E. Sci. Astronomy Notes
... The moon orbits the earth counterclockwise in an elliptical orbit on a 5o tilt Gravity and Inertia keeps moon in revolution, 1/2 illuminated by sunlight Moon ¼ dia. of Earth, 1/6th gravity, 120 lbs on earth = 20 lbs on moon One moon revolution = one moon rotation, back side of moon never faces Earth ...
... The moon orbits the earth counterclockwise in an elliptical orbit on a 5o tilt Gravity and Inertia keeps moon in revolution, 1/2 illuminated by sunlight Moon ¼ dia. of Earth, 1/6th gravity, 120 lbs on earth = 20 lbs on moon One moon revolution = one moon rotation, back side of moon never faces Earth ...
Astronomy 101 Review - Physics and Astronomy
... • Mass is given in mass / volume • Example: Earth’s density is 5500 kg / m 3 • Example: Water is 1000 kg / m 3 (at 5 degrees C) ...
... • Mass is given in mass / volume • Example: Earth’s density is 5500 kg / m 3 • Example: Water is 1000 kg / m 3 (at 5 degrees C) ...
University Mohamed Khider- Biskra Faculty of letters and
... What do scientists think are in the middle of the Milky Way? □ the sun □ a black hole □ an asteroid belt □ a star What kind of stars are in the Milky Way? □ blue stars □ red stars □ white stars □ both blue and red stars What do you need for an eclipse to occur? □ the sun □ the moon and the sun □ Ear ...
... What do scientists think are in the middle of the Milky Way? □ the sun □ a black hole □ an asteroid belt □ a star What kind of stars are in the Milky Way? □ blue stars □ red stars □ white stars □ both blue and red stars What do you need for an eclipse to occur? □ the sun □ the moon and the sun □ Ear ...
answer key
... Use an appendix to find the length of a light year. White this length with regular numerals. 9.46 x 1015m. 9,460,000,000,000,000m ...
... Use an appendix to find the length of a light year. White this length with regular numerals. 9.46 x 1015m. 9,460,000,000,000,000m ...
The Earth in Space
... Equal length day and night When both poles are equidistant from sun Spring/Vernal (March) and fall/Autumnal (Sept) ...
... Equal length day and night When both poles are equidistant from sun Spring/Vernal (March) and fall/Autumnal (Sept) ...
Jeopardy Questions
... A: Greenhouse effect is when an object is surrounded by an outer layer (like an atmosphere or a pane of glass) that only allows certain wavelengths of light through. For a planet, like the Earth or Venus, the atmosphere allows in UV and visible light, but blocks some infrared light. The Earth radiat ...
... A: Greenhouse effect is when an object is surrounded by an outer layer (like an atmosphere or a pane of glass) that only allows certain wavelengths of light through. For a planet, like the Earth or Venus, the atmosphere allows in UV and visible light, but blocks some infrared light. The Earth radiat ...
Terrestrial planets
... • The “red” colour we see is from the large deposits of iron that are spread throughout the planet. • The word “Mars” comes from the Roman God of War. • Pieces of Mars have fallen to Earth. • On Mars, the sun appears smaller than it does here on Earth. • The Olympus Mons on Mars is the largest mount ...
... • The “red” colour we see is from the large deposits of iron that are spread throughout the planet. • The word “Mars” comes from the Roman God of War. • Pieces of Mars have fallen to Earth. • On Mars, the sun appears smaller than it does here on Earth. • The Olympus Mons on Mars is the largest mount ...
Astronomical Terms - Crossroads Academy
... zodiac…made of twelve signs or constellations ecliptic…apparent path (as seen for earth) of the sun in the sky over an entire year, also where the zodiacal signs roughly are found within about 10 degrees above it and below it celestial equator…plane extending into space from earth’s equator celestia ...
... zodiac…made of twelve signs or constellations ecliptic…apparent path (as seen for earth) of the sun in the sky over an entire year, also where the zodiacal signs roughly are found within about 10 degrees above it and below it celestial equator…plane extending into space from earth’s equator celestia ...
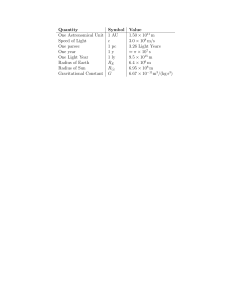
Quantity Symbol Value One Astronomical Unit 1 AU 1.50 × 10
... 1 pc ' 3.1 × 1016 m ' 3.3 ly (a) Explain how such a curious unit of measure came to be defined. Why is it called parsec? (b) What is the distance to the nearest stars and how was this distance measured? 4. Describe qualitatively what is the precession of perihelion. (a) What are the dominant cause o ...
... 1 pc ' 3.1 × 1016 m ' 3.3 ly (a) Explain how such a curious unit of measure came to be defined. Why is it called parsec? (b) What is the distance to the nearest stars and how was this distance measured? 4. Describe qualitatively what is the precession of perihelion. (a) What are the dominant cause o ...
Seasons
... appears to move, but does not actually move in that direction or does not move at all. WHAT DIRECTION DO OBJECTS APPEAR TO MOVE IN THE SKY? ...
... appears to move, but does not actually move in that direction or does not move at all. WHAT DIRECTION DO OBJECTS APPEAR TO MOVE IN THE SKY? ...
The Inner Planets
... is covered by a thick, dense cloud of mostly carbon dioxide. This atmosphere is 90 times heavier than the Earth’s atmosphere which make the atmospheric pressure at sea level on Venus 90 times that of Earth’s. ...
... is covered by a thick, dense cloud of mostly carbon dioxide. This atmosphere is 90 times heavier than the Earth’s atmosphere which make the atmospheric pressure at sea level on Venus 90 times that of Earth’s. ...
Monday, March 31 - Otterbein University
... Atmospheric Histories - Venus • Venus is closer to Sun than Earth hotter ...
... Atmospheric Histories - Venus • Venus is closer to Sun than Earth hotter ...
May 2016 - Faculty
... We have two relatively unique astronomical events that will take place in May 2016. The first of these events is the transit of planet Mercury across the face of the sun on May 9th. The transit will begin early in the morning on this day at 7:12 a.m. EDT, reach transit midpoint at 10:58 a.m., then l ...
... We have two relatively unique astronomical events that will take place in May 2016. The first of these events is the transit of planet Mercury across the face of the sun on May 9th. The transit will begin early in the morning on this day at 7:12 a.m. EDT, reach transit midpoint at 10:58 a.m., then l ...
Notes 21 Inner Solar System
... Solid Surface High Density (rocky) Few or no moons No Rings Weak Magnetic Field Close to the Sun Slow rotation Closely spaced orbits Small mass/size Mercury: 2nd hottest 1/3 gravity and 1/3 size of Earth has most craters (of all planets) ...
... Solid Surface High Density (rocky) Few or no moons No Rings Weak Magnetic Field Close to the Sun Slow rotation Closely spaced orbits Small mass/size Mercury: 2nd hottest 1/3 gravity and 1/3 size of Earth has most craters (of all planets) ...
Stars, Sun, and Moon Test Study Guide
... 3. What season is the Northern hemisphere experiencing when it is tilted towards the sun? ...
... 3. What season is the Northern hemisphere experiencing when it is tilted towards the sun? ...
solar_system
... Mars has two small moons. Mars has seasons similar to ours. The climate changes widely between seasons. There are ice caps on both poles. A year on Mars takes as long as two Earth years. A day on Mars lasts only thirty minutes longer than a day on Earth ...
... Mars has two small moons. Mars has seasons similar to ours. The climate changes widely between seasons. There are ice caps on both poles. A year on Mars takes as long as two Earth years. A day on Mars lasts only thirty minutes longer than a day on Earth ...
Observing the Universe 1
... 14. The diagram in Figure 4 shows the movement of an object seen in the sky from November 2005 to January 2006. Is this object likely to be (a) a planet (b) a star ? (The lines show a grid of latitude and longitude on the star sphere) ...
... 14. The diagram in Figure 4 shows the movement of an object seen in the sky from November 2005 to January 2006. Is this object likely to be (a) a planet (b) a star ? (The lines show a grid of latitude and longitude on the star sphere) ...
Test#2
... 8. Which of the following is a consequence of the fact that the rotation and revolution periods of the moon are the same? a) the moon keeps the same face turned toward the Earth b) the moon can never be seen from one hemisphere of the Earth c) all lunar phases can be seen from the Earth d) there are ...
... 8. Which of the following is a consequence of the fact that the rotation and revolution periods of the moon are the same? a) the moon keeps the same face turned toward the Earth b) the moon can never be seen from one hemisphere of the Earth c) all lunar phases can be seen from the Earth d) there are ...
Planets and Other Objects in Space test study
... sedimentary rocks- which are formed by water. Polar ice caps. 20. What does Earth have that other planets do not? liquid water (also living things) 21. What is the source of almost all the energy in our solar system? the sun 22. How long does the moon’s cycle of phases take to complete? ...
... sedimentary rocks- which are formed by water. Polar ice caps. 20. What does Earth have that other planets do not? liquid water (also living things) 21. What is the source of almost all the energy in our solar system? the sun 22. How long does the moon’s cycle of phases take to complete? ...
U4W6 Fluency - Mars, the red planet
... and bean plants, because Earth has so much water. Mars has no flowing water, so plants cannot grow. In 2003, we sent rovers like this to Mars. A rover can ride, turn, and grab with its claws. It jerks back and forth and drills out a chunk of rock. It measures the rock to see if it’s true that Mars h ...
... and bean plants, because Earth has so much water. Mars has no flowing water, so plants cannot grow. In 2003, we sent rovers like this to Mars. A rover can ride, turn, and grab with its claws. It jerks back and forth and drills out a chunk of rock. It measures the rock to see if it’s true that Mars h ...
Excerpts from
... moving up and down. Then, as we move farther along our curved orbit and see the planet from a different angle, the illusion will disappear and we will once again see Mars move in a straight line. This apparent erratic movement is called "retrograde motion." The illusion also happens with Jupiter and ...
... moving up and down. Then, as we move farther along our curved orbit and see the planet from a different angle, the illusion will disappear and we will once again see Mars move in a straight line. This apparent erratic movement is called "retrograde motion." The illusion also happens with Jupiter and ...
Sample Assessment Items
... The stars in the night sky look as if they are slowly moving because _______________. a. the Earth is moving b. they rotate around the Sun c. they rotate around the Earth d. the Sun blocks them out at times Answer: a Stars are organized into patterns called constellations. One constellation is named ...
... The stars in the night sky look as if they are slowly moving because _______________. a. the Earth is moving b. they rotate around the Sun c. they rotate around the Earth d. the Sun blocks them out at times Answer: a Stars are organized into patterns called constellations. One constellation is named ...
Astronomy on Mars
.jpg?width=300)
In many cases astronomical phenomena viewed from the planet Mars are the same or similar to those seen from Earth but sometimes (as with the view of Earth as an evening/morning star) they can be quite different. For example, because the atmosphere of Mars does not contain an ozone layer, it is also possible to make UV observations from the surface of Mars.