doc - University of Rochester
... literature [1,2]. Recently, the question of whether the resolution of ghost imaging is improved using non-degenerate biphotons (biphotons with pairs of photons of different frequency) has been raised. In this paper we consider the ghost imaging systems shown in Fig.1. A pump from a laser is incident ...
... literature [1,2]. Recently, the question of whether the resolution of ghost imaging is improved using non-degenerate biphotons (biphotons with pairs of photons of different frequency) has been raised. In this paper we consider the ghost imaging systems shown in Fig.1. A pump from a laser is incident ...
... In recent years important progress has been made in the generation of ultrashort laser pulses. The maximum intensity is fundamental in many applications, therefore the measurement of these pulses is also fundamental. It is important that these measurements be performed with optical elements that do ...
Geometric Optics - IndiaStudyChannel.com
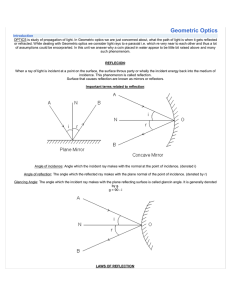
... OPTICS is study of propagation of light. In Geometric optics we are just concerned about, what the path of light is when it gets reflected or refracted. While dealing with Geometric optics we consider light rays to e paraxial i.e. which re very near to each other and thus a lot of assumptions could ...
... OPTICS is study of propagation of light. In Geometric optics we are just concerned about, what the path of light is when it gets reflected or refracted. While dealing with Geometric optics we consider light rays to e paraxial i.e. which re very near to each other and thus a lot of assumptions could ...
Snell`s Law - Initial Set Up
... When light travels from a less optically dense material to a more optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? When light travels from a more optically dense material to a less optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? ...
... When light travels from a less optically dense material to a more optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? When light travels from a more optically dense material to a less optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... converging lens has two foci: one on each side; i.e., a plane wave coming from one side focuses to the other, and vice versa. In stark contrast, a hyperbolic metalens works like a converging lens from one side but a diverging lens from the other. Similar to a recent “Janus device” [26] showing diffe ...
... converging lens has two foci: one on each side; i.e., a plane wave coming from one side focuses to the other, and vice versa. In stark contrast, a hyperbolic metalens works like a converging lens from one side but a diverging lens from the other. Similar to a recent “Janus device” [26] showing diffe ...
The diffraction of light by sound waves of high
... other hand, the optical length of C'D' is greater than that of CD, for the refractive index is minimum along CD. A simple consideration of the above shows that the difference between the optical lengths of A'B' and C'D' is less than that between those of AB and CD. As this difference gives twice the ...
... other hand, the optical length of C'D' is greater than that of CD, for the refractive index is minimum along CD. A simple consideration of the above shows that the difference between the optical lengths of A'B' and C'D' is less than that between those of AB and CD. As this difference gives twice the ...
Geometrical Optics 101: Paraxial Ray Tracing
... position of the object and can have an arbitrary incident angle. For an object at infinity, the ray can begin at an arbitrary height, but must have an incident angle of 0°. Once this is accomplished, the aperture stop is simply the surface that has the smallest CA/yp value, where CA is the surface ...
... position of the object and can have an arbitrary incident angle. For an object at infinity, the ray can begin at an arbitrary height, but must have an incident angle of 0°. Once this is accomplished, the aperture stop is simply the surface that has the smallest CA/yp value, where CA is the surface ...
ellip
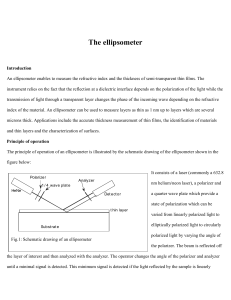
... An ellipsometer enables to measure the refractive index and the thickness of semi-transparent thin films. The instrument relies on the fact that the reflection at a dielectric interface depends on the polarization of the light while the transmission of light through a transparent layer changes the p ...
... An ellipsometer enables to measure the refractive index and the thickness of semi-transparent thin films. The instrument relies on the fact that the reflection at a dielectric interface depends on the polarization of the light while the transmission of light through a transparent layer changes the p ...
Click To
... infrared sensor. The number of pixels (individual sensing elements) in the FPA ultimately dictates the spatial resolution of the sensor; therefore, a sensor designer will generally seek to maximize the pixel count when selecting the FPA. Unfortunately, as pixel count increases, the likelihood of FPA ...
... infrared sensor. The number of pixels (individual sensing elements) in the FPA ultimately dictates the spatial resolution of the sensor; therefore, a sensor designer will generally seek to maximize the pixel count when selecting the FPA. Unfortunately, as pixel count increases, the likelihood of FPA ...
fourier optics - The Institute of Optics
... This monograph on Fourier Optics contains a rigorous treatment of this important topic based on Maxwells Equations and Electromagnetic Theory. One need know only the elements of calculus and vector analysis in order to understand the contents of this work. In the emerging field of Image Science it i ...
... This monograph on Fourier Optics contains a rigorous treatment of this important topic based on Maxwells Equations and Electromagnetic Theory. One need know only the elements of calculus and vector analysis in order to understand the contents of this work. In the emerging field of Image Science it i ...
ray_optics_su2014
... normal when enters media with lower wavespeed (i.e. higher index of refraction) ...
... normal when enters media with lower wavespeed (i.e. higher index of refraction) ...
W11Physics1CLec26Afkw
... As we have noted before, light rays can be diverted by optical systems to fool your eye into thinking an object is somewhere that it is not. The simplest optical systems are mirrors and lenses. ...
... As we have noted before, light rays can be diverted by optical systems to fool your eye into thinking an object is somewhere that it is not. The simplest optical systems are mirrors and lenses. ...
Aberrations
... So far, we haven’t asked what the functional form of W might be. If we restrict ourselves to rotationally symmetric optical systems, we can limit the possible forms W might take. If we assume a 2-Dimensional polynomial form for W, and eliminate all terms and combination of terms that are not rotatio ...
... So far, we haven’t asked what the functional form of W might be. If we restrict ourselves to rotationally symmetric optical systems, we can limit the possible forms W might take. If we assume a 2-Dimensional polynomial form for W, and eliminate all terms and combination of terms that are not rotatio ...
JOURNAL OF T O THE EUROPEAN OPTI CAL SOCI ETY
... and the diameter of the aperture stop D is small in comparison with the distance z between an image plane and aperture stop, the natural vignetting is described by the “cosine fourth” law of illumination fall-off [3]–[5]. Natural vignetting is inherent to each lens design and becomes more troublesom ...
... and the diameter of the aperture stop D is small in comparison with the distance z between an image plane and aperture stop, the natural vignetting is described by the “cosine fourth” law of illumination fall-off [3]–[5]. Natural vignetting is inherent to each lens design and becomes more troublesom ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... immersion medium of a digital holographic microscope was changed to obtain a set of optical thickness maps, from which the refractive index and physical thickness was calculated [24]. The disadvantage of all these methods is that they involve an extensive additional measurement system before the tar ...
... immersion medium of a digital holographic microscope was changed to obtain a set of optical thickness maps, from which the refractive index and physical thickness was calculated [24]. The disadvantage of all these methods is that they involve an extensive additional measurement system before the tar ...
of Refraction 2.0
... change in pressure Δp = Δn/k = mλ/2Lk. Therefore, the unknown constant, k, is given by k = mλ/2LΔp. Thus if you measure m fringes while the pressure changes by an amount Δp, you can calculate the refraction index of air at room temperature using, ...
... change in pressure Δp = Δn/k = mλ/2Lk. Therefore, the unknown constant, k, is given by k = mλ/2LΔp. Thus if you measure m fringes while the pressure changes by an amount Δp, you can calculate the refraction index of air at room temperature using, ...
Modulation Transfer Function
... in a passive system. A value of 0 means that frequency will not appear at all in the image. The object- and image-space spatial frequencies are related as s0 = s/|M | where M is the magnification. This definition of MTF, based on image quality, is identical to that obtained from diffraction theory ( ...
... in a passive system. A value of 0 means that frequency will not appear at all in the image. The object- and image-space spatial frequencies are related as s0 = s/|M | where M is the magnification. This definition of MTF, based on image quality, is identical to that obtained from diffraction theory ( ...
Michelson interferometer
... film applied on the denser medium (glass). In the latter case, for reasons that are not obvious, a phase shift of π occurs, corresponding to a change in the optical path of λ/2. In the former case there is no change. For paths of equal optical length, or with a difference of an integer number of wav ...
... film applied on the denser medium (glass). In the latter case, for reasons that are not obvious, a phase shift of π occurs, corresponding to a change in the optical path of λ/2. In the former case there is no change. For paths of equal optical length, or with a difference of an integer number of wav ...
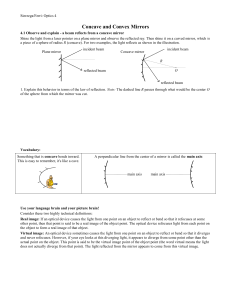
NCEA Level 1 Physics (90938) 2012
... incident ray to mirror = 90° and the angle of reflection + angle of reflected ray to mirror = 90° AND i = r, so angle of incident ray to mirror = angle of reflected ray to mirror ...
... incident ray to mirror = 90° and the angle of reflection + angle of reflected ray to mirror = 90° AND i = r, so angle of incident ray to mirror = angle of reflected ray to mirror ...
626KB - NZQA
... incident ray to mirror = 90° and the angle of reflection + angle of reflected ray to mirror = 90° AND i = r, so angle of incident ray to mirror = angle of reflected ray to mirror ...
... incident ray to mirror = 90° and the angle of reflection + angle of reflected ray to mirror = 90° AND i = r, so angle of incident ray to mirror = angle of reflected ray to mirror ...