based on textbook section 3.7, most of chapter 4 (except for section 4.7), sections 5.1-3.3, and Math Insight parts 18-25. Using the book sections as a guide, the following highlights what is and what is not good potential material for the third exam. 1. Taylor polynomials (section ...
... The third exam is based on textbook section 3.7, most of chapter 4 (except for section 4.7), sections 5.1-3.3, and Math Insight parts 18-25. Using the book sections as a guide, the following highlights what is and what is not good potential material for the third exam. 1. Taylor polynomials (section ...
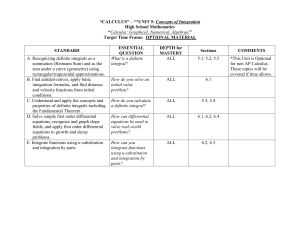
lesson 29 the first fundamental theorem of calculus
... say that x 2 is an antiderivative of 2x . Notice, however, that 2x actually has many antiderivatives. x 2 , x 2 1, x 2 2 , etc. all have a derivative of 2x . In fact, if C is any d 2 x C 2 x 0 2 x , so any function of the form x 2 C is an constant, we have dx antiderivative of 2x . ...
... say that x 2 is an antiderivative of 2x . Notice, however, that 2x actually has many antiderivatives. x 2 , x 2 1, x 2 2 , etc. all have a derivative of 2x . In fact, if C is any d 2 x C 2 x 0 2 x , so any function of the form x 2 C is an constant, we have dx antiderivative of 2x . ...















![The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/020099492_1-4a7fbd2304ff84025ef2f0bc4ff924ca-300x300.png)