Dryland Landscapes
... When filled by seasonal rains, these features can be important temporary water sources for humans and animals. They can also have economic importance as some desert lakes are mined for salt. Role of the wind The lack of vegetation means wind can be a more effective geomorphological agent in drylands ...
... When filled by seasonal rains, these features can be important temporary water sources for humans and animals. They can also have economic importance as some desert lakes are mined for salt. Role of the wind The lack of vegetation means wind can be a more effective geomorphological agent in drylands ...
Desert Tortoise
... years to reach sexual maturity. Until this time, all desert tortoises have flat plastrons. Upon reaching sexual maturity, female plastrons remain flat while male plastrons become slightly concave. How do they behave? ...
... years to reach sexual maturity. Until this time, all desert tortoises have flat plastrons. Upon reaching sexual maturity, female plastrons remain flat while male plastrons become slightly concave. How do they behave? ...
Ecosystems
... yard. Thousands of species of plants and animals live in the rain forests of the world. But what makes them so different? • Rain forests get 80 inches of rain a year! That is a lot compared to the rest of the world. The temperature almost never changes. It is always warm and muggy! • You have probab ...
... yard. Thousands of species of plants and animals live in the rain forests of the world. But what makes them so different? • Rain forests get 80 inches of rain a year! That is a lot compared to the rest of the world. The temperature almost never changes. It is always warm and muggy! • You have probab ...
Desert Tortoise
... History and Conservation • An average of 200 adult desert tortoises per square mile in the ‘50s • Original conservation started in 1971 in California City, CA (The Desert Tortoise Natural Area) • Mojave Desert population was considered endangered in 1989 • 1989 quarantined part of southwest, CA in ...
... History and Conservation • An average of 200 adult desert tortoises per square mile in the ‘50s • Original conservation started in 1971 in California City, CA (The Desert Tortoise Natural Area) • Mojave Desert population was considered endangered in 1989 • 1989 quarantined part of southwest, CA in ...
Biomes
... Restricted to equatorial zone Stable warm temperatures (~18°C) with abundant rainfall (>60mm month) High diversity Rapid decomposition Soils are oxisols and utisols, andosols in volcanic areas ...
... Restricted to equatorial zone Stable warm temperatures (~18°C) with abundant rainfall (>60mm month) High diversity Rapid decomposition Soils are oxisols and utisols, andosols in volcanic areas ...
How Does Climate Affect the Nature and Locations of Biomes?
... Sanctuaries for migrating animals (low to high) Help regulate the earth’s climate • Ice and snow reflect solar radiation back into space • Opposite – dark exposed rock absorbs energy? ...
... Sanctuaries for migrating animals (low to high) Help regulate the earth’s climate • Ice and snow reflect solar radiation back into space • Opposite – dark exposed rock absorbs energy? ...
Regions of Africa
... Earth. Even though temperatures there may rise to 136 F (57.7 C), its dryness, not heat, that makes a place like the Sahara a desert. • As the world's largest desert, the Sahara receives less than three inches (7.6 cm) of rain a year. Even in its wettest areas, rain may arrive twice in one week, the ...
... Earth. Even though temperatures there may rise to 136 F (57.7 C), its dryness, not heat, that makes a place like the Sahara a desert. • As the world's largest desert, the Sahara receives less than three inches (7.6 cm) of rain a year. Even in its wettest areas, rain may arrive twice in one week, the ...
Blister beetle
... Antarctica it is the world's driest place. It receives less than two inches of precipitation annually. Antarctica is 5.5 million square miles in area. ...
... Antarctica it is the world's driest place. It receives less than two inches of precipitation annually. Antarctica is 5.5 million square miles in area. ...
SCIENCE NOTES
... - Even in the summer the sun rays only strike the tundra at a low glancing angle. - Not many plants are found here because of the cold and poor soil. What is the Desert Biome Like? - A sandy or rocky biome with little precipitation and little plant life or animal life. - The desert is like the tund ...
... - Even in the summer the sun rays only strike the tundra at a low glancing angle. - Not many plants are found here because of the cold and poor soil. What is the Desert Biome Like? - A sandy or rocky biome with little precipitation and little plant life or animal life. - The desert is like the tund ...
Here - helpforias
... 2. Stems are sometimes modified into fleshy, spongy structure that can store moisture. Plants with such fleshy stem are called succulents ...
... 2. Stems are sometimes modified into fleshy, spongy structure that can store moisture. Plants with such fleshy stem are called succulents ...
File
... Grasslands are covered by tall grasses and wildflowers. Summers are very hot and winters are very cold. These regions suffer from droughts, periods without rain, as well as regular wildfires. The wildfires are set off by lightning strikes in the dry grasses. The fires prevent trees from growing. ...
... Grasslands are covered by tall grasses and wildflowers. Summers are very hot and winters are very cold. These regions suffer from droughts, periods without rain, as well as regular wildfires. The wildfires are set off by lightning strikes in the dry grasses. The fires prevent trees from growing. ...
Populations, Competition, Predation, Migration, Disease
... • For food, water and space • Predators will eat prey and reduce the population (including the number of offspring) • Members of the population may leave the area • A disease could kill some of the ...
... • For food, water and space • Predators will eat prey and reduce the population (including the number of offspring) • Members of the population may leave the area • A disease could kill some of the ...
Grassland, Desert, and Tundra Biomes
... Dominated by grasses, very few trees Hot summers, cold winters 50 to 88 cm of precipitation per year Most fertile soil of any biome Most have been replaced by farms and ...
... Dominated by grasses, very few trees Hot summers, cold winters 50 to 88 cm of precipitation per year Most fertile soil of any biome Most have been replaced by farms and ...
Lab Exam 2 Review Sheet - University of San Diego
... What are the factors that lead to the creation of the Anza-Borrego Desert in eastern San Diego County? How much rainfall occurs on average in the Anza-Borrego desert compared to San Diego’s coast? Know the three different sub-communities or ecosystems of the desert: Low desert scrub; Desert Wash; De ...
... What are the factors that lead to the creation of the Anza-Borrego Desert in eastern San Diego County? How much rainfall occurs on average in the Anza-Borrego desert compared to San Diego’s coast? Know the three different sub-communities or ecosystems of the desert: Low desert scrub; Desert Wash; De ...
World Biomes
... cannot grow. The growing season is approximately 180 days. The nighttime temperature is usually below freezing. Unlike the arctic tundra, the soil in the alpine is well drained. Plants in this region include tussock grasses, dwarf trees, and small-leafed shrubs. ...
... cannot grow. The growing season is approximately 180 days. The nighttime temperature is usually below freezing. Unlike the arctic tundra, the soil in the alpine is well drained. Plants in this region include tussock grasses, dwarf trees, and small-leafed shrubs. ...
Terrestrial biomes
... Shallow, wide roots Many have spines The plant at right is the prickly pear cactus ...
... Shallow, wide roots Many have spines The plant at right is the prickly pear cactus ...
Earth,Notes,RevQs,Ch19
... and much drier, true deserts. Steppes and deserts generally lie between 15 and 35 degrees north and south latitude; the Sahara Desert (Africa) and its bordering plains and semiarid grasslands are a good example. The desert and steppe regions of North America and central Asia extend to higher latitud ...
... and much drier, true deserts. Steppes and deserts generally lie between 15 and 35 degrees north and south latitude; the Sahara Desert (Africa) and its bordering plains and semiarid grasslands are a good example. The desert and steppe regions of North America and central Asia extend to higher latitud ...
Open Journal of Ecology Special Issue on Desert Ecosystem
... Though a desert may seem like a barren land, the desert ecosystem is one of the most diverse when it comes to ‘unique’ flora and fauna. In the harsh environment, the key to survival is adaptation, and that is made obvious by several plants and animals over the years. The desert ecosystem offers many ...
... Though a desert may seem like a barren land, the desert ecosystem is one of the most diverse when it comes to ‘unique’ flora and fauna. In the harsh environment, the key to survival is adaptation, and that is made obvious by several plants and animals over the years. The desert ecosystem offers many ...
APES- Terrestrial Biomes Review
... 1. Describe the rainshadow effect and explain how it can alter the climate of the windward and leeward sides of a mountain range. The mountains block the passage of rain-producing weather systems casting a shadow of dryness behind them. ...
... 1. Describe the rainshadow effect and explain how it can alter the climate of the windward and leeward sides of a mountain range. The mountains block the passage of rain-producing weather systems casting a shadow of dryness behind them. ...
Advance desertification_Lecture 3
... because animals would move in response to rainfall, people would move with the animals so it prevented overgrazing in such areas. Now, humans have a steady food supply so they do not have to move about. Therefore, people use fences to keep their animals in one place which causes overgrazing. ...
... because animals would move in response to rainfall, people would move with the animals so it prevented overgrazing in such areas. Now, humans have a steady food supply so they do not have to move about. Therefore, people use fences to keep their animals in one place which causes overgrazing. ...
nandi central joint examinations – 2009
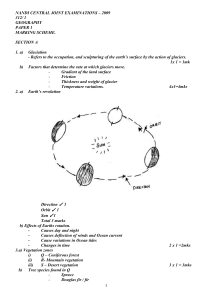
... V .E 10 7. a) Aridity Process through which the soil experiences insufficient moisture leading to scanty vegetation or barren land. b) Reasons winds is a major agent of land sculpture in the desert. Deserts mostly consist of Sand and dust that are easily transported and deposited by wind. Deserts ...
... V .E 10 7. a) Aridity Process through which the soil experiences insufficient moisture leading to scanty vegetation or barren land. b) Reasons winds is a major agent of land sculpture in the desert. Deserts mostly consist of Sand and dust that are easily transported and deposited by wind. Deserts ...
GEOL 1e Lecture Outlines
... a. Longitudinal dunes form long, parallel ridges of sand aligned roughly parallel to the prevailing wind direction. They typically form where sand supplies are limited. b. Longitudinal dunes, 15 m high, in the Gibson Desert, west central Australia. The bright blue areas between the dunes are shallow ...
... a. Longitudinal dunes form long, parallel ridges of sand aligned roughly parallel to the prevailing wind direction. They typically form where sand supplies are limited. b. Longitudinal dunes, 15 m high, in the Gibson Desert, west central Australia. The bright blue areas between the dunes are shallow ...
Leaving Certificate Geography: Mr. McMahon Geoecology Soils
... they become saturated and dense and precipitation occurs on the windward side of the mountains which are the side facing the ocean. Around 80 % of rainfall falls on this area. As a result of this the clouds have lost their moisture before moving inland. The leeward side of the mountain receives only ...
... they become saturated and dense and precipitation occurs on the windward side of the mountains which are the side facing the ocean. Around 80 % of rainfall falls on this area. As a result of this the clouds have lost their moisture before moving inland. The leeward side of the mountain receives only ...
Biomes - davis.k12.ut.us
... types of plants. Beech or Maple or bigger trees or conifers take over, depending on the climate. This is called succession and happens over hundreds of years. ...
... types of plants. Beech or Maple or bigger trees or conifers take over, depending on the climate. This is called succession and happens over hundreds of years. ...
Desert

A desert is a barren area of land where little precipitation occurs and consequently living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to the processes of denudation. About one third of the land surface of the world is arid or semi-arid. This includes much of the polar regions where little precipitation occurs and which are sometimes called ""cold deserts"". Deserts can be classified by the amount of precipitation that falls, by the temperature that prevails, by the causes of desertification or by their geographical location.Deserts are formed by weathering processes as large variations in temperature between day and night put strains on the rocks which consequently break in pieces. Although rain seldom occurs in deserts, there are occasional downpours that can result in flash floods. Rain falling on hot rocks can cause them to shatter and the resulting fragments and rubble strewn over the desert floor is further eroded by the wind. This picks up particles of sand and dust and wafts them aloft in sand or dust storms. Wind-blown sand grains striking any solid object in their path can abrade the surface. Rocks are smoothed down, and the wind sorts sand into uniform deposits. The grains end up as level sheets of sand or are piled high in billowing sand dunes. Other deserts are flat, stony plains where all the fine material has been blown away and the surface consists of a mosaic of smooth stones. These areas are known as desert pavements and little further erosion takes place. Other desert features include rock outcrops, exposed bedrock and clays once deposited by flowing water. Temporary lakes may form and salt pans may be left when waters evaporate. There may be underground sources of water in the form of springs and seepages from aquifers. Where these are found, oases can occur.Plants and animals living in the desert need special adaptations to survive in the harsh environment. Plants tend to be tough and wiry with small or no leaves, water-resistant cuticles and often spines to deter herbivory. Some annual plants germinate, bloom and die in the course of a few weeks after rainfall while other long-lived plants survive for years and have deep root systems able to tap underground moisture. Animals need to keep cool and find enough food and water to survive. Many are nocturnal and stay in the shade or underground during the heat of the day. They tend to be efficient at conserving water, extracting most of their needs from their food and concentrating their urine. Some animals remain in a state of dormancy for long periods, ready to become active again when the rare rains fall. They then reproduce rapidly while conditions are favorable before returning to dormancy.People have struggled to live in deserts and the surrounding semi-arid lands for millennia. Nomads have moved their flocks and herds to wherever grazing is available and oases have provided opportunities for a more settled way of life. The cultivation of semi-arid regions encourages erosion of soil and is one of the causes of increased desertification. Desert farming is possible with the aid of irrigation and the Imperial Valley in California provides an example of how previously barren land can be made productive by the import of water from an outside source. Many trade routes have been forged across deserts, especially across the Sahara Desert, and traditionally were used by caravans of camels carrying salt, gold, ivory and other goods. Large numbers of slaves were also taken northwards across the Sahara. Some mineral extraction also takes place in deserts and the uninterrupted sunlight gives potential for the capture of large quantities of solar energy.