Etymology Physical characteristics
... increased collisions among gas particles would include a fixed volume of gas, which upon heating would contain very fast particles. What this means to us is that these ideal equations provide reasonable results except for extremely high pressure [compressible] or high temperature [ionized] condition ...
... increased collisions among gas particles would include a fixed volume of gas, which upon heating would contain very fast particles. What this means to us is that these ideal equations provide reasonable results except for extremely high pressure [compressible] or high temperature [ionized] condition ...
Modelling Thermodynamic Systems with Changing Gas Mi
... tion of the individual constituents of the mixture. N is the number of constituents of the mixture. The relation for the total internal energy, E , of the mixture can be expressed in i similar way by neglecting some minor important energy contributions like kinetic and potential energy together with ...
... tion of the individual constituents of the mixture. N is the number of constituents of the mixture. The relation for the total internal energy, E , of the mixture can be expressed in i similar way by neglecting some minor important energy contributions like kinetic and potential energy together with ...
Report
... conservation of energy. This states the total energy within an isolated system remains constant, thus energy cannot be created or destroyed, though it can change form; an example of this would be a conversion of potential to kinetic to thermal. (Heat is both potential and kinetic) Exchange interacti ...
... conservation of energy. This states the total energy within an isolated system remains constant, thus energy cannot be created or destroyed, though it can change form; an example of this would be a conversion of potential to kinetic to thermal. (Heat is both potential and kinetic) Exchange interacti ...
Martin Cunningham`s Unit One Higher Notes
... Two or more vector quantities can be added together to produce a single vector if they have the same unit - but their directions must be taken into account. We do this using the "tip to tail" rule. The single vector obtained is known as the resultant vector. ...
... Two or more vector quantities can be added together to produce a single vector if they have the same unit - but their directions must be taken into account. We do this using the "tip to tail" rule. The single vector obtained is known as the resultant vector. ...
Tg - Glass Transition Temperature for Epoxies
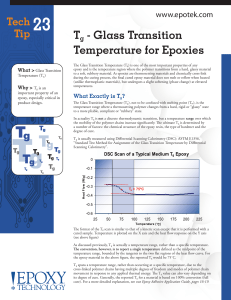
... As discussed previously, Tg is actually a temperature range, rather than a specific temperature. The convention, however, is to report a single temperature defined as the midpoint of the temperature range, bounded by the tangents to the two flat regions of the heat flow curve. For the epoxy material ...
... As discussed previously, Tg is actually a temperature range, rather than a specific temperature. The convention, however, is to report a single temperature defined as the midpoint of the temperature range, bounded by the tangents to the two flat regions of the heat flow curve. For the epoxy material ...
The importance of vacuum and the control of
... Freeze drying involves energy transfers and balancing of energy equations From the 1st Law of Thermodynamics, energy can neither be created nor destroyed It can however exist in many forms – mass, light, chemical, gravity, electrical, mechanical etc. In freeze drying we are most interested in heat e ...
... Freeze drying involves energy transfers and balancing of energy equations From the 1st Law of Thermodynamics, energy can neither be created nor destroyed It can however exist in many forms – mass, light, chemical, gravity, electrical, mechanical etc. In freeze drying we are most interested in heat e ...
Part III: Second Law of Thermodynamics
... process to take heat from a reservoir and to convert it into work without simultaneously transferring heat from a hot to a cold reservoir.' This statement of the second law is related to equilibrium, i.e. work can be obtained from a system only when the system is not already at equilibrium. If a sys ...
... process to take heat from a reservoir and to convert it into work without simultaneously transferring heat from a hot to a cold reservoir.' This statement of the second law is related to equilibrium, i.e. work can be obtained from a system only when the system is not already at equilibrium. If a sys ...
The Third Law of Quantum Thermodynamics in the Presence of
... in elucidating such problems as why the Carnot engine can never reach 100% efficiency at finite temperatures. Although some unfulfillment may still exist the known deviations from the third law will all be cured by quantum mechanics, quantum statistics and interactions among particles according to commo ...
... in elucidating such problems as why the Carnot engine can never reach 100% efficiency at finite temperatures. Although some unfulfillment may still exist the known deviations from the third law will all be cured by quantum mechanics, quantum statistics and interactions among particles according to commo ...
GCSE P1 1.1.3 Energy Transfer by Heating
... In the marble, the thermal energy is transferred from particle to particle. Particles at the hot end vibrate more strongly and this increased vibration is slowly passed onto neighbouring particles along the length of the rod. Copper contains free electrons and these provide an additional thermal ene ...
... In the marble, the thermal energy is transferred from particle to particle. Particles at the hot end vibrate more strongly and this increased vibration is slowly passed onto neighbouring particles along the length of the rod. Copper contains free electrons and these provide an additional thermal ene ...
Lecture 2: Energy, Exergy, and Thermodynamics
... some systems without a loss of potential energy to heat.. The amount of kinetic energy that a body possesses is dependent on the speed of its motion and its mass. At the atomic scale, the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules is sometimes referred to as heat energy. ...
... some systems without a loss of potential energy to heat.. The amount of kinetic energy that a body possesses is dependent on the speed of its motion and its mass. At the atomic scale, the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules is sometimes referred to as heat energy. ...