Mechanisms of Perception: Hearing, Touch, Smell, Taste & Attention
... Astereognosia Inability to recognize objects by touch Rare ...
... Astereognosia Inability to recognize objects by touch Rare ...
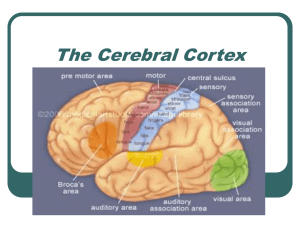
The Cerebral Cortex
... of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
... of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
BOX 28.5 NEURAL CONTROL OF HUMAN WALKING Human
... electromyographic (EMG) activity in the plantarflexor muscles, even when the common peroneal nerve that innervates the ankle dorsiflexor muscles was blocked by local anesthesia (Sinkjaer, Anderson, Ladouceur, Christenson, & Nielson, 2000). These results demonstrated that sensory feedback from planta ...
... electromyographic (EMG) activity in the plantarflexor muscles, even when the common peroneal nerve that innervates the ankle dorsiflexor muscles was blocked by local anesthesia (Sinkjaer, Anderson, Ladouceur, Christenson, & Nielson, 2000). These results demonstrated that sensory feedback from planta ...
Neurobiology of the Senses
... Cochlear duct Bone Vestibular canal Auditory nerve Basilar membrane ...
... Cochlear duct Bone Vestibular canal Auditory nerve Basilar membrane ...
Sensory System –L4
... keep brain apprised of the status of the body with respect to its surroundings will adapt to extinction as long as the stimulus is present, however, this may take hours or days these receptors include: muscle spindle, golgi tendon apparatus, Ruffini’s endings, Merkels ...
... keep brain apprised of the status of the body with respect to its surroundings will adapt to extinction as long as the stimulus is present, however, this may take hours or days these receptors include: muscle spindle, golgi tendon apparatus, Ruffini’s endings, Merkels ...
Nervous System
... –Rods: Black and White –Cones: Color • Optic nerve takes electric signals from eye to brain ...
... –Rods: Black and White –Cones: Color • Optic nerve takes electric signals from eye to brain ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... the bony labyrinth, consisting of the vestibule, which enables the maintenance of static equilibrium, and the semicircular canals, which maintain dynamic equilibrium. The combined action of the vestibule and semicircular canals enables us to always be aware of the position of our body relative to th ...
... the bony labyrinth, consisting of the vestibule, which enables the maintenance of static equilibrium, and the semicircular canals, which maintain dynamic equilibrium. The combined action of the vestibule and semicircular canals enables us to always be aware of the position of our body relative to th ...
SENSORY AND MOTOR SYSTEMS: REFLEXES
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
The Nervous System
... • picks up sensory information and delivers it to the CNS Motor Division • carries information to muscles and glands Divisions of the Motor Division • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
... • picks up sensory information and delivers it to the CNS Motor Division • carries information to muscles and glands Divisions of the Motor Division • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
Revision material
... What are the principal differences between control of eye movements and limb movements? The fly employs a number of different sensory mechanisms to keep its eyes aligned with the external horizon irrespective body orientation. What might be the advantages of using more than one sensory mechanism? Ac ...
... What are the principal differences between control of eye movements and limb movements? The fly employs a number of different sensory mechanisms to keep its eyes aligned with the external horizon irrespective body orientation. What might be the advantages of using more than one sensory mechanism? Ac ...
Sensation and Perception Unit IV
... – You will not consciously notice you are affected by this stimuli ...
... – You will not consciously notice you are affected by this stimuli ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... world and translating it into language • Damage causes people to not see motion ...
... world and translating it into language • Damage causes people to not see motion ...
Nervous System - ocw@unimas - Universiti Malaysia Sarawak
... spiraled neuroglia -‐ cells that provide support and nourishment to the neuron. ...
... spiraled neuroglia -‐ cells that provide support and nourishment to the neuron. ...
Sensory modalities are not separate modalities: plasticity and
... neither able to identify exactly which part of the brain is responsible for the enhanced activity, nor able to examine functional relevance of the activity. Studies that use a perceptual task have been more informative in this regard. For example, Uhl et al. [10] have provided evidence for posterior ...
... neither able to identify exactly which part of the brain is responsible for the enhanced activity, nor able to examine functional relevance of the activity. Studies that use a perceptual task have been more informative in this regard. For example, Uhl et al. [10] have provided evidence for posterior ...
Lecture 12
... 3. Golgi (tendon) organs a. at junction of tendon and muscle 4. Joint Kinesthetic receptors a. within/around synovial joints IV. Classification of Special Senses ...
... 3. Golgi (tendon) organs a. at junction of tendon and muscle 4. Joint Kinesthetic receptors a. within/around synovial joints IV. Classification of Special Senses ...
Auditory: Stimulus Auditory
... • Stimulus: mechanical, thermal, and chemical • Receptors: Mechanoreceptors & Free nerve endings • Transduction: Physical movement, change in temp., or chemicals released by tissue damage • Afferent Pathway: Dorsal column pathway for touch, anterolateral pathway for temp and pain • CNS Areas & Pe ...
... • Stimulus: mechanical, thermal, and chemical • Receptors: Mechanoreceptors & Free nerve endings • Transduction: Physical movement, change in temp., or chemicals released by tissue damage • Afferent Pathway: Dorsal column pathway for touch, anterolateral pathway for temp and pain • CNS Areas & Pe ...
Document
... 3. Auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify vibrations 4. Stapes hits oval window and transmits vibrations to cochlea 5. Organs of corti contain receptor cells (hair cells) that deform from vibrations 6. Impulses sent to the vestibulocochlear nerve 7. Auditory cortex of the temporal lobe i ...
... 3. Auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify vibrations 4. Stapes hits oval window and transmits vibrations to cochlea 5. Organs of corti contain receptor cells (hair cells) that deform from vibrations 6. Impulses sent to the vestibulocochlear nerve 7. Auditory cortex of the temporal lobe i ...