chapter20 - HCC Learning Web
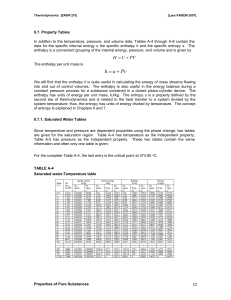
... This may be accomplished by clamping the piston at a fixed position. Since the volume does not change, W = 0. From the first law, DEint = Q If energy is added by heat to a system kept at constant volume, all of the transferred energy remains in the system as an increase in its internal energy. ...
... This may be accomplished by clamping the piston at a fixed position. Since the volume does not change, W = 0. From the first law, DEint = Q If energy is added by heat to a system kept at constant volume, all of the transferred energy remains in the system as an increase in its internal energy. ...
chapter20
... This may be accomplished by clamping the piston at a fixed position. Since the volume does not change, W = 0. From the first law, DEint = Q If energy is added by heat to a system kept at constant volume, all of the transferred energy remains in the system as an increase in its internal energy. ...
... This may be accomplished by clamping the piston at a fixed position. Since the volume does not change, W = 0. From the first law, DEint = Q If energy is added by heat to a system kept at constant volume, all of the transferred energy remains in the system as an increase in its internal energy. ...
states of matter
... what will be the state of the substance? 53. Why does sharp glass edge become smooth on heating it upto its melting point in a flame? Explain which property of liquids is responsible for this phenomenon. ...
... what will be the state of the substance? 53. Why does sharp glass edge become smooth on heating it upto its melting point in a flame? Explain which property of liquids is responsible for this phenomenon. ...
Thermodynamics: Notes
... exchange energy and matter, depending on the nature of the wall. A closed system is one where there is no exchange of matter. An equilibrium state is one in which all the bulk physical properties of the system are uniform throughout the system and do not change with time. An equilibrium state will b ...
... exchange energy and matter, depending on the nature of the wall. A closed system is one where there is no exchange of matter. An equilibrium state is one in which all the bulk physical properties of the system are uniform throughout the system and do not change with time. An equilibrium state will b ...
teaching nerve conduction to undergraduates
... spreads out from the active region and raises the temperature of the neighboring region. When the temperature here reaches a critical value, this region will also become active and so propagation will proceed. If this paragraph is now reread substituting the words nerve for cigarette, electricity fo ...
... spreads out from the active region and raises the temperature of the neighboring region. When the temperature here reaches a critical value, this region will also become active and so propagation will proceed. If this paragraph is now reread substituting the words nerve for cigarette, electricity fo ...
• Conservation of energy principle • Total energy • Energy transfer
... when increasing x. Therefore, a negative sign is added in eq. 3-5 to make heat transf er in the positive x direction a positive quantity. CONVE CTION: Is the mode of energy transfer between a solid surface and the adjacent liquid or gas which in motion and it involves the combined effects of “condu ...
... when increasing x. Therefore, a negative sign is added in eq. 3-5 to make heat transf er in the positive x direction a positive quantity. CONVE CTION: Is the mode of energy transfer between a solid surface and the adjacent liquid or gas which in motion and it involves the combined effects of “condu ...
Resonance Superfluidity in a Quantum Degenerate Fermi Gas
... atoms equally distributed between the two hyperfine states which have the lowest internal energy in the presence of a magnetic field. The values of our interaction parameters abg 苷 176a0 and k兾kb 苷 657 mK are obtained from [15]. We fix the total density to be n 苷 1014 cm23 , a typical experimental v ...
... atoms equally distributed between the two hyperfine states which have the lowest internal energy in the presence of a magnetic field. The values of our interaction parameters abg 苷 176a0 and k兾kb 苷 657 mK are obtained from [15]. We fix the total density to be n 苷 1014 cm23 , a typical experimental v ...
Kinetic Energy Kinetic Energy Potential Energy
... or state, heat is added or removed without changing the temperature. Instead, the state of matter changes: solid to liquid, for example. • The amount of heat needed per unit mass to produce a phase change is called the latent heat. – The latent heat of fusion of water corresponds to the amount of he ...
... or state, heat is added or removed without changing the temperature. Instead, the state of matter changes: solid to liquid, for example. • The amount of heat needed per unit mass to produce a phase change is called the latent heat. – The latent heat of fusion of water corresponds to the amount of he ...