Phy. Sci Mid-term review
... 19. Fill in the following table. Use a periodic table Remember: (atomic number = number of protons), (number of electrons = number of protons), (mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons.) ...
... 19. Fill in the following table. Use a periodic table Remember: (atomic number = number of protons), (number of electrons = number of protons), (mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons.) ...
Class 9 CBSE Test paper Solved Chapter 3: Atoms and...
... 2. Q. If the valency of an element ‘X’ is 3, write the chemical formula of its Sulphide and Chloride. Ans: X2(SO4)3 and Xcl3 3. Q. Which the unit is used to measure the atomic radius ? Convert this unit in metre. Ans: ...
... 2. Q. If the valency of an element ‘X’ is 3, write the chemical formula of its Sulphide and Chloride. Ans: X2(SO4)3 and Xcl3 3. Q. Which the unit is used to measure the atomic radius ? Convert this unit in metre. Ans: ...
Bohr model and electron configuration
... Energy is quantized. It comes in chunks. A quantum is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the elec ...
... Energy is quantized. It comes in chunks. A quantum is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the elec ...
03 Atoms – Nuclides
... a gamma ray (γ), which is a photon, a particle with a exceedingly high wave frequency and energy (visible light and radio waves are also photons, as well as all other electromagnetic radiation). An additional radioactive process is nuclear fission, where some elements can split as a result of absorb ...
... a gamma ray (γ), which is a photon, a particle with a exceedingly high wave frequency and energy (visible light and radio waves are also photons, as well as all other electromagnetic radiation). An additional radioactive process is nuclear fission, where some elements can split as a result of absorb ...
CHAPTER 2: THE ATOMS AND MOLECULES OF ANCIENT EARTH
... B. For carbon to be reduced, early atmosphere must have contained CH 4, H2, and NH3 (molecules that can give up electrons). 1. Volcanic ash is known to be rich in CO2, H2O, and N2. 2. Recent evidence indicates it also has small amounts of CH4, H2, and NH3. C. Once organic molecules formed, only heat ...
... B. For carbon to be reduced, early atmosphere must have contained CH 4, H2, and NH3 (molecules that can give up electrons). 1. Volcanic ash is known to be rich in CO2, H2O, and N2. 2. Recent evidence indicates it also has small amounts of CH4, H2, and NH3. C. Once organic molecules formed, only heat ...
o Schrödinger equation for o Two-electron atoms. o Multi
... The “+” sign applies if the particles are bosons. These are said to be symmetric with respect to particle exchange. The “-” sign applies to fermions, which are antisymmetric with respect to particle exchange. ...
... The “+” sign applies if the particles are bosons. These are said to be symmetric with respect to particle exchange. The “-” sign applies to fermions, which are antisymmetric with respect to particle exchange. ...
Chapter 2
... We cannot create or destroy matter. • Law of conservation of matter: Whenever matter undergoes a physical or chemical change, no atoms are created or destroyed. • This means that we can never really throw anything “away,” because the atoms in any form of matter cannot be destroyed as it undergoes p ...
... We cannot create or destroy matter. • Law of conservation of matter: Whenever matter undergoes a physical or chemical change, no atoms are created or destroyed. • This means that we can never really throw anything “away,” because the atoms in any form of matter cannot be destroyed as it undergoes p ...
Atomic Physics
... An electron is moving at a speed of 2.1 × 106 m/s in the first Bohr orbit. Determine its de Broglie wavelength. a. b. c. d. e. ...
... An electron is moving at a speed of 2.1 × 106 m/s in the first Bohr orbit. Determine its de Broglie wavelength. a. b. c. d. e. ...
Chapter 2 - profpaz.com
... a) Mg b) N c) F d) Na 2. Determine the number of protons and electrons in each ion listed below: a) Al3+ b) Se2– c) Sr2+ ...
... a) Mg b) N c) F d) Na 2. Determine the number of protons and electrons in each ion listed below: a) Al3+ b) Se2– c) Sr2+ ...
Unit 11: The Mole
... 1.) How many atoms would there be in one mole? 2.) What would be the mass of one mole of Carbon atoms? ...
... 1.) How many atoms would there be in one mole? 2.) What would be the mass of one mole of Carbon atoms? ...
Photoreflectance of Semiconductors
... Defects cause strain on the surface Cracks form Periodicity lost ...
... Defects cause strain on the surface Cracks form Periodicity lost ...
introduction - 123seminarsonly.com
... dielectric. As may be concluded from equation that the SPW may be supported by the structure providing that emr < -ns2 ...
... dielectric. As may be concluded from equation that the SPW may be supported by the structure providing that emr < -ns2 ...
Compton Effect and Spectral Lines
... which is initially at rest. What is the wavelength of the scattered photon? What energy (in eV) does the electron acquire in the collision? What is the velocity of the recoil electron? 2) An electron and a photon have the same energy E= 25 keV. Compare the momenta of the two. 3) Calculate the percen ...
... which is initially at rest. What is the wavelength of the scattered photon? What energy (in eV) does the electron acquire in the collision? What is the velocity of the recoil electron? 2) An electron and a photon have the same energy E= 25 keV. Compare the momenta of the two. 3) Calculate the percen ...
ICP Plasma
... excited electrons emit certain wavelengths when they return to ground state Each element emits a specific wavelength particular to its chemical make-up Intensity of wavelength is proportional to concentration of element in analyzed sample Used to determine elemental composition ...
... excited electrons emit certain wavelengths when they return to ground state Each element emits a specific wavelength particular to its chemical make-up Intensity of wavelength is proportional to concentration of element in analyzed sample Used to determine elemental composition ...
Chapter 10 - Chemical Reactions
... Many times, Balancing equations is a trial & error process Ex: Combustion of Gasoline (Octane) 2C8H18(g) + 25O2(g) 16CO2(g) + 18H2O(g) However, you should be familiar with the rules which describe balanced chemical reactions. 1. Number of Atoms of each element conserved in reactants and products 2. ...
... Many times, Balancing equations is a trial & error process Ex: Combustion of Gasoline (Octane) 2C8H18(g) + 25O2(g) 16CO2(g) + 18H2O(g) However, you should be familiar with the rules which describe balanced chemical reactions. 1. Number of Atoms of each element conserved in reactants and products 2. ...
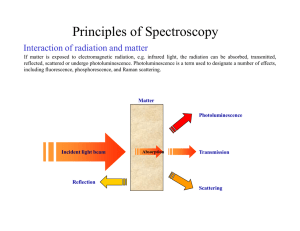
Principles of Spectroscopy
... Spectrometers are equipped with a broadband light source, which yields a continuous, infinite number, of wavelengths, as shown in the figure on the left. The interferogram is the continuous sum, i.e. the integral, of all the interference patterns produced by each wavelength. This results in the inte ...
... Spectrometers are equipped with a broadband light source, which yields a continuous, infinite number, of wavelengths, as shown in the figure on the left. The interferogram is the continuous sum, i.e. the integral, of all the interference patterns produced by each wavelength. This results in the inte ...
Just a Few Things 2012
... nucleons: protons and neutrons mass number = # (protons) + # (neutrons) atomic number = # (protons) ...
... nucleons: protons and neutrons mass number = # (protons) + # (neutrons) atomic number = # (protons) ...
Atomic Term Symbols
... respectively, 9 states in total. A 2 D level (S=1/2, L=2), splits into J=5/2 (6 states) and J=3/2 (4 states), hence 10 states in total. The atomic term values are 2 D5/ 2 , 2 D3/ 2 . You may notice that the splittings discussed for the hydrogen atom follow this rule also. The energy splittings betwe ...
... respectively, 9 states in total. A 2 D level (S=1/2, L=2), splits into J=5/2 (6 states) and J=3/2 (4 states), hence 10 states in total. The atomic term values are 2 D5/ 2 , 2 D3/ 2 . You may notice that the splittings discussed for the hydrogen atom follow this rule also. The energy splittings betwe ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.