Basic Fiber Optic Theory
... the various fiber-optic parameters (and the technical terms), further, the reasons on how to choose the right optical fiber cable, how to install a fiber network, how cables and fibers are spliced and measured. Much of the second day is devoted to FTTX networks. ...
... the various fiber-optic parameters (and the technical terms), further, the reasons on how to choose the right optical fiber cable, how to install a fiber network, how cables and fibers are spliced and measured. Much of the second day is devoted to FTTX networks. ...
Refraction - School
... The ray within the block hits the side at a large angle of incidence: if this angle is large enough, the entire ray reflects and stays inside the block This is TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION This happens inside an optical fibre ...
... The ray within the block hits the side at a large angle of incidence: if this angle is large enough, the entire ray reflects and stays inside the block This is TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION This happens inside an optical fibre ...
as a PDF - Department of Engineering Science
... this does not affect standard microscope operation. However, extra phase curvature introduced for axially displaced points in the current system would lead to a degradation of system performance. We also note that rays from the object space are mapped onto conjugate rays with the same angle in image ...
... this does not affect standard microscope operation. However, extra phase curvature introduced for axially displaced points in the current system would lead to a degradation of system performance. We also note that rays from the object space are mapped onto conjugate rays with the same angle in image ...
Fiber Optics - University of Calgary
... fiber makes possible the transmission of digital data at several gigabits per second (Gbps) over long distances with very low error rates ...
... fiber makes possible the transmission of digital data at several gigabits per second (Gbps) over long distances with very low error rates ...
Optics and Human Vision
... The lowest (darkest) perceptible intensity is the scotopic threshold The highest (brightest) perceptible intensity is the glare limit The difference between these two levels is on the order of 1010 We can’t discriminate all these intensities at the same time! We adjust to an average value of light i ...
... The lowest (darkest) perceptible intensity is the scotopic threshold The highest (brightest) perceptible intensity is the glare limit The difference between these two levels is on the order of 1010 We can’t discriminate all these intensities at the same time! We adjust to an average value of light i ...
Opto acoustic
... and phase function p(), using Mie theory the scattering may be determined knowing; the size parameter (perimeter compared to wavelength), refractive index ratio between particle and media. ...
... and phase function p(), using Mie theory the scattering may be determined knowing; the size parameter (perimeter compared to wavelength), refractive index ratio between particle and media. ...
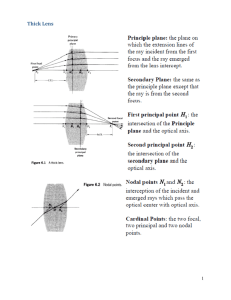
Thick Lens 1
... For the telescopic system shown above, the second lens (eyepiece) is the field stop for very distant objects. The following is simply a recipe for finding the field stop, entrance window, and exit window, given a lens system. Image all optical elements in the system into object space. Find the angl ...
... For the telescopic system shown above, the second lens (eyepiece) is the field stop for very distant objects. The following is simply a recipe for finding the field stop, entrance window, and exit window, given a lens system. Image all optical elements in the system into object space. Find the angl ...
Nonlinear Optics
... Non co-linear – third order Spatial effects: Third order example: two different input beams, whose frequencies can be different. So in addition to generating the third harmonic of each input beam, the medium will generate interesting sum and difference frequencies with spatial separation. ...
... Non co-linear – third order Spatial effects: Third order example: two different input beams, whose frequencies can be different. So in addition to generating the third harmonic of each input beam, the medium will generate interesting sum and difference frequencies with spatial separation. ...
Location of Cardinal Points from the ABCD Matrix for the General
... First Focal Plane: The first focal plane is in the left hand space of the optical system, which by our convention corresponds to the object space of the imaging system. The intersection of the first focal plane with the optical axis is the first focal point F1. Rays originating from this point will ...
... First Focal Plane: The first focal plane is in the left hand space of the optical system, which by our convention corresponds to the object space of the imaging system. The intersection of the first focal plane with the optical axis is the first focal point F1. Rays originating from this point will ...
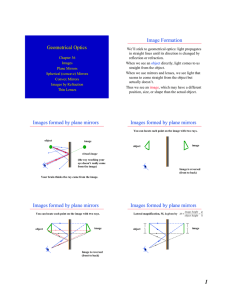
Geometrical Optics Image Formation Images formed by plane
... Note: every ray which leaves the tip of the object will go through the tip of the image! All other rays leaving from other locations on the object will go through that corresponding location on the image!!! Thus, the image looks like the object to the eye. ...
... Note: every ray which leaves the tip of the object will go through the tip of the image! All other rays leaving from other locations on the object will go through that corresponding location on the image!!! Thus, the image looks like the object to the eye. ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... multiple choice. Write the question and correct answer and explain why. 1) Diffuse reflection occurs when light is refracted in many directions from a rough surface. 2) Reflection occurs when one part of a wave travels more slowly than another. 3) Mirages occur because of the reflection of light on ...
... multiple choice. Write the question and correct answer and explain why. 1) Diffuse reflection occurs when light is refracted in many directions from a rough surface. 2) Reflection occurs when one part of a wave travels more slowly than another. 3) Mirages occur because of the reflection of light on ...
Optical Fiber and Communication Course Code: Credit
... Course Title: Optical Fiber and Communication Course Code: ...
... Course Title: Optical Fiber and Communication Course Code: ...
Overview
... Energy Exchange Between Parallel Disc’s What is the flux from a Lambertain source of radiance L, onto a receive at distance r? We will first use point source approximations…..that is, we are at least 10 x the radius of the source (i.e., 1% error). ...
... Energy Exchange Between Parallel Disc’s What is the flux from a Lambertain source of radiance L, onto a receive at distance r? We will first use point source approximations…..that is, we are at least 10 x the radius of the source (i.e., 1% error). ...
unit –iii fiber optics and applications part-a 2
... form through which light is transmitted by total internal reflection. An optical fiber consists of a central core glass about 50μm diameter surrounded by a cladding about 125μm to 200μm diameter which is of slightly lower refractive index than core material. 2. Define fiber optics? Fiber optics is d ...
... form through which light is transmitted by total internal reflection. An optical fiber consists of a central core glass about 50μm diameter surrounded by a cladding about 125μm to 200μm diameter which is of slightly lower refractive index than core material. 2. Define fiber optics? Fiber optics is d ...
oAkLey si BALListic det cord
... The SI Ballistic Det Cord is the perfect blend of ballistic protection and Oakley fashion. Fully compliant with the ballistic and optical standards of MIL PRF32432 and ANSI Z87.1 (2010), the SI Ballistic Det Cord is balanced for aggressive environments and covert capabilities. The SI Ballistic Det C ...
... The SI Ballistic Det Cord is the perfect blend of ballistic protection and Oakley fashion. Fully compliant with the ballistic and optical standards of MIL PRF32432 and ANSI Z87.1 (2010), the SI Ballistic Det Cord is balanced for aggressive environments and covert capabilities. The SI Ballistic Det C ...
Plane Mirrors
... A source (light bulb, the sun, etc) Another object (that is not creating the light ray, but rather reflects light that strikes it) ...
... A source (light bulb, the sun, etc) Another object (that is not creating the light ray, but rather reflects light that strikes it) ...
lecture_three_2016
... serves as the source of spherical secondary waves also called wavelets, such that the primary wavefront at some later time is the envelope of these wavelets. Moreover, the wavelets advance with a speed and frequency equal to those of the primary wave at each point in space. This has since become kno ...
... serves as the source of spherical secondary waves also called wavelets, such that the primary wavefront at some later time is the envelope of these wavelets. Moreover, the wavelets advance with a speed and frequency equal to those of the primary wave at each point in space. This has since become kno ...
The ins and outs of conical refraction
... the optic axes of wave normals, or binormals (or several other names), in the case of the wave-normal surface. At first sight these binormals might seem less interesting than the general directions that yield two distinct wave velocities and hence are associated with double refraction, but Hamilton ...
... the optic axes of wave normals, or binormals (or several other names), in the case of the wave-normal surface. At first sight these binormals might seem less interesting than the general directions that yield two distinct wave velocities and hence are associated with double refraction, but Hamilton ...
AQA GCSE Physics P3 Revision Worksheet
... How does a transformer work? Fill the missing words: An …………………………………………………………… current in the primary coil produces a changing magnetic ………………………. in the iron core and hence in the secondary coil. This …………………………………………………….. an alternating ………………..………………… difference across the ends of the ……………………… ...
... How does a transformer work? Fill the missing words: An …………………………………………………………… current in the primary coil produces a changing magnetic ………………………. in the iron core and hence in the secondary coil. This …………………………………………………….. an alternating ………………..………………… difference across the ends of the ……………………… ...