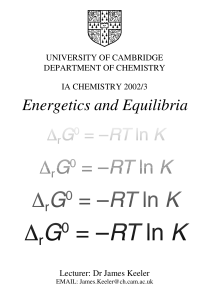Thermodynamics and Kinetics
... reactants: In the above reaction, n and m are the coefficients of the products and the reactants in the balanced equation. As with H, entropies have been measured and tabulated. When: S > 0 disorder increases (which favors spontaneity). S < 0 disorder decreases (does not favor spontaneity). ...
... reactants: In the above reaction, n and m are the coefficients of the products and the reactants in the balanced equation. As with H, entropies have been measured and tabulated. When: S > 0 disorder increases (which favors spontaneity). S < 0 disorder decreases (does not favor spontaneity). ...
Meaning of Entropy in Classical Thermodynamics
... as a subject with an unusually high ratio of words to equations. In modern thermodynamics textbooks, this difficulty is circumvented by defining reversible, internally reversible, and externally or fully reversible processes [12,13]. Uffink, in his criticism of the liberal extrapolation of the Secon ...
... as a subject with an unusually high ratio of words to equations. In modern thermodynamics textbooks, this difficulty is circumvented by defining reversible, internally reversible, and externally or fully reversible processes [12,13]. Uffink, in his criticism of the liberal extrapolation of the Secon ...
CCC HOH FUK TONG COLLEGE
... 20. Which of the following is NOT a basic assumption of the kinetic theory of an ideal gas ? A. All molecules move with the same speed at a certain temperature. B. All molecules are point particles that have no physical size. C. All collisions are perfectly elastic. D. All molecules do not exert for ...
... 20. Which of the following is NOT a basic assumption of the kinetic theory of an ideal gas ? A. All molecules move with the same speed at a certain temperature. B. All molecules are point particles that have no physical size. C. All collisions are perfectly elastic. D. All molecules do not exert for ...
Chapter 7 – Energy and Energy Balances
... Once a system is defined, a certain number of variables will specify its state fully. For example, one may need to provide the temperature, pressure, composition, total amount of material, velocity, and position in order to specify a system’s “state.” The exact information that is needed to specify ...
... Once a system is defined, a certain number of variables will specify its state fully. For example, one may need to provide the temperature, pressure, composition, total amount of material, velocity, and position in order to specify a system’s “state.” The exact information that is needed to specify ...
Chapter 3: Properties of Pure Substances
... for a substance that contracts on freezing and a substance that expands on freezing. Constant pressure curves on a temperature-volume diagram are shown in Figure 311. ...
... for a substance that contracts on freezing and a substance that expands on freezing. Constant pressure curves on a temperature-volume diagram are shown in Figure 311. ...
Modelling and Examining Open Circuit Voltage for PEM Fuel Cells
... At the anode side of the PEM fuel cell, the hydrogen will be ionized in the existence of platinum catalyst to release electrons and H+ ions in a process called oxidization, each molecule of hydrogen H2 will produce two free electrons and two positive ions. The existence of platinum catalyst is impor ...
... At the anode side of the PEM fuel cell, the hydrogen will be ionized in the existence of platinum catalyst to release electrons and H+ ions in a process called oxidization, each molecule of hydrogen H2 will produce two free electrons and two positive ions. The existence of platinum catalyst is impor ...
This is a heat engine
... 20% and produces an average of 23 kJ of mechanical work per second during operation. Remember: QH = W/e . (a) How much heat input is required, and QH = W/e = 23 kJ/0.20 = 115 kJ (b) How much heat is discharged as waste heat from this engine, per second? QL = (1-e) QH = (0.8) 115 kJ = 92 kJ Copyright ...
... 20% and produces an average of 23 kJ of mechanical work per second during operation. Remember: QH = W/e . (a) How much heat input is required, and QH = W/e = 23 kJ/0.20 = 115 kJ (b) How much heat is discharged as waste heat from this engine, per second? QL = (1-e) QH = (0.8) 115 kJ = 92 kJ Copyright ...
Review of Chemical Thermodynamics 7.51 September 1999 ∆G
... Thermodynamics allows us to predict how chemical reactions will change as a function of temperature and how changes in the structure of molecules might affect the equilibrium properties of a population of these molecules. There are four basic thermodynamic properties: ∆G — Change in free energy betw ...
... Thermodynamics allows us to predict how chemical reactions will change as a function of temperature and how changes in the structure of molecules might affect the equilibrium properties of a population of these molecules. There are four basic thermodynamic properties: ∆G — Change in free energy betw ...
heat engine - Energi Masa Depan Weblog
... process of transforming heat into mechanical energy. Goal to increase inefficiency. In 1824 Carnot invented, on paper, the Carnot engine. This is the ideal engine. ...
... process of transforming heat into mechanical energy. Goal to increase inefficiency. In 1824 Carnot invented, on paper, the Carnot engine. This is the ideal engine. ...
The engine converts the chemical energy stored in the fuel
... energy any further. Therefore, there can be no lower temperature than — 273°C. This is called absolute zero. The Kelvin temperature scale is based on absolute zero. Absolute zero is the zero point of the Kelvin scale. On the Kelvin scale, the freezing point of water (0°C) is 273K and the boiling poi ...
... energy any further. Therefore, there can be no lower temperature than — 273°C. This is called absolute zero. The Kelvin temperature scale is based on absolute zero. Absolute zero is the zero point of the Kelvin scale. On the Kelvin scale, the freezing point of water (0°C) is 273K and the boiling poi ...
calcijlation of elastic properties from thermodynamic equation of
... The variety of approaches involved in these studies demonstrates the need for a review of the methodology used to compute elastic wave speeds, in the spirit of an earlier review by Anderson et a1 (1968). Three broad areas bear on this topic: thermodynamic analysis, continuum mechanics, and solid sta ...
... The variety of approaches involved in these studies demonstrates the need for a review of the methodology used to compute elastic wave speeds, in the spirit of an earlier review by Anderson et a1 (1968). Three broad areas bear on this topic: thermodynamic analysis, continuum mechanics, and solid sta ...
transport processes and cross-coupling effects in non
... VV (vibration-vibration) transitions are much more probable than VT (vibration-translation) energy exchanges, which justifies such an assumption for the case of vibrational non-equilibrium. This allows introducing temperatures of different internal modes [6]; populations of internal states follow qu ...
... VV (vibration-vibration) transitions are much more probable than VT (vibration-translation) energy exchanges, which justifies such an assumption for the case of vibrational non-equilibrium. This allows introducing temperatures of different internal modes [6]; populations of internal states follow qu ...