Nanofabrication with Holographic Optical Tweezers
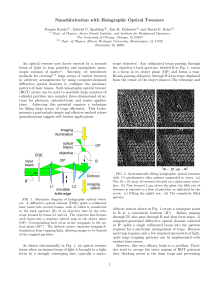
... An optical tweezer uses forces exerted by a focused beam of light to trap particles and manipulate mesoscopic volumes of matter1 . Recently, we introduced methods for creating2–4 large arrays of optical tweezers in arbitrary arrangements by using computer-designed diffractive optical elements to con ...
... An optical tweezer uses forces exerted by a focused beam of light to trap particles and manipulate mesoscopic volumes of matter1 . Recently, we introduced methods for creating2–4 large arrays of optical tweezers in arbitrary arrangements by using computer-designed diffractive optical elements to con ...
The page, which you have just visited, was created for students of
... larger n means greater c, and so more light (from a broader distribution of incident angles) will be internally reflected. High index materials (diamonds, PbO glasses) look 'brilliant' when facets are cut so that internal reflection returns light from large faces that originally collected the lig ...
... larger n means greater c, and so more light (from a broader distribution of incident angles) will be internally reflected. High index materials (diamonds, PbO glasses) look 'brilliant' when facets are cut so that internal reflection returns light from large faces that originally collected the lig ...
Physics 300 - WordPress.com
... Answer the multiple choice questions by placing the letter for the best answer on the line provided. Provide complete solutions to the questions on the back in the space provided. Do not use a separate piece of paper. 1-5. Definitions B • The number of oscillations per second is called… a. period b. ...
... Answer the multiple choice questions by placing the letter for the best answer on the line provided. Provide complete solutions to the questions on the back in the space provided. Do not use a separate piece of paper. 1-5. Definitions B • The number of oscillations per second is called… a. period b. ...
Interference effects Thin film interference Phase
... In thin film interference the phase difference is due to reflection at either side of a thin film of transparent material. • The phase difference is due to two factors: – Path difference through the film (corrected for the change in speed of light in the material) – Phase shift at the inter ...
... In thin film interference the phase difference is due to reflection at either side of a thin film of transparent material. • The phase difference is due to two factors: – Path difference through the film (corrected for the change in speed of light in the material) – Phase shift at the inter ...
Diffusion-controlled optical elements for
... convenient and flexible devices for optical filtering because the optical properties 共e.g., refractive index, absorption, and fluorescence兲 of the core can be adjusted easily by changing the liquid 共the fluid itself or its solutes兲.1,7 In each of these systems, however, a solid component defines the ...
... convenient and flexible devices for optical filtering because the optical properties 共e.g., refractive index, absorption, and fluorescence兲 of the core can be adjusted easily by changing the liquid 共the fluid itself or its solutes兲.1,7 In each of these systems, however, a solid component defines the ...
Full Article
... Medical devices accomplish big feats on a small scale. This is especially the case with ophthalmic applications like contact or intraocular lenses, in which whole devices are no larger than the eye and virtually unnoticeable. Intraocular lenses, or IOLs, are similar to contact lenses, except that t ...
... Medical devices accomplish big feats on a small scale. This is especially the case with ophthalmic applications like contact or intraocular lenses, in which whole devices are no larger than the eye and virtually unnoticeable. Intraocular lenses, or IOLs, are similar to contact lenses, except that t ...
SPIE2005 5754-12-b
... addressed in the initial stages of the technology but instead the problems associated with very large angles, and associated polarization, reflection and refraction effects. Hyper-NA lithography is generally considered to be imaging with angles close to 90° in any media within an imaging system to a ...
... addressed in the initial stages of the technology but instead the problems associated with very large angles, and associated polarization, reflection and refraction effects. Hyper-NA lithography is generally considered to be imaging with angles close to 90° in any media within an imaging system to a ...
375_Lo.pdf
... phase retardation are correctly chosen. It should be noticed that the dynamic range in measuring the apparent phase retardation is restricted in the range of 0~90°. Thus, the measured apparent phase retardation is needed to be verified and modified by the above reason and the further discussion is i ...
... phase retardation are correctly chosen. It should be noticed that the dynamic range in measuring the apparent phase retardation is restricted in the range of 0~90°. Thus, the measured apparent phase retardation is needed to be verified and modified by the above reason and the further discussion is i ...
On-chip gas detection in silicon optical microcavities
... because in high index contrast structures (unlike weakly confined waveguides such as fibers) the relationship between E and H is no longer linear. Since the polarizability of matter (and thus its refractive index) is determined by the material response to the electric field, it is the concentration ...
... because in high index contrast structures (unlike weakly confined waveguides such as fibers) the relationship between E and H is no longer linear. Since the polarizability of matter (and thus its refractive index) is determined by the material response to the electric field, it is the concentration ...
Dispersion staining

The optical properties of all liquid and solid materials change as a function of the wavelength of light used to measure them. This change as a function of wavelength is called the dispersion of the optical properties. The graph created by plotting the optical property of interest by the wavelength at which it is measured is called a dispersion curve.The dispersion staining is an analytical technique used in light microscopy that takes advantage of the differences in the dispersion curve of the refractive index of an unknown material relative to a standard material with a known dispersion curve to identify or characterize that unknown material. These differences become manifest as a color when the two dispersion curves intersect for some visible wavelength. This is an optical staining technique and requires no stains or dyes to produce the color. Its primary use today is in the conformation of the presence of asbestos in construction materials but it has many other applications.























