RFC_Cp_C_Wyart_def_EUK-v
... team studies motor activity in the zebrafish. This transparent vertebrate species is particularly suited to optogenetics, an innovative technology that allows stimulation of target neurons using light. In this method, the stimulated neurons light up and are visible in the transparent animal. The res ...
... team studies motor activity in the zebrafish. This transparent vertebrate species is particularly suited to optogenetics, an innovative technology that allows stimulation of target neurons using light. In this method, the stimulated neurons light up and are visible in the transparent animal. The res ...
BIOL 218 F 2012 MTX 4 Q NS 121121
... ………about how you are kinda sure that you are never ever ever ever going to be a Nurse, let alone an MD and now you will probably have to settle for orderly or bank clerk or waitress but you are only monolingual and even those jobs require you to speak at least two languages and you have trouble writ ...
... ………about how you are kinda sure that you are never ever ever ever going to be a Nurse, let alone an MD and now you will probably have to settle for orderly or bank clerk or waitress but you are only monolingual and even those jobs require you to speak at least two languages and you have trouble writ ...
Lecture notes for October 9, 2015 FINAL
... o If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) o If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract that delivers information from the ves ...
... o If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) o If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract that delivers information from the ves ...
Nervous System
... The involuntary nervous system (autonomic nervous system) maintains homeostasis. As its name implies, this system works automatically and without voluntary input. Its parts include receptors within viscera (internal organs), the afferent nerves that relay the information to the CNS, and the efferent ...
... The involuntary nervous system (autonomic nervous system) maintains homeostasis. As its name implies, this system works automatically and without voluntary input. Its parts include receptors within viscera (internal organs), the afferent nerves that relay the information to the CNS, and the efferent ...
Reading_Nervous_System
... transmit from special sensory receptors information on the senses of balance, smell, sight, taste, and hearing. Cranial nerves also carry information from general sensory receptors in the body, mostly from the head region. This information is processed in the CNS; the resulting orders travel back th ...
... transmit from special sensory receptors information on the senses of balance, smell, sight, taste, and hearing. Cranial nerves also carry information from general sensory receptors in the body, mostly from the head region. This information is processed in the CNS; the resulting orders travel back th ...
Hearing - RaduegeAP
... Sensory Adaptation Why does sensory adaptation occur? Sensory adaptation allows us to detect potentially important changes in our surroundings while ignoring unchanging aspects of them. ...
... Sensory Adaptation Why does sensory adaptation occur? Sensory adaptation allows us to detect potentially important changes in our surroundings while ignoring unchanging aspects of them. ...
Chapter 9 Part 3 Central Nervous System
... Once sensory information has reached its appropriate spot in the cortex (e.g. visual information goes to visual cortex, etc.) Then, the information proceeds on to its association area (e.g. visual cortex sends visual information on to the visual association area, etc.) Association areas integrate al ...
... Once sensory information has reached its appropriate spot in the cortex (e.g. visual information goes to visual cortex, etc.) Then, the information proceeds on to its association area (e.g. visual cortex sends visual information on to the visual association area, etc.) Association areas integrate al ...
Chapter 4: The Central Nervous System
... The parietal lobes receive information about touch, pressure, temperature, muscle movement and position. These are known as somatosensory functions. The somatosensory cortex is located in the parietal lobe behind the PMC. The parietal love also contains association areas which integrate information ...
... The parietal lobes receive information about touch, pressure, temperature, muscle movement and position. These are known as somatosensory functions. The somatosensory cortex is located in the parietal lobe behind the PMC. The parietal love also contains association areas which integrate information ...
Powerpoint
... cerebral cortex – frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobe Grey matter on outer surface, white matter inner surface Cerebral cortex is highly folded to increase the surface area for holding more neurones for more complicated coordination. ...
... cerebral cortex – frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobe Grey matter on outer surface, white matter inner surface Cerebral cortex is highly folded to increase the surface area for holding more neurones for more complicated coordination. ...
10 Control of Movement
... instructions coming from higher levels in the motor program • Adjusting motor unit activity to local conditions (obstacles to movement, pain) ...
... instructions coming from higher levels in the motor program • Adjusting motor unit activity to local conditions (obstacles to movement, pain) ...
While it may not be obvious from observing very young children
... is reflected in behavioral performance. This holds true both for fundamental perceptual and motor skills and for higher-order aspects of behavior such as cognitive and social abilities. While it may not be obvious from observing very young children, studies of the developing visual systems of childr ...
... is reflected in behavioral performance. This holds true both for fundamental perceptual and motor skills and for higher-order aspects of behavior such as cognitive and social abilities. While it may not be obvious from observing very young children, studies of the developing visual systems of childr ...
view - Queen`s University
... which form connections with the motor neurons after the synapse, and permit substantial processing of signals. But the direct projection from sensory afferents to motor neurons precludes such processing. Instead, the activity of these synapses (and other afferent synapses in the spinal cord) is regu ...
... which form connections with the motor neurons after the synapse, and permit substantial processing of signals. But the direct projection from sensory afferents to motor neurons precludes such processing. Instead, the activity of these synapses (and other afferent synapses in the spinal cord) is regu ...
Document
... further support to our hypothesis of Mrg receptor involvement in the mast cell-sensory neuron cross-talk. β-alanine, a ligand for MrgD, could be a possible candidate mediator in the neuroimmune interactions. In this regard, it would be interesting to further explore the MrgD-mediated interaction bet ...
... further support to our hypothesis of Mrg receptor involvement in the mast cell-sensory neuron cross-talk. β-alanine, a ligand for MrgD, could be a possible candidate mediator in the neuroimmune interactions. In this regard, it would be interesting to further explore the MrgD-mediated interaction bet ...
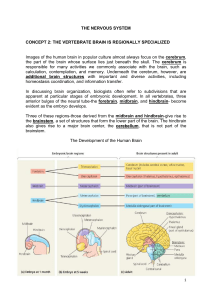
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... similar circumstances. In the case of fear, emotional memory is stored separately from the memory system that supports explicit recall of events. The focus of emotional memory is the amygdala, which is located in the temporal lobe To study the function of the human amygdala, researchers sometimes pr ...
... similar circumstances. In the case of fear, emotional memory is stored separately from the memory system that supports explicit recall of events. The focus of emotional memory is the amygdala, which is located in the temporal lobe To study the function of the human amygdala, researchers sometimes pr ...
Test Questions (Chapter13)
... 23. Hanna's mom had a stroke about a month ago. Her mom is telling Hanna that she cannot feel half of her face. Which disorder does Hanna's mom have? 24. The well documented horse riding accident of Christopher Reeve resulted in a spinal cord injury above C3 and he had to use a mechanical ventilato ...
... 23. Hanna's mom had a stroke about a month ago. Her mom is telling Hanna that she cannot feel half of her face. Which disorder does Hanna's mom have? 24. The well documented horse riding accident of Christopher Reeve resulted in a spinal cord injury above C3 and he had to use a mechanical ventilato ...
Anatomy Questions 3/2/16 1. The dorsal gray horns of the spinal
... i. It is part of the limbic system ii. It plays a role in controlling circadian rhythms iii. It regulates body temperature iv. It controls specific involuntary somatic motor activities a. 1 and 3 b. 2 and 4 c. 1, 2, and 3 d. All of the above e. None of the above 4. Non-fluent aphasia is a condition ...
... i. It is part of the limbic system ii. It plays a role in controlling circadian rhythms iii. It regulates body temperature iv. It controls specific involuntary somatic motor activities a. 1 and 3 b. 2 and 4 c. 1, 2, and 3 d. All of the above e. None of the above 4. Non-fluent aphasia is a condition ...
NOB Ch 6 Answers - MCC Year 12 Biology
... Why is it important for all individuals to have regular eye checks, particularly as they age? Many eye defects can occur as one ages. In some cases where treatment is available, early detection means that treatment can begin sooner, and this may halt or slow the progress of the disease. ...
... Why is it important for all individuals to have regular eye checks, particularly as they age? Many eye defects can occur as one ages. In some cases where treatment is available, early detection means that treatment can begin sooner, and this may halt or slow the progress of the disease. ...
Coding of Visual Information in the Retina Coding of Light d D k and
... Problem: how does one cell code for yp of information? two types A neuron can only vary its frequency of action potentials. If the cone’s response indicates brightness then it cannot signal for brightness, color. ...
... Problem: how does one cell code for yp of information? two types A neuron can only vary its frequency of action potentials. If the cone’s response indicates brightness then it cannot signal for brightness, color. ...
Sensory System –L4
... keep brain apprised of the status of the body with respect to its surroundings will adapt to extinction as long as the stimulus is present, however, this may take hours or days these receptors include: muscle spindle, golgi tendon apparatus, Ruffini’s endings, Merkels ...
... keep brain apprised of the status of the body with respect to its surroundings will adapt to extinction as long as the stimulus is present, however, this may take hours or days these receptors include: muscle spindle, golgi tendon apparatus, Ruffini’s endings, Merkels ...
Adaptive, behaviorally gated, persistent encoding of task
... sensory stimuli, depending on current task and context, is an essential component of flexible, goal-directed behavior. Neurons in frontal cortex are likely to contribute to this adaptive ability because of their extraordinary flexibility, responding differently to identical stimuli depending on the ...
... sensory stimuli, depending on current task and context, is an essential component of flexible, goal-directed behavior. Neurons in frontal cortex are likely to contribute to this adaptive ability because of their extraordinary flexibility, responding differently to identical stimuli depending on the ...
Area MST has been thought be involved in heading perception not
... Optic flow patterns generated during self-motion provide a strong cue for the perception of our own movement through space (heading). However, accurate judgments of heading often require integration of visual and nonvisual cues, including vestibular, kinesthetic, and eye movement signals. This senso ...
... Optic flow patterns generated during self-motion provide a strong cue for the perception of our own movement through space (heading). However, accurate judgments of heading often require integration of visual and nonvisual cues, including vestibular, kinesthetic, and eye movement signals. This senso ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Reflexes are rapid, automatic responses to stimuli. They serve to protect the body and maintain homeostasis • ____________ reflexes - involve contraction of skeletal muscles • _______________ reflexes - regulate smooth muscle, cardiac ...
... Reflexes are rapid, automatic responses to stimuli. They serve to protect the body and maintain homeostasis • ____________ reflexes - involve contraction of skeletal muscles • _______________ reflexes - regulate smooth muscle, cardiac ...
Lecture 18: Sensation
... 1. General sensation relies on sensory receptors that are widely distributed throughout the body. A. Usually. general sensory receptors are the dendrites of a sensory neuron. B. There are a diverse set of different kinds of general receptors, including free dendrites (pain, hair movement, light t ...
... 1. General sensation relies on sensory receptors that are widely distributed throughout the body. A. Usually. general sensory receptors are the dendrites of a sensory neuron. B. There are a diverse set of different kinds of general receptors, including free dendrites (pain, hair movement, light t ...