Structural engineering
... injured. Following the collapse The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA)advised states to inspect the 700 U.S. bridges of similar construction after a possible design flaw in the bridge was discovered, related to large steel sheets called gusset plates which were used to connect girders together in ...
... injured. Following the collapse The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA)advised states to inspect the 700 U.S. bridges of similar construction after a possible design flaw in the bridge was discovered, related to large steel sheets called gusset plates which were used to connect girders together in ...
- Catalyst
... b. horizontal accelerations of incoming shear and surface waves c. enhanced wave amplification in some unconsolidated substrates d. all of the above answers are correct e. only answers b and c are correct 24. How is the recurrence interval of volcanic eruptions related to explosivity index? a. there ...
... b. horizontal accelerations of incoming shear and surface waves c. enhanced wave amplification in some unconsolidated substrates d. all of the above answers are correct e. only answers b and c are correct 24. How is the recurrence interval of volcanic eruptions related to explosivity index? a. there ...
Earthquakes: Basic Principles
... destruction of the city. The survivors that had fled to the waterside were drowned by the great waves that raced on them from the Atlantic. The motion of this first earthquake had not ceased for more than a few minutes when a second shock came, only slightly less severe than the first. A third and l ...
... destruction of the city. The survivors that had fled to the waterside were drowned by the great waves that raced on them from the Atlantic. The motion of this first earthquake had not ceased for more than a few minutes when a second shock came, only slightly less severe than the first. A third and l ...
the 1985 mexico earthquake
... Zone Structure, roughly 10 km. thick, dipping 14 degrees at N23E. This is in good agreement with the geometry source obtained by waveform modeling of the 1985 mainshock, and the large 1979 Petatlan earthquake in the adjoining region. The earthquake epicentral resolution, obtained with this program, ...
... Zone Structure, roughly 10 km. thick, dipping 14 degrees at N23E. This is in good agreement with the geometry source obtained by waveform modeling of the 1985 mainshock, and the large 1979 Petatlan earthquake in the adjoining region. The earthquake epicentral resolution, obtained with this program, ...
STRUCTURE OF THE MOON BY SEISMIC DATA
... Between 1969 and 1972 by the American lunar program "Apollo" was deployed a network of high-sensitivity seismometers in the central part of the visible side of the Moon. Seismometers, "Apollo" continued to work for eight years, during which they passed on information about the natural seismic activi ...
... Between 1969 and 1972 by the American lunar program "Apollo" was deployed a network of high-sensitivity seismometers in the central part of the visible side of the Moon. Seismometers, "Apollo" continued to work for eight years, during which they passed on information about the natural seismic activi ...
Chapter 12 Section 1
... Seismic Waves and Earth’s Interior • By studying the speed and direction of seismic waves, scientists can learn more about the makeup and structure of Earth’s interior. Earth’s Internal Layers • In 1909, Andrija Mohorovičić discovered that the speed of seismic waves increases abruptly at about 30 km ...
... Seismic Waves and Earth’s Interior • By studying the speed and direction of seismic waves, scientists can learn more about the makeup and structure of Earth’s interior. Earth’s Internal Layers • In 1909, Andrija Mohorovičić discovered that the speed of seismic waves increases abruptly at about 30 km ...
Earthquake geotechnical engineering practice
... foundation design, and advanced numerical modelling using finite element and finite difference methods. The benefits include increased productivity and, when used properly, useful additional insights from parametric studies and rapid prototyping. However, users need to have a sound understanding of ...
... foundation design, and advanced numerical modelling using finite element and finite difference methods. The benefits include increased productivity and, when used properly, useful additional insights from parametric studies and rapid prototyping. However, users need to have a sound understanding of ...
Chapter 8 Earthquakes
... Scientists who study earthquakes use an important tool called a seismograph. A seismograph records vibrations that are caused by seismic waves. When the waves from an earthquake reach a seismograph, it records them as lines on a chart called a seismogram. ...
... Scientists who study earthquakes use an important tool called a seismograph. A seismograph records vibrations that are caused by seismic waves. When the waves from an earthquake reach a seismograph, it records them as lines on a chart called a seismogram. ...
Episodic Tremor and Slip
... motions over time as small as a millimeter per year. Careful analysis of the relative positions of instruments near the edge of the plate relative to those in the interior found that some instruments occasionally moved back toward the trench, instead of towards North America as would be expected alo ...
... motions over time as small as a millimeter per year. Careful analysis of the relative positions of instruments near the edge of the plate relative to those in the interior found that some instruments occasionally moved back toward the trench, instead of towards North America as would be expected alo ...
Seismic reflection imaging of mineral systems
... Mineral deposits can be described in terms of their mineral systems, ie., fluid source, migration pathway and trap. Source regions are difficult to recognise in seismic images. Many orebodies lie on or adjacent to major fault systems, suggesting that the faults acted as fluid migration pathways thro ...
... Mineral deposits can be described in terms of their mineral systems, ie., fluid source, migration pathway and trap. Source regions are difficult to recognise in seismic images. Many orebodies lie on or adjacent to major fault systems, suggesting that the faults acted as fluid migration pathways thro ...
Quaking, Shaking, Earth
... past each other without much upward or downward movement. • The San Andreas Fault is the boundary between two of Earth’s plates that are moving sideways past each other. ...
... past each other without much upward or downward movement. • The San Andreas Fault is the boundary between two of Earth’s plates that are moving sideways past each other. ...
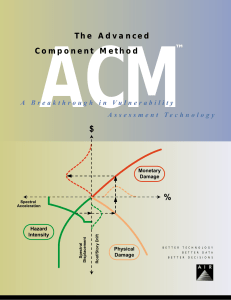
The Advanced Component Method
... associated with a different cost; the appropriate method may depend on the degree of damage and accessibility. At high levels of damage, replacing the affected member may be considered. Repair costs are determined by identifying the repair strategies for each damaged component on each floor of the b ...
... associated with a different cost; the appropriate method may depend on the degree of damage and accessibility. At high levels of damage, replacing the affected member may be considered. Repair costs are determined by identifying the repair strategies for each damaged component on each floor of the b ...
Recent progress of seismic observation networks in Japan
... observation system in Japan. A large number of strong-motion, high-sensitivity, and broadband seismographs were installed to construct dense and uniform networks covering the whole of Japan. The new high-sensitivity seismograph network consisting of 696 stations is called Hi-net, while the broadband ...
... observation system in Japan. A large number of strong-motion, high-sensitivity, and broadband seismographs were installed to construct dense and uniform networks covering the whole of Japan. The new high-sensitivity seismograph network consisting of 696 stations is called Hi-net, while the broadband ...
3-D Pushover Analysis for Damage Assessment of Buildings
... uniform seven-storey reinforced concrete buildings to illustrate the procedure. Building S is symmetric and Building A is plan-eccentric. Each building has a rectangular plan measuring 24m by 17m. The lateral load resisting elements in the y-direction consist of three identical ductile moment resist ...
... uniform seven-storey reinforced concrete buildings to illustrate the procedure. Building S is symmetric and Building A is plan-eccentric. Each building has a rectangular plan measuring 24m by 17m. The lateral load resisting elements in the y-direction consist of three identical ductile moment resist ...
earthquakes and earth`s interior
... a land-based quake, no major tsunami was generated like the famous one triggered by the Boxing Day earthquake under the Indian Ocean in 2004. In 1946 a more powerful 8.1 quake struck the northeast corner of Haiti, but the damage was greater in 2010 because the quake was near the capital city, it was ...
... a land-based quake, no major tsunami was generated like the famous one triggered by the Boxing Day earthquake under the Indian Ocean in 2004. In 1946 a more powerful 8.1 quake struck the northeast corner of Haiti, but the damage was greater in 2010 because the quake was near the capital city, it was ...
FIFTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES
... caused when energy is released as the lithosphere (crust and upper mantle) of the Earth moves. Energy is emitted in the form of waves. There are different types of waves, some move faster, slower, sideways, or up and down. A seismograph records these waves on a seismogram. When an earthquake is reco ...
... caused when energy is released as the lithosphere (crust and upper mantle) of the Earth moves. Energy is emitted in the form of waves. There are different types of waves, some move faster, slower, sideways, or up and down. A seismograph records these waves on a seismogram. When an earthquake is reco ...
Subsurface Structure Model of Mount Merapi Using Receiver
... amplitude of the arrival S in the receiver function are sensitive to the local earth structure. This method applies deconvolution of P wave from radial component to isolate receiver function response (Ammon, 1997). In many Countries, researches of crust and upper mantle were modeled by using receive ...
... amplitude of the arrival S in the receiver function are sensitive to the local earth structure. This method applies deconvolution of P wave from radial component to isolate receiver function response (Ammon, 1997). In many Countries, researches of crust and upper mantle were modeled by using receive ...
Structural Stone Surfaces
... of the individual blocks. For example, with a typical limestone used in cathedrals, in order for the bottom stone of a column to be crushed by the weight of the stones above it, the column should be 2 kilometres (1.2 miles) tall. In general, ‘good structural form’, that is, a geometry that follows t ...
... of the individual blocks. For example, with a typical limestone used in cathedrals, in order for the bottom stone of a column to be crushed by the weight of the stones above it, the column should be 2 kilometres (1.2 miles) tall. In general, ‘good structural form’, that is, a geometry that follows t ...
Pounding between adjacent buildings: comparison
... for factoring in the ground motions characteristics (Table 2). ...
... for factoring in the ground motions characteristics (Table 2). ...
Induced Seismicity: The Potential for Triggered Earthquakes in Kansas
... increases (Ellsworth, 2013). Because of their depth, faults within the basement rock are hard to locate. Oil and gas exploration companies, which provide much of the data about the state’s subsurface geology, rarely drill that deep. Seismic-reflection techniques used to identify subsurface rocks and ...
... increases (Ellsworth, 2013). Because of their depth, faults within the basement rock are hard to locate. Oil and gas exploration companies, which provide much of the data about the state’s subsurface geology, rarely drill that deep. Seismic-reflection techniques used to identify subsurface rocks and ...
Induced Seismicity - the Kansas Geological Survey
... increases (Ellsworth, 2013). Because of their depth, faults within the basement rock are hard to locate. Oil and gas exploration companies, which provide much of the data about the state’s subsurface geology, rarely drill that deep. Seismic-reflection techniques used to identify subsurface rocks and ...
... increases (Ellsworth, 2013). Because of their depth, faults within the basement rock are hard to locate. Oil and gas exploration companies, which provide much of the data about the state’s subsurface geology, rarely drill that deep. Seismic-reflection techniques used to identify subsurface rocks and ...
Earthquakes Jeopardy
... three seismograph stations are used to determine an epicenter . What is triangulation? Template created by Theresa Meyer ...
... three seismograph stations are used to determine an epicenter . What is triangulation? Template created by Theresa Meyer ...
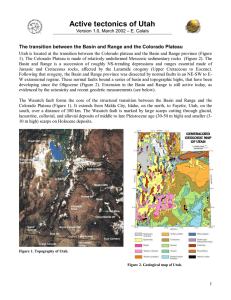
Active tectonics of Utah
... therefore important to, eventually, forecast the next event. Also, if the fault slip rate is known (from geodetic studies, for instance), then the date of the last earthquake can tell us how much elastic strain is currently accommodated on a particular fault. For instance, a fault slipping at 5 mm/y ...
... therefore important to, eventually, forecast the next event. Also, if the fault slip rate is known (from geodetic studies, for instance), then the date of the last earthquake can tell us how much elastic strain is currently accommodated on a particular fault. For instance, a fault slipping at 5 mm/y ...
Earthquake engineering

Earthquake engineering or Seismic engineering is a branch of engineering that searches for ways to make structures, such as buildings and bridges, resistant to earthquake damage. Earthquake engineer, better known as a seismic engineer aim to develop building techniques that will prevent any damage in a minor quake and avoid serious damage or collapse in a major shake. It is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of both structural and geotechnical engineering. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an expansion of its scope to encompass disciplines from the wider field of civil engineering, mechanical engineering and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics and finance. The main objectives of earthquake engineering are: Foresee the potential consequences of strong earthquakes on urban areas and civil infrastructure. Design, construct and maintain structures to perform at earthquake exposure up to the expectations and in compliance with building codes.A properly engineered structure does not necessarily have to be extremely strong or expensive. It has to be properly designed to withstand the seismic effects while sustaining an acceptable level of damage.