Earth Forces - Jordanhill School
... Stage 2: Suddenly, the pressure is too much and the plates jerk past each other. The place where this happens is called the focus ______________. Stage 3: Vibrations go out in all directions through the rocks. These shockwaves vibrations are called ______________. Earth Stage 4: When the shock waves ...
... Stage 2: Suddenly, the pressure is too much and the plates jerk past each other. The place where this happens is called the focus ______________. Stage 3: Vibrations go out in all directions through the rocks. These shockwaves vibrations are called ______________. Earth Stage 4: When the shock waves ...
Seismological Analysis and the Effect of Earthquakes in the New
... is the first to arrive at a seismic station after movement. It compresses and dilates the rock as it travels. Its usual speed is less than 6km/s in the crust and can get up to 13km/s traveling through the core. The speed is comparable to that of sound waves. S-waves, second preliminary waves, follow ...
... is the first to arrive at a seismic station after movement. It compresses and dilates the rock as it travels. Its usual speed is less than 6km/s in the crust and can get up to 13km/s traveling through the core. The speed is comparable to that of sound waves. S-waves, second preliminary waves, follow ...
Earthquakes - Cal State LA
... Rescue efforts were complicated by the time of the event. Lack of power throughout the city. Poor building codes led to many deaths. Many were rescued but not until hours or days later. ...
... Rescue efforts were complicated by the time of the event. Lack of power throughout the city. Poor building codes led to many deaths. Many were rescued but not until hours or days later. ...
Magnitude 7.1 SOUTHERN EAST PACIFIC RISE
... sized earthquakes are not uncommon in this region, though events of this size are rare. Fifteen other M 6+ earthquakes have occurred within 500 km of this earthquake over the past century – until today none had been larger than a M 7.0 in March 1920, 400 km south of the this earthquake. ...
... sized earthquakes are not uncommon in this region, though events of this size are rare. Fifteen other M 6+ earthquakes have occurred within 500 km of this earthquake over the past century – until today none had been larger than a M 7.0 in March 1920, 400 km south of the this earthquake. ...
There are 3 types of faults 1 Normal Faults
... – These are the waves that produce the most destruction. – Surface waves are limited to travel along only the surface of the Earth. ...
... – These are the waves that produce the most destruction. – Surface waves are limited to travel along only the surface of the Earth. ...
Phyical geology
... – Around the Pacific Ocean (Circum-Pacific belt is major site of earthquakes) ()الحزام المطوق للمحيط الهادي – Mediterranean Sea area through Iran and on the ...
... – Around the Pacific Ocean (Circum-Pacific belt is major site of earthquakes) ()الحزام المطوق للمحيط الهادي – Mediterranean Sea area through Iran and on the ...
Finding an Earthquakes Epicenter
... the earth. Most earthquakes take place along faults in the upper 25 miles of the earth's surface when one side ________________________ relative to the other side of the fault. This sudden motion causes shock waves (_____________________) to radiate from their point of origin called the ____________ ...
... the earth. Most earthquakes take place along faults in the upper 25 miles of the earth's surface when one side ________________________ relative to the other side of the fault. This sudden motion causes shock waves (_____________________) to radiate from their point of origin called the ____________ ...
earthquakes
... coasts of most landmasses bordering the Indian Ocean, killing more than 225,000 people in eleven countries, and inundating coastal communities with waves up to 30 meters (100 feet). This was the ninth-deadliest natural disaster in modern history. Indonesia, Sri Lanka, India, Thailand, and Myanmar we ...
... coasts of most landmasses bordering the Indian Ocean, killing more than 225,000 people in eleven countries, and inundating coastal communities with waves up to 30 meters (100 feet). This was the ninth-deadliest natural disaster in modern history. Indonesia, Sri Lanka, India, Thailand, and Myanmar we ...
Earthquake Study Guide Key
... earthquake. It is a measure of the effect of an earthquake on the structures, people and environment. The intensity of an earthquake may vary depending on where it occurs. 5. What scale is used to measure intensity? Modified-Mercalli Scale 6. What do the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes have i ...
... earthquake. It is a measure of the effect of an earthquake on the structures, people and environment. The intensity of an earthquake may vary depending on where it occurs. 5. What scale is used to measure intensity? Modified-Mercalli Scale 6. What do the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes have i ...
Chapter: Chapter 5: Earthquakes and Earth`s Interior
... 8. The Earth's density as a whole is approximately 2.8 g/cm3.F 9. P-waves travel by compression-expansion. T 10. The mantle makes up roughly 80% of the Earth's volume. T ...
... 8. The Earth's density as a whole is approximately 2.8 g/cm3.F 9. P-waves travel by compression-expansion. T 10. The mantle makes up roughly 80% of the Earth's volume. T ...
Earthquakes - Laconia School District
... the Richter scale. Earthquakes below 4.0 on the Richter scale usually do not cause damage, and earthquakes below 2.0 usually can’t be felt. Earthquakes over 5.0 on the scale can cause damage. A magnitude 6.0 earthquake is considered strong and a magnitude 7.0 is a major earthquake. The Northridge Ea ...
... the Richter scale. Earthquakes below 4.0 on the Richter scale usually do not cause damage, and earthquakes below 2.0 usually can’t be felt. Earthquakes over 5.0 on the scale can cause damage. A magnitude 6.0 earthquake is considered strong and a magnitude 7.0 is a major earthquake. The Northridge Ea ...
Section 19.1 Forces Within Earth
... • Pancaking - shaking causes a building’s supporting walls to collapse and the upper floors to fall one on top of the other like a stack of pancakes. • If the shaking caused by an earthquake has the same frequency of vibration as the natural sway of buildings of certain heights, those buildings will ...
... • Pancaking - shaking causes a building’s supporting walls to collapse and the upper floors to fall one on top of the other like a stack of pancakes. • If the shaking caused by an earthquake has the same frequency of vibration as the natural sway of buildings of certain heights, those buildings will ...
GEOLOGY Test Study Guide
... USING KEY TERMS (WORD BANK WILL BE PROVIDED) 19. The lithosphere floats on a layer of the Earth’s mantle called the ______________________ 20. The mantle mainly consists of a dense layer called the ______________________ 21. The liquid layer at the Earth’s center is known as the ____________________ ...
... USING KEY TERMS (WORD BANK WILL BE PROVIDED) 19. The lithosphere floats on a layer of the Earth’s mantle called the ______________________ 20. The mantle mainly consists of a dense layer called the ______________________ 21. The liquid layer at the Earth’s center is known as the ____________________ ...
EARTHQUAKES AND PLATE TECTONICS
... ready to follow a few simple earthquake safety rules to help prevent death, injury, and property damage ...
... ready to follow a few simple earthquake safety rules to help prevent death, injury, and property damage ...
Name: ___________________________ Chapter 6 Notes: Earthquakes Stress
... Richter Scale: rates earthquakes according to the magnitude of the seismic waves. Magnitude: is the number assigned to the earthquake based on the size. The magnitude tells how much energy was released by an earthquake. Moment Magnitude Scale: rating that estimates the energy released by an ...
... Richter Scale: rates earthquakes according to the magnitude of the seismic waves. Magnitude: is the number assigned to the earthquake based on the size. The magnitude tells how much energy was released by an earthquake. Moment Magnitude Scale: rating that estimates the energy released by an ...
earthquakes II
... detector. Use a ruler and scissors to cut 4-inch (10 cm) slits in the bottom edges of the two long sides of the box. Cut paper into strips slightly smaller than 4 inches (10 cm) wide. Attach pieces together with clear adhesive tape to form a long strip. Insert the strip of paper into the slits so th ...
... detector. Use a ruler and scissors to cut 4-inch (10 cm) slits in the bottom edges of the two long sides of the box. Cut paper into strips slightly smaller than 4 inches (10 cm) wide. Attach pieces together with clear adhesive tape to form a long strip. Insert the strip of paper into the slits so th ...
earthquakes - englishgaresti2
... • If you're indoors, stay there. Get under -- and hold onto --a desk or table, or stand against an interior wall. Stay clear of exterior walls, glass, heavy furniture, fireplaces and appliances. The kitchen is a particularly dangerous spot. If you’re in an office building, stay away from windows and ...
... • If you're indoors, stay there. Get under -- and hold onto --a desk or table, or stand against an interior wall. Stay clear of exterior walls, glass, heavy furniture, fireplaces and appliances. The kitchen is a particularly dangerous spot. If you’re in an office building, stay away from windows and ...
What is an Earthquake?
... 3. Moment Magnitude Scale -combine how rigid the Earth is and the distance the Earth moves along the fault -scientists use this method the most ...
... 3. Moment Magnitude Scale -combine how rigid the Earth is and the distance the Earth moves along the fault -scientists use this method the most ...
The Role of Architectural Considerations in Seismic Performance of
... buildings) are analyzed with details. Results showed that the most of damages are occurred in the old steel structures and masonry buildings which their ages are more than 25 years. The study showed that most of the buildings in the study area are steel structure and masonry buildings while concrete ...
... buildings) are analyzed with details. Results showed that the most of damages are occurred in the old steel structures and masonry buildings which their ages are more than 25 years. The study showed that most of the buildings in the study area are steel structure and masonry buildings while concrete ...
Quiz 5
... 15. _______ are fragments of unmelted rock that are sometimes incorporated in magma. 16. The area inside the Earth where rocks start to turn plastic is known as the _______. ...
... 15. _______ are fragments of unmelted rock that are sometimes incorporated in magma. 16. The area inside the Earth where rocks start to turn plastic is known as the _______. ...
Review for Exam 3
... 11. What factors determine the seismic intensity of a particular event at a given location? 12. Why do insurance companies use the Modified Mecalli intensity scale instead of a magnitude scale in classifying earthquakes? 13. Describe how a tsunami is generated by an earthquake. 14. Describe the two ...
... 11. What factors determine the seismic intensity of a particular event at a given location? 12. Why do insurance companies use the Modified Mecalli intensity scale instead of a magnitude scale in classifying earthquakes? 13. Describe how a tsunami is generated by an earthquake. 14. Describe the two ...
Montana Bureau of Mines and Geology and Montana Disaster and
... Troy Mine in northwestern Montana. These unusual low-frequency events apparently correlate with rooffalls in an abandoned part of the mine. Event magnitudes ranged from 1.2 to 3.7. Twelve seismic events with magnitudes ranging from 1.3 to 2.3 occurred throughout the year in the Coeur d’Alene Mining ...
... Troy Mine in northwestern Montana. These unusual low-frequency events apparently correlate with rooffalls in an abandoned part of the mine. Event magnitudes ranged from 1.2 to 3.7. Twelve seismic events with magnitudes ranging from 1.3 to 2.3 occurred throughout the year in the Coeur d’Alene Mining ...
Earth Forces - Jordanhill School
... Stage 2: Suddenly, the pressure is too much and the plates jerk past each other. The place where this happens is called the Focus ______________. Stage 3: Vibrations go out in all directions through the rocks. These Shockwaves vibrations are called ______________. Earth Stage 4: When the shock waves ...
... Stage 2: Suddenly, the pressure is too much and the plates jerk past each other. The place where this happens is called the Focus ______________. Stage 3: Vibrations go out in all directions through the rocks. These Shockwaves vibrations are called ______________. Earth Stage 4: When the shock waves ...
I gained more knowledge and skills. I was also able to network and
... alternatives but some are expensive. Among the most practically feasible and economically viable methods are wall jacketing and introduction of shear walls. The estimated cost for such intervention is 15% to 40% of reconstruction. There is a plan to pilot this technique in one of the school building ...
... alternatives but some are expensive. Among the most practically feasible and economically viable methods are wall jacketing and introduction of shear walls. The estimated cost for such intervention is 15% to 40% of reconstruction. There is a plan to pilot this technique in one of the school building ...
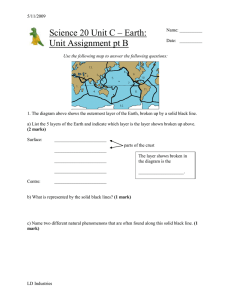
Unit C UA pt B - LD Industries
... ________ - a crack in Earth’s crust due to the motion of one tectonic plate relative to another ________ - a number assigned to an earthquake based on the amount of vertical ground motion at its epicentre ________ - a seismic wave that travels through rock as a series of compressions and expansions ...
... ________ - a crack in Earth’s crust due to the motion of one tectonic plate relative to another ________ - a number assigned to an earthquake based on the amount of vertical ground motion at its epicentre ________ - a seismic wave that travels through rock as a series of compressions and expansions ...
Earthquake engineering

Earthquake engineering or Seismic engineering is a branch of engineering that searches for ways to make structures, such as buildings and bridges, resistant to earthquake damage. Earthquake engineer, better known as a seismic engineer aim to develop building techniques that will prevent any damage in a minor quake and avoid serious damage or collapse in a major shake. It is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of both structural and geotechnical engineering. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an expansion of its scope to encompass disciplines from the wider field of civil engineering, mechanical engineering and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics and finance. The main objectives of earthquake engineering are: Foresee the potential consequences of strong earthquakes on urban areas and civil infrastructure. Design, construct and maintain structures to perform at earthquake exposure up to the expectations and in compliance with building codes.A properly engineered structure does not necessarily have to be extremely strong or expensive. It has to be properly designed to withstand the seismic effects while sustaining an acceptable level of damage.