course objectives - Metropolitan Community College
... Define and explain the following terms, principles and ideas: light, white light, wavefront, a ray, a plane wave, parallel light, specular versus diffuse reflection, virtual versus real image, focal point, focal length, index of refraction, Snell’s law, total internal reflection, critical angle, con ...
... Define and explain the following terms, principles and ideas: light, white light, wavefront, a ray, a plane wave, parallel light, specular versus diffuse reflection, virtual versus real image, focal point, focal length, index of refraction, Snell’s law, total internal reflection, critical angle, con ...
Physical Optics
... description review of, physical optics unex uci edu - learn about the principles and use of optical components and physical optics systems gain knowledge about diffraction grating polarizers interference filters and, experiment 4 physical optics ucla physics astronomy experiment 4 physical optics cl ...
... description review of, physical optics unex uci edu - learn about the principles and use of optical components and physical optics systems gain knowledge about diffraction grating polarizers interference filters and, experiment 4 physical optics ucla physics astronomy experiment 4 physical optics cl ...
5.3.2 Processing Light
... Instead of (birefringent) herapathite crystals embedded in a stretched plastic foil, we now use aligned (again by stretching) polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) foils and dope the molecules with Iodine. In other words, we produce a more or less conducting polymer in one direction. Polarizing foils of this type ...
... Instead of (birefringent) herapathite crystals embedded in a stretched plastic foil, we now use aligned (again by stretching) polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) foils and dope the molecules with Iodine. In other words, we produce a more or less conducting polymer in one direction. Polarizing foils of this type ...
Prism Design
... representing the reflecting surface, the real image and the solid-line rays would coincide exactly with the virtual image and the dashed-line rays. A diagram showing both the original prism (ABC) and the folded counterpart (ABC′) is called a “tunnel diagram” (see Fig. 6.2). The rays a-a′ and b-b′ re ...
... representing the reflecting surface, the real image and the solid-line rays would coincide exactly with the virtual image and the dashed-line rays. A diagram showing both the original prism (ABC) and the folded counterpart (ABC′) is called a “tunnel diagram” (see Fig. 6.2). The rays a-a′ and b-b′ re ...
JC2315121515
... compress continuous real-world analog signals. It can also used to convert the signal from an analog to a digital form, by sampling and then digitizing it using an analogto-digital converter (ADC), which turns the analog signal into a stream of numbers [10]. ...
... compress continuous real-world analog signals. It can also used to convert the signal from an analog to a digital form, by sampling and then digitizing it using an analogto-digital converter (ADC), which turns the analog signal into a stream of numbers [10]. ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2013 Semester Lecture 30 – Geometric Optics
... • All you need to know about a lens is its focal length ...
... • All you need to know about a lens is its focal length ...
Diffractive Optical Elements
... design and simulation of diffractive optical elements to offer its customers a ...
... design and simulation of diffractive optical elements to offer its customers a ...
Lab 11: Index of Refraction (n) of Air
... Therefore the unknown constant, k, is given by k = mλ/2L∆p. Thus if you measure m fringes while the pressure changes by an amount ∆p, you can calculate the refraction index of air at room temperature using n = 1 + mλp/2L∆p ...
... Therefore the unknown constant, k, is given by k = mλ/2L∆p. Thus if you measure m fringes while the pressure changes by an amount ∆p, you can calculate the refraction index of air at room temperature using n = 1 + mλp/2L∆p ...
Lecture 2A: Ray Optics of Fibers
... Step-Index Fiber • Cladding typically pure silica • Core doped with germanium to increase index • Index difference referred to as “delta” in units of percent (typically 0.3-1.0%) • Tradeoff between coupling and bending losses • Index discontinuity at core-clad boundary ...
... Step-Index Fiber • Cladding typically pure silica • Core doped with germanium to increase index • Index difference referred to as “delta” in units of percent (typically 0.3-1.0%) • Tradeoff between coupling and bending losses • Index discontinuity at core-clad boundary ...
Imaging of Intrinsic Signals in the Retina
... Adaptive optics (AO) is used to correct ocular aberrations of the human eye and so improves lateral and axial resolution and brightness of images of the retina. The Adaptive Optics Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope (AOSLO) can be used to image intrinsic signals of the retina by monitoring image reflecta ...
... Adaptive optics (AO) is used to correct ocular aberrations of the human eye and so improves lateral and axial resolution and brightness of images of the retina. The Adaptive Optics Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope (AOSLO) can be used to image intrinsic signals of the retina by monitoring image reflecta ...
Midterm Exam
... published textbook. Please be neat and professional in your presentation. Include plots and words to expand on your results. A perfect score on this exam is 40 points. 1. Beam Optics and Laser Resonators (10 points) Consider the following laser resonator comprising a curved mirror (radius Rc) and a ...
... published textbook. Please be neat and professional in your presentation. Include plots and words to expand on your results. A perfect score on this exam is 40 points. 1. Beam Optics and Laser Resonators (10 points) Consider the following laser resonator comprising a curved mirror (radius Rc) and a ...
1 CHAPTER 4 OPTICAL ABERRATIONS 4.1 Introduction We have
... The angle of incidence of the ray at R is 25.442 358 40 degrees to the normal, and the angle of refraction is 43.421 850 83 degrees. The net result of this is that there is a short linear “image” at T perpendicular to the tangential plane, and a short linear “image” at S perpendicular to the sagitta ...
... The angle of incidence of the ray at R is 25.442 358 40 degrees to the normal, and the angle of refraction is 43.421 850 83 degrees. The net result of this is that there is a short linear “image” at T perpendicular to the tangential plane, and a short linear “image” at S perpendicular to the sagitta ...
Presentation
... The lens is placed in front of the eye and is synchronized to the graphic display such that each depth region in the simulated scene is presented when the lens is in the appropriate state. In this way, they construct a temporally multiplexed image with correct focus cues. ...
... The lens is placed in front of the eye and is synchronized to the graphic display such that each depth region in the simulated scene is presented when the lens is in the appropriate state. In this way, they construct a temporally multiplexed image with correct focus cues. ...
Direct index of refraction measurement at extreme
... is given by the square of its coefficient [2(1/π)(1/π)]2 = 4/π 4 , which is a factor of 4 increase in optical throughput as compared with separate grating and zoneplate. Since the membranes on which these optical elements are fabricated have finite absorption, there is an additional gain of efficiency du ...
... is given by the square of its coefficient [2(1/π)(1/π)]2 = 4/π 4 , which is a factor of 4 increase in optical throughput as compared with separate grating and zoneplate. Since the membranes on which these optical elements are fabricated have finite absorption, there is an additional gain of efficiency du ...
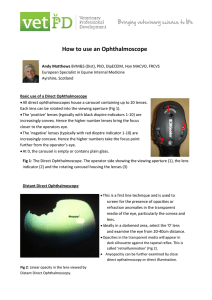
How to use an Ophthalmoscope
... The ‘positive’ lenses (typically with black dioptre indicators 1-10) are increasingly convex. Hence the higher number lenses bring the focus closer to the operators eye. The ‘negative’ lenses (typically with red dioptre indicator 1-10) are increasingly concave. Hence the higher numbers take the ...
... The ‘positive’ lenses (typically with black dioptre indicators 1-10) are increasingly convex. Hence the higher number lenses bring the focus closer to the operators eye. The ‘negative’ lenses (typically with red dioptre indicator 1-10) are increasingly concave. Hence the higher numbers take the ...