Creation of ultracold molecules from a Fermi gas of atoms
... Scattering resonances known as Feshbach resonances occur when the collision energy of two free atoms coincides with that of a quasi-bound molecular state [5, 6, 7]. By varying the strength of an external magnetic field experimenters can tune the relative atom-molecule energy through the Zeeman effec ...
... Scattering resonances known as Feshbach resonances occur when the collision energy of two free atoms coincides with that of a quasi-bound molecular state [5, 6, 7]. By varying the strength of an external magnetic field experimenters can tune the relative atom-molecule energy through the Zeeman effec ...
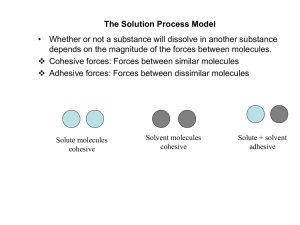
The Solution Process Model
... If Ct is very small (Ct >0.1 Cs), then dissolution rate is directly proportional to the saturation solubility (Cs). This assumes that S is constant which is only true at the very beginning of the experiment when only a small amount (>0.5%) of the solid drug has dissolved. When these two requirements ...
... If Ct is very small (Ct >0.1 Cs), then dissolution rate is directly proportional to the saturation solubility (Cs). This assumes that S is constant which is only true at the very beginning of the experiment when only a small amount (>0.5%) of the solid drug has dissolved. When these two requirements ...
Inverse scattering for frequency-scanned full-field
... When the reference arm is adjusted such that the reference field is synchronized with the scattered field returned from a plane other than (and far removed from) the focal plane, the interference image obtained at the CCD appears to be an image of the scatterers in that plane but out of focus. For a ...
... When the reference arm is adjusted such that the reference field is synchronized with the scattered field returned from a plane other than (and far removed from) the focal plane, the interference image obtained at the CCD appears to be an image of the scatterers in that plane but out of focus. For a ...
SEPARATION OF MATTER - Los Angeles City College
... chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. • Elements: a specific substance which can not be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means, an atom with a specific number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
... chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. • Elements: a specific substance which can not be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means, an atom with a specific number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 2 8thed - Chemistry
... o The mass of a neutron or a proton is close to 1 dalton. The mass of an electron is about 1/2,000 the mass of a neutron or proton. o We typically ignore the contribution of electrons when determining the total mass o f an atom. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in th ...
... o The mass of a neutron or a proton is close to 1 dalton. The mass of an electron is about 1/2,000 the mass of a neutron or proton. o We typically ignore the contribution of electrons when determining the total mass o f an atom. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in th ...
Analysis of a Matter
... chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. • Elements: a specific substance which can not be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means, an atom with a specific number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
... chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. • Elements: a specific substance which can not be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means, an atom with a specific number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
Three-dimensional depth profiling of molecular structures
... generates many displacements within a subsurface region, and molecules can be relocated across the original interface. This is a dynamical effect which is caused during the erosion cycles and cannot be avoided in a sputter depth profile. It can be expected to significantly influence the interface wi ...
... generates many displacements within a subsurface region, and molecules can be relocated across the original interface. This is a dynamical effect which is caused during the erosion cycles and cannot be avoided in a sputter depth profile. It can be expected to significantly influence the interface wi ...
Semiconductor Devices
... It is important to note that the sample had to be biased in the NDR region to produce a Gunn-domain. Once a domain has formed, the electric field in the rest of the sample falls below the NDR region and will therefore inhibit the formation of a second Gunn-domain. As soon as the domain is absorbed b ...
... It is important to note that the sample had to be biased in the NDR region to produce a Gunn-domain. Once a domain has formed, the electric field in the rest of the sample falls below the NDR region and will therefore inhibit the formation of a second Gunn-domain. As soon as the domain is absorbed b ...
File
... 2. Masses of all elements are determined in comparison to the carbon 12 12 atom ( C), the most common isotope of carbon 3. Comparisons are made using a mass spectrometer B. Atomic Mass (Average atomic mass, atomic weight) 1. Atomic masses are the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an ele ...
... 2. Masses of all elements are determined in comparison to the carbon 12 12 atom ( C), the most common isotope of carbon 3. Comparisons are made using a mass spectrometer B. Atomic Mass (Average atomic mass, atomic weight) 1. Atomic masses are the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an ele ...
Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering in Noble
... underscreening of SP field in the surface layer. The calculated local field, E, at resonance frequency is plotted in Fig. 3(inset) versus molecule-nanoparticle distance, d = r0 − R. The gradual rise of field magnitude on the length scale of electron spillover replaces the discontinuity (for ²d , ²m ...
... underscreening of SP field in the surface layer. The calculated local field, E, at resonance frequency is plotted in Fig. 3(inset) versus molecule-nanoparticle distance, d = r0 − R. The gradual rise of field magnitude on the length scale of electron spillover replaces the discontinuity (for ²d , ²m ...
Major 1 Term 101 - KFUPM Faculty List
... D) No precipitate will form. Nonsense, just as D) E) PbI2 will precipitate, K+ and NO3- are spectator ions Correct, PbI2 is insoluble, while KNO3 is soluble 14. Determine the number of oxygen atoms in 1.5 g Fe2(SO4)3 A) 6.8 x 1021 B) 2.3 x 1021 C) 2.7 x 1022 D) 9.0 x 1021 E) 1.4 x 1022 To get the n ...
... D) No precipitate will form. Nonsense, just as D) E) PbI2 will precipitate, K+ and NO3- are spectator ions Correct, PbI2 is insoluble, while KNO3 is soluble 14. Determine the number of oxygen atoms in 1.5 g Fe2(SO4)3 A) 6.8 x 1021 B) 2.3 x 1021 C) 2.7 x 1022 D) 9.0 x 1021 E) 1.4 x 1022 To get the n ...
An element`s properties depend on the structure of its atoms
... become a dipole. • Now the two are more attracted to each other than they were before the induction occurred. • Ever induced behavior in another ...
... become a dipole. • Now the two are more attracted to each other than they were before the induction occurred. • Ever induced behavior in another ...
852_1.pdf
... polarization channel (Figure 4b). The first wavefront is followed by gradually decreasing oscillations due to multiple reflections of the acoustic wave in the superficial layer. Periodically modulated laser radiation can be used to produce a temperature increase, which is often referred to as a ther ...
... polarization channel (Figure 4b). The first wavefront is followed by gradually decreasing oscillations due to multiple reflections of the acoustic wave in the superficial layer. Periodically modulated laser radiation can be used to produce a temperature increase, which is often referred to as a ther ...
chapter
... maximum of 2 electrons: one spherical (2s) and three dumbbell-shaped (2p) orbitals at right angles to one another. ...
... maximum of 2 electrons: one spherical (2s) and three dumbbell-shaped (2p) orbitals at right angles to one another. ...
Physical concept of the surface tension of the liquid until some time
... The difference between the two concepts mentioned above is solely in the geometric interpretations of the evaporation process and surface tension, as well as in the areas of application of these theoretical studies. In the theory of the «unpacking» - method of 1983 [1] in contrast to the «salami met ...
... The difference between the two concepts mentioned above is solely in the geometric interpretations of the evaporation process and surface tension, as well as in the areas of application of these theoretical studies. In the theory of the «unpacking» - method of 1983 [1] in contrast to the «salami met ...
group iv elements
... The reason for the reversal in difference in stabilities of the +II and +IV oxidation state for lead is the inert pair effect. On descending group IV, the atoms get larger. The shielding of the nuclear charge from the valence electrons by the core electrons gets more and more ineffective. At lead, t ...
... The reason for the reversal in difference in stabilities of the +II and +IV oxidation state for lead is the inert pair effect. On descending group IV, the atoms get larger. The shielding of the nuclear charge from the valence electrons by the core electrons gets more and more ineffective. At lead, t ...
HOMEWORK 6-1 - losbanosusd.k12.ca.us
... 1. Noble-gas atoms are able to exist independently in nature because a. they are exceptions to the octet rule. b. their bond energies are low compared to their bond lengths. c. their electron configurations are more stable than those of other atoms. d. they share electrons in overlapping orbitals wi ...
... 1. Noble-gas atoms are able to exist independently in nature because a. they are exceptions to the octet rule. b. their bond energies are low compared to their bond lengths. c. their electron configurations are more stable than those of other atoms. d. they share electrons in overlapping orbitals wi ...
Hydrogen atom
... In 1925 a new kind of mechanics was proposed, quantum mechanics, in which Bohr's model of electrons traveling in quantized orbits was extended into a more accurate model of electron motion. The new theory was proposed by Werner Heisenberg. Another form of the same theory, wave mechanics, was discove ...
... In 1925 a new kind of mechanics was proposed, quantum mechanics, in which Bohr's model of electrons traveling in quantized orbits was extended into a more accurate model of electron motion. The new theory was proposed by Werner Heisenberg. Another form of the same theory, wave mechanics, was discove ...
Time-Dependent Electron Interactions in Double
... complete spatial overlap between WP1 and WP2 is not required for energy transfer. This represents a refinement of a simple model of DRW autoionization as the result of the sudden change in ion-core screening that occurs when one wave packet passes through the other [6]. In an attempt to better under ...
... complete spatial overlap between WP1 and WP2 is not required for energy transfer. This represents a refinement of a simple model of DRW autoionization as the result of the sudden change in ion-core screening that occurs when one wave packet passes through the other [6]. In an attempt to better under ...
BRIEF REPORTS
... shown that the information thus obtained cannot be measured using the more typical energy-dependent response of the system to the field. Relative phase information between different energy-states may be obtained. These measurements are not restricted to atomic systems, although both examples given i ...
... shown that the information thus obtained cannot be measured using the more typical energy-dependent response of the system to the field. Relative phase information between different energy-states may be obtained. These measurements are not restricted to atomic systems, although both examples given i ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.