20170327_AH_Interference
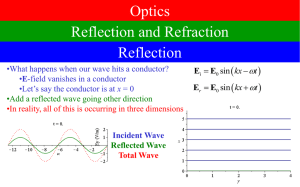
... You’ll have met Young’s double slit experiment – landmark experiment proving light was a wave. You will also seen time when your image has been reflected in some glass and not in other, picture framers and opticians often sell their products as no reflective. This also uses interference and we’ll ex ...
... You’ll have met Young’s double slit experiment – landmark experiment proving light was a wave. You will also seen time when your image has been reflected in some glass and not in other, picture framers and opticians often sell their products as no reflective. This also uses interference and we’ll ex ...
S.72-227 Digital Communication Systems
... One should also estimate required margins with respect of temperature, aging and stability For rise-time budget one should take into account all the rise times in the link (tx, fiber, rx) If the link does not fit into specifications – more repeaters – change components – change specifications Often ...
... One should also estimate required margins with respect of temperature, aging and stability For rise-time budget one should take into account all the rise times in the link (tx, fiber, rx) If the link does not fit into specifications – more repeaters – change components – change specifications Often ...
Refractive Indices, Order Parameter and Optical Transmittance
... corresponding author; e-mail: [email protected] ...
... corresponding author; e-mail: [email protected] ...
X-ray Optics - Studentportalen
... as long as one can use materials like Si, out of which large ‘perfect’ crystals can be made this is no limitation. A table of used crystal planes are found in the CXRO yellow booklet. The shortest 2d of any practical crystal are the ( 50 5 2 ) planes of -quartz: 2d=1.624 Å. One of the largest 2d fo ...
... as long as one can use materials like Si, out of which large ‘perfect’ crystals can be made this is no limitation. A table of used crystal planes are found in the CXRO yellow booklet. The shortest 2d of any practical crystal are the ( 50 5 2 ) planes of -quartz: 2d=1.624 Å. One of the largest 2d fo ...
Lecture 22 - LSU Physics
... Each wavelength is 360o, so N=496.41 means =Nx360o=0.41x360o=148o •How thick should the glass be so that the beams are exactly out of phase at the exit (destructive interference!) N=D/ s- D/ g= (D/ )(n2–n1)=0.31 (D/ )=m+1/2 A thickness D=(m+0.5) 2.02 mm would make the waves OUT of phase. Fo ...
... Each wavelength is 360o, so N=496.41 means =Nx360o=0.41x360o=148o •How thick should the glass be so that the beams are exactly out of phase at the exit (destructive interference!) N=D/ s- D/ g= (D/ )(n2–n1)=0.31 (D/ )=m+1/2 A thickness D=(m+0.5) 2.02 mm would make the waves OUT of phase. Fo ...
optical trap
... without damaging them. Optical tweezers prove very useful for this because, not only can they manipulate small particles very precisely, but, using infrared light, they can do so without causing damage. The development of the single beam optical trap was an important advance in optical tweezers, bec ...
... without damaging them. Optical tweezers prove very useful for this because, not only can they manipulate small particles very precisely, but, using infrared light, they can do so without causing damage. The development of the single beam optical trap was an important advance in optical tweezers, bec ...
offr-ee230
... DG Rabus, Integrated Ring Resonators: The Compendium (Springer Series in Optical Sciences) (Springer Series in Optical Sciences) (Springer, 2007) ...
... DG Rabus, Integrated Ring Resonators: The Compendium (Springer Series in Optical Sciences) (Springer Series in Optical Sciences) (Springer, 2007) ...
Simplified description of optical forces acting on a nanoparticle in
... us to perform the integration analytically even for off-axis positions of the sphere center (i.e., r s ⫽ 0). According to Eq. (17) the sign of the force is determined by the product of two terms. The first one, sin s , comes from the spatial intensity profile described by the interference term in E ...
... us to perform the integration analytically even for off-axis positions of the sphere center (i.e., r s ⫽ 0). According to Eq. (17) the sign of the force is determined by the product of two terms. The first one, sin s , comes from the spatial intensity profile described by the interference term in E ...
The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4th ed Donald R
... ©2003 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. ...
... ©2003 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. ...
Biomolecular and cellular research devices.
... always compared with the intensity of the same beam passed through the measured ...
... always compared with the intensity of the same beam passed through the measured ...
Optical Fiber Communication
... - Higher Numerical Aperature (NA) mean higher coupling from source to fiber, and less losses across joints. ...
... - Higher Numerical Aperature (NA) mean higher coupling from source to fiber, and less losses across joints. ...
Tomographic Interference Microscopy of Living Cells
... technique is suitable only for small samples. The size of sample must be smaller than the diameter of the beam waist near the focal plane of the objective. For large objects it is necessary to use the technique represented in Fig 1e. The original procedure of the collected data processing, patented ...
... technique is suitable only for small samples. The size of sample must be smaller than the diameter of the beam waist near the focal plane of the objective. For large objects it is necessary to use the technique represented in Fig 1e. The original procedure of the collected data processing, patented ...
Dispersion staining

The optical properties of all liquid and solid materials change as a function of the wavelength of light used to measure them. This change as a function of wavelength is called the dispersion of the optical properties. The graph created by plotting the optical property of interest by the wavelength at which it is measured is called a dispersion curve.The dispersion staining is an analytical technique used in light microscopy that takes advantage of the differences in the dispersion curve of the refractive index of an unknown material relative to a standard material with a known dispersion curve to identify or characterize that unknown material. These differences become manifest as a color when the two dispersion curves intersect for some visible wavelength. This is an optical staining technique and requires no stains or dyes to produce the color. Its primary use today is in the conformation of the presence of asbestos in construction materials but it has many other applications.