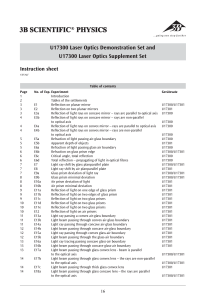
Chapter 25
... The interference pattern for the two rays is determined by the difference in their path lengths When M1 is moved a distance of /4, successive light and dark fringes are formed This change in a fringe from light to dark is called fringe shift The wavelength can be measured by counting the number o ...
... The interference pattern for the two rays is determined by the difference in their path lengths When M1 is moved a distance of /4, successive light and dark fringes are formed This change in a fringe from light to dark is called fringe shift The wavelength can be measured by counting the number o ...
Topic 4.5 - Aurora City School
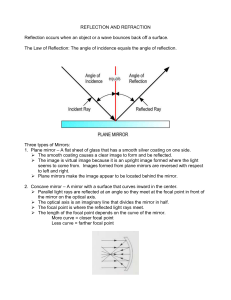
... The Law for Reflection • The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection -keep in mind that angles are measured with respect to the normal at point of contact ...
... The Law for Reflection • The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection -keep in mind that angles are measured with respect to the normal at point of contact ...
Geometric limits to geometric optical imaging with infinite, planar
... • Eqn (5) describes a mapping, defined by two object-image pairs, (P1 , P10 ) and (P2 , P20 ), from an object position to a corresponding image position. This can be used to define a third object-image pair, which we call (P3 , P30 ). It is relatively straightforward to show that the mapping defined ...
... • Eqn (5) describes a mapping, defined by two object-image pairs, (P1 , P10 ) and (P2 , P20 ), from an object position to a corresponding image position. This can be used to define a third object-image pair, which we call (P3 , P30 ). It is relatively straightforward to show that the mapping defined ...
Wavefront Technology
... Zernike polynomials (mathematical formulae used to describe surfaces). These mathematical models are adequate for describing the wavefront measurements of the eye, because they are defined based on a circular form. The shape of the wavefront is described in the x and y coordinates while the third di ...
... Zernike polynomials (mathematical formulae used to describe surfaces). These mathematical models are adequate for describing the wavefront measurements of the eye, because they are defined based on a circular form. The shape of the wavefront is described in the x and y coordinates while the third di ...
CP2: Optics Why study optics? The problem of teaching optics
... at the same speed in a direction normal to the wavefront. All points on a wavefront correspond to the same point in time. ...
... at the same speed in a direction normal to the wavefront. All points on a wavefront correspond to the same point in time. ...
1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 31 — LIGHT AND OPTICS (3) In lecture 30
... plane and curved mirrors. In this lecture we will use the law of refraction to describe how images are formed by lenses – curved pieces of glass or transparent plastic. The law of refraction allows us to determine how a light ray is bent when it travels from air into glass or clear plastic. We wil ...
... plane and curved mirrors. In this lecture we will use the law of refraction to describe how images are formed by lenses – curved pieces of glass or transparent plastic. The law of refraction allows us to determine how a light ray is bent when it travels from air into glass or clear plastic. We wil ...
Introduction to Drawing Ray Diagrams Types of
... For (1-3): Draw ray #1 // to PA, stopping at the mirror. Angle ruler, so the same ray is refracted through F. Draw ray #2 through F, touching mirror below PA. Continue this ray // to PA. Place a dot at the intersection. Draw ray #3 to O, and angle ruler so that this ray reaches the point of intersec ...
... For (1-3): Draw ray #1 // to PA, stopping at the mirror. Angle ruler, so the same ray is refracted through F. Draw ray #2 through F, touching mirror below PA. Continue this ray // to PA. Place a dot at the intersection. Draw ray #3 to O, and angle ruler so that this ray reaches the point of intersec ...
laser optical disk set
... holes on the Laser Ray Box and identify the order of the exit rays compared to their entry order (see Diagram 5.5a) Although the order of the rays as shown appears to have been reversed (ABC becomes CBA), this is not so if viewed against the direction of the oncoming light. Diagram 5.5b To confirm ...
... holes on the Laser Ray Box and identify the order of the exit rays compared to their entry order (see Diagram 5.5a) Although the order of the rays as shown appears to have been reversed (ABC becomes CBA), this is not so if viewed against the direction of the oncoming light. Diagram 5.5b To confirm ...
Resins for Optics
... and it is expected to be used in various fields. Signal attenuation of optical fiber is small and it allows long distance and large capacity, compared to conventional metallic cables. Therefore, if optical fiber cables are connected to general houses, its advantages are inestimable. To complete fibe ...
... and it is expected to be used in various fields. Signal attenuation of optical fiber is small and it allows long distance and large capacity, compared to conventional metallic cables. Therefore, if optical fiber cables are connected to general houses, its advantages are inestimable. To complete fibe ...
used to cook Infrared - “heat waves” Visible Light
... • The speed of light is the same for all seven forms of light. • It is 300,000,000 meters per second or 186,000 miles per ...
... • The speed of light is the same for all seven forms of light. • It is 300,000,000 meters per second or 186,000 miles per ...
Focal length
... especially at lower magnifications. This makes it difficult to see fine detail. • A standard lunar filter may block 80% or more of all visible light. • A polarizing filter uses two polarized elements that can be rotated to vary the amount of light blocked. ...
... especially at lower magnifications. This makes it difficult to see fine detail. • A standard lunar filter may block 80% or more of all visible light. • A polarizing filter uses two polarized elements that can be rotated to vary the amount of light blocked. ...
Lecture 11
... M matricies can be used to propagate either left to right or right to left (input to output or output to input). The output to input formulation is both a bit more numerically friendly, and much more useful if you want to explore the field distribution inside the dielectric stack. High reflectivity ...
... M matricies can be used to propagate either left to right or right to left (input to output or output to input). The output to input formulation is both a bit more numerically friendly, and much more useful if you want to explore the field distribution inside the dielectric stack. High reflectivity ...
geometrical optics
... direct or control rays of light. The refraction of light at the surface of a lens depends on its shape, its index of refraction, and the nature of the medium surrounding it (usually air), in accordance with Snell’s Law. Lenses that are thicker in the center than at their edges are called positive, o ...
... direct or control rays of light. The refraction of light at the surface of a lens depends on its shape, its index of refraction, and the nature of the medium surrounding it (usually air), in accordance with Snell’s Law. Lenses that are thicker in the center than at their edges are called positive, o ...
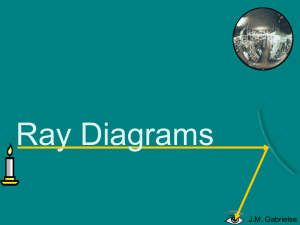
Ray Diagrams
... Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Lecture 11
... M matricies can be used to propagate either left to right or right to left (input to output or output to input). The output to input formulation is both a bit more numerically friendly, and much more useful if you want to explore the field distribution inside the dielectric stack. High reflectivity ...
... M matricies can be used to propagate either left to right or right to left (input to output or output to input). The output to input formulation is both a bit more numerically friendly, and much more useful if you want to explore the field distribution inside the dielectric stack. High reflectivity ...
CCD-Based Instrumentation for Radiometric
... aberration. It can be obtained by determining the size of the exit pupil in direction cosine space, using the appropriate coordinate system. In general, the calculation is done by tracing bundles of rays through the system. In many cases of interest, it is possible to calculate relative illumination ...
... aberration. It can be obtained by determining the size of the exit pupil in direction cosine space, using the appropriate coordinate system. In general, the calculation is done by tracing bundles of rays through the system. In many cases of interest, it is possible to calculate relative illumination ...
image
... spherical wave, according to the Huygens principle. • A few microns away from the object surface, the rays emanating from all object points become entangled, delocalizing object details. • To relocalize object details, a method must be found to reassign (“focus”) all the rays that emanated from a si ...
... spherical wave, according to the Huygens principle. • A few microns away from the object surface, the rays emanating from all object points become entangled, delocalizing object details. • To relocalize object details, a method must be found to reassign (“focus”) all the rays that emanated from a si ...
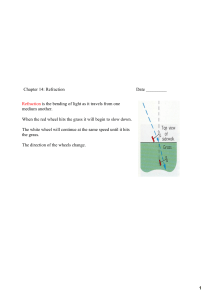
1 Chapter 14: Refraction
... dimensionless number that is always greater than one. The larger the index of refraction the slower light travels in that substance. The amount that light bends when entering a medium depends on the wavelength of the light as well as the speed. ...
... dimensionless number that is always greater than one. The larger the index of refraction the slower light travels in that substance. The amount that light bends when entering a medium depends on the wavelength of the light as well as the speed. ...
Dr. Shin - Northern Illinois University
... procedure, with some theory for guidance. You will be responsible for the theory part, in some cases, along with the presentation of data and some kind of discussion. I regard the discussion as the most important part, as this is where you give thought to the results and explain how well they verify ...
... procedure, with some theory for guidance. You will be responsible for the theory part, in some cases, along with the presentation of data and some kind of discussion. I regard the discussion as the most important part, as this is where you give thought to the results and explain how well they verify ...