Title A Global Energy Transfer Process of Tsunamigenic Earthquake
... This work should be taken as one ofthe extellsive research work. There have been the researches in selslnology7 geodesy and plate tectonlcs on the bases of ...
... This work should be taken as one ofthe extellsive research work. There have been the researches in selslnology7 geodesy and plate tectonlcs on the bases of ...
Variations of fluid pressure within the subducting oceanic crust and
... reduce the strength of crustal rocks, enhancing ductile creep [Carter and Tsenn, 1987], so weak shear zones could develop at the deep extension of the MTL, which in turn leads to loading on brittle faults in the upper crust. This implies that deep subduction fluids can induce crustal seismogenesis [ ...
... reduce the strength of crustal rocks, enhancing ductile creep [Carter and Tsenn, 1987], so weak shear zones could develop at the deep extension of the MTL, which in turn leads to loading on brittle faults in the upper crust. This implies that deep subduction fluids can induce crustal seismogenesis [ ...
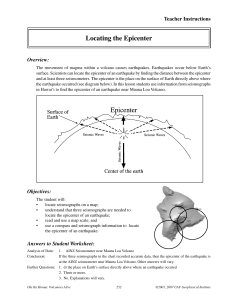
Locating the Epicenter
... and at least three seismometers. The epicenter is the place on the surface of Earth directly above where the earthquake occurred (see diagram below). In this lesson students use information from seismographs in Hawaiÿi to find the epicenter of an earthquake near Mauna Loa Volcano. ...
... and at least three seismometers. The epicenter is the place on the surface of Earth directly above where the earthquake occurred (see diagram below). In this lesson students use information from seismographs in Hawaiÿi to find the epicenter of an earthquake near Mauna Loa Volcano. ...
butfem_5
... (deep or soft soil). The shear wave velocity was taken as 160m/s based on the investigation for the site subsoil classification (Boon et al. 2011) and correspondingly dynamic shear modulus as 47GPa considering the typical values of soil class D. Since the structure under study is an office building, ...
... (deep or soft soil). The shear wave velocity was taken as 160m/s based on the investigation for the site subsoil classification (Boon et al. 2011) and correspondingly dynamic shear modulus as 47GPa considering the typical values of soil class D. Since the structure under study is an office building, ...
A seismotectonic study for the Heraklion basin in Crete (Southern
... direction but also in N-S. We divided the Cretan crust in five units. The upper layer, showing a velocity range between 1.5– 2.2 km/s, corresponds to the seawater layer and the upper series of the post-Alpine sediments. The second layer has a velocity between 2.3 and 4.4 km/s and could represent the ...
... direction but also in N-S. We divided the Cretan crust in five units. The upper layer, showing a velocity range between 1.5– 2.2 km/s, corresponds to the seawater layer and the upper series of the post-Alpine sediments. The second layer has a velocity between 2.3 and 4.4 km/s and could represent the ...
All About Earthquakes
... other plate might move the other way. Or one plate might move up and the other might move down. Many earthquakes occur along the San Andreas Fault, which stretches about 650 miles along the coast of California. The San Andreas Fault is a boundary area between two plates that are still moving, so it ...
... other plate might move the other way. Or one plate might move up and the other might move down. Many earthquakes occur along the San Andreas Fault, which stretches about 650 miles along the coast of California. The San Andreas Fault is a boundary area between two plates that are still moving, so it ...
Repeating earthquakes and quasi-static slip on the plate boundary east... northern Honshu, Japan Toru Matsuzawa , Naoki Uchida
... increase, the stresses on the asperities located at the edge of the afterslip area become large enough to rupture them even if their sizes are large. In this way, a rupture of an asperity (earthquake) generates its afterslip and the afterslip triggers the next earthquake (Fig. 5(d)). When no loaded ...
... increase, the stresses on the asperities located at the edge of the afterslip area become large enough to rupture them even if their sizes are large. In this way, a rupture of an asperity (earthquake) generates its afterslip and the afterslip triggers the next earthquake (Fig. 5(d)). When no loaded ...
SEISMIC AND ASEISMIC SLIP ALONG SUBDUCTION ZONES AND
... in the oceanic lithosphere, which does not represent slip on the inter-plate boundary. The location of the 1896 Sanriku earthquake is not known accurately, but macro-seismic data and some instrumental data strongly suggest that this is a tsunami earthquake, or, in more general terms, a silent earthq ...
... in the oceanic lithosphere, which does not represent slip on the inter-plate boundary. The location of the 1896 Sanriku earthquake is not known accurately, but macro-seismic data and some instrumental data strongly suggest that this is a tsunami earthquake, or, in more general terms, a silent earthq ...
Measuring the Magnitude of an Earthquake
... The scale was developed in Southern California. The conditions in the rest of the world may not be the same as they are in California. ...
... The scale was developed in Southern California. The conditions in the rest of the world may not be the same as they are in California. ...
Earthquakes
... has area the same as a normal above seathe level. fault, but blocks move in the opposite direction. ...
... has area the same as a normal above seathe level. fault, but blocks move in the opposite direction. ...
Base Isolation in Hospitals
... construction was 267 square meters per bed. The site cost is not included. Several buildings form up the complex. The clinical and emergency services are located in a base-isolated structure, (Figure 1) in order to protect the investment and the functionality of their services. The structural system ...
... construction was 267 square meters per bed. The site cost is not included. Several buildings form up the complex. The clinical and emergency services are located in a base-isolated structure, (Figure 1) in order to protect the investment and the functionality of their services. The structural system ...
surface wave - Madison Local Schools
... • focus the location within Earth along a fault at which the first motion of an earthquake occurs • epicenter the point on Earth’s surface above an earthquake’s starting point, or focus • Although the focus depths of earthquakes vary, about 90% of continental earthquakes have shallow foci. • Earthqu ...
... • focus the location within Earth along a fault at which the first motion of an earthquake occurs • epicenter the point on Earth’s surface above an earthquake’s starting point, or focus • Although the focus depths of earthquakes vary, about 90% of continental earthquakes have shallow foci. • Earthqu ...
Dynamic Earth Unit 4 lesson 5 Earthquakes
... • Most earthquakes do not cause damage, but some strong earthquakes can cause major damage and loss of life, especially in areas closest to the epicenter. • When the shaking of an earthquake is more than structures can withstand, major destruction can occur. • Much of the injury and loss of life aft ...
... • Most earthquakes do not cause damage, but some strong earthquakes can cause major damage and loss of life, especially in areas closest to the epicenter. • When the shaking of an earthquake is more than structures can withstand, major destruction can occur. • Much of the injury and loss of life aft ...
Tsunami Lecture
... UN categorizes disasters as follows: Hydro-meteorological disasters: including floods and wave surges, storms, droughts and related disasters (extreme temperatures and forest/scrub fires), and landslides & ...
... UN categorizes disasters as follows: Hydro-meteorological disasters: including floods and wave surges, storms, droughts and related disasters (extreme temperatures and forest/scrub fires), and landslides & ...
8.1 What Is an Earthquake?
... Before the great 1906 San Francisco earthquake, the actual causes and effects of earthquakes were not understood. The San Fransisco earthquake caused horizontal shifts in Earth’s surface of several meters along the northern portion of the San Andreas Fault. The 1300-kilometer San Andreas fracture ex ...
... Before the great 1906 San Francisco earthquake, the actual causes and effects of earthquakes were not understood. The San Fransisco earthquake caused horizontal shifts in Earth’s surface of several meters along the northern portion of the San Andreas Fault. The 1300-kilometer San Andreas fracture ex ...
Earthquake engineering

Earthquake engineering or Seismic engineering is a branch of engineering that searches for ways to make structures, such as buildings and bridges, resistant to earthquake damage. Earthquake engineer, better known as a seismic engineer aim to develop building techniques that will prevent any damage in a minor quake and avoid serious damage or collapse in a major shake. It is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of both structural and geotechnical engineering. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an expansion of its scope to encompass disciplines from the wider field of civil engineering, mechanical engineering and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics and finance. The main objectives of earthquake engineering are: Foresee the potential consequences of strong earthquakes on urban areas and civil infrastructure. Design, construct and maintain structures to perform at earthquake exposure up to the expectations and in compliance with building codes.A properly engineered structure does not necessarily have to be extremely strong or expensive. It has to be properly designed to withstand the seismic effects while sustaining an acceptable level of damage.