Transmission Electron Microscopy -TEM
... Coherence: a prerequisite for interference is a superposition of wave systems whose phase difference remains constant in time. Two beams are coherent if, when combined, they produce an interference pattern. Two beams of light from self luminous sources are incoherent. In practice an emitting source ...
... Coherence: a prerequisite for interference is a superposition of wave systems whose phase difference remains constant in time. Two beams are coherent if, when combined, they produce an interference pattern. Two beams of light from self luminous sources are incoherent. In practice an emitting source ...
Transfer of orbital angular momentum on a macroscopic object
... frequency of 9.3 GHz. Continuous rotation of a small dipole, delicately suspended in a circular waveguide, has been observed using an incident circular polarized wave of low power (less than 1 W). On the other hand, according to the Maxwell equations, electromagnetic fields can also carry orbital an ...
... frequency of 9.3 GHz. Continuous rotation of a small dipole, delicately suspended in a circular waveguide, has been observed using an incident circular polarized wave of low power (less than 1 W). On the other hand, according to the Maxwell equations, electromagnetic fields can also carry orbital an ...
Young`s Double Slits
... Physics 1 – Young’s Double Slits Demonstrators' Answers, Hints, Marking Scheme and Equipment List ...
... Physics 1 – Young’s Double Slits Demonstrators' Answers, Hints, Marking Scheme and Equipment List ...
CMP4203 Lasers and Photonics
... Atomic Theory Pertaining to Laser Development Review of atomic theory Radiation and Infrared frequencies. Wavelength bands Gases in lasers. Solid state lasers Interaction of Light with Matter Optimal Mirror Cavities Three and Four Level Lasers Types of Lasers Molecular lasers Semicondu ...
... Atomic Theory Pertaining to Laser Development Review of atomic theory Radiation and Infrared frequencies. Wavelength bands Gases in lasers. Solid state lasers Interaction of Light with Matter Optimal Mirror Cavities Three and Four Level Lasers Types of Lasers Molecular lasers Semicondu ...
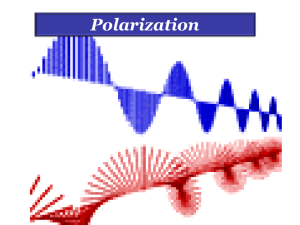
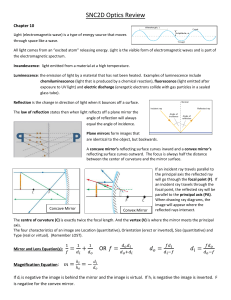
SNC2D Optics Review
... Light (electromagnetic wave) is a type of energy source that moves through space like a wave. All light comes from an “excited atom” releasing energy. Light is the visible form of electromagnetic waves and is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Incandescence: light emitted from a material at a hig ...
... Light (electromagnetic wave) is a type of energy source that moves through space like a wave. All light comes from an “excited atom” releasing energy. Light is the visible form of electromagnetic waves and is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Incandescence: light emitted from a material at a hig ...
Environmental Physics for Freshman Geography Students Professor
... We refer to λ as the wavelength of the wave, and ν as the frequency of the wave. For example, if ν = 5 crests per second (which is denoted 5 Hz, or simply 5 s-1), and λ = 10 cm, then from eq. (7.10), the wave spreads out at a speed v = 50 cm s-1. In the case of water waves, wave motion is easy to un ...
... We refer to λ as the wavelength of the wave, and ν as the frequency of the wave. For example, if ν = 5 crests per second (which is denoted 5 Hz, or simply 5 s-1), and λ = 10 cm, then from eq. (7.10), the wave spreads out at a speed v = 50 cm s-1. In the case of water waves, wave motion is easy to un ...
arXiv:quant-ph/0602132 v2 20 Feb 2006
... The RF photo-current for all segments of the split detectors are then calculated similarly to the previous section. The overlap integrals in the expressions for the photo-current sum and difference operators are simplified using the respective orthogonality properties of the un (x) and ufn (x) modes ...
... The RF photo-current for all segments of the split detectors are then calculated similarly to the previous section. The overlap integrals in the expressions for the photo-current sum and difference operators are simplified using the respective orthogonality properties of the un (x) and ufn (x) modes ...
All solid-state continuous wave tunable blue light source by
... a Nd:YAG laser operating at 946 nm??? it is also possible to generate blue light at 473 nm. These sources have a high doubling efficiency, but they are not tunable. Compact sources generating tunable blue light could be particularly useful for spectroscopic experiments. One possibility is an intraca ...
... a Nd:YAG laser operating at 946 nm??? it is also possible to generate blue light at 473 nm. These sources have a high doubling efficiency, but they are not tunable. Compact sources generating tunable blue light could be particularly useful for spectroscopic experiments. One possibility is an intraca ...
Invariant Imbedding Equations for Electromagnetic Waves in
... When the inhomogeneity is random, it can be used to obtain the exact disorder-averaged reflection and transmission coefficients and field amplitudes [27]. The invariant imbedding method can also be used to study the wave propagation in nonlinear dielectric media [23, 26] and the propagation of sever ...
... When the inhomogeneity is random, it can be used to obtain the exact disorder-averaged reflection and transmission coefficients and field amplitudes [27]. The invariant imbedding method can also be used to study the wave propagation in nonlinear dielectric media [23, 26] and the propagation of sever ...
PII: 0030-4018(95)00743-1
... crystal, let us first consider an optical wave that propagates along the z-axis and is allowed to diffract only along the x-direction. In doing so, our diffraction theory is one-dimensional and any y-dependent perturbations have been implicitly omitted [ 111. For demonstration purposes, let the PR c ...
... crystal, let us first consider an optical wave that propagates along the z-axis and is allowed to diffract only along the x-direction. In doing so, our diffraction theory is one-dimensional and any y-dependent perturbations have been implicitly omitted [ 111. For demonstration purposes, let the PR c ...
Irradiance transport equation from geometrical - E
... there are no free charges or other singular points such as point sources or ray caustics. On the other hand, it is well known that the eikonal equation [11,12], which describes the behavior of light rays in geometrical optics, is given by ...
... there are no free charges or other singular points such as point sources or ray caustics. On the other hand, it is well known that the eikonal equation [11,12], which describes the behavior of light rays in geometrical optics, is given by ...
(III) Laser Detection of Wave Motion in Solids
... highly-directed beam are often needed for engineering applications. This situation is relatively easy to achieve with mechanical waves and some electromagnetic waves such as RADAR. However it is not easy to achieve with visible light using standard technology. The advent of lasers now allows single ...
... highly-directed beam are often needed for engineering applications. This situation is relatively easy to achieve with mechanical waves and some electromagnetic waves such as RADAR. However it is not easy to achieve with visible light using standard technology. The advent of lasers now allows single ...
Electrodynamics of Solids
... above statement needs clarification. Throughout the book our main concern will be the optical properties of electrons in solids, and a short guide of the various states which may arise is in order. In the absence of interaction with the underlying lattice, and also without electron–electron or elect ...
... above statement needs clarification. Throughout the book our main concern will be the optical properties of electrons in solids, and a short guide of the various states which may arise is in order. In the absence of interaction with the underlying lattice, and also without electron–electron or elect ...