6-5.3 Magnetism and Electricity Support Doc
... producing a magnetic field. The magnet that results loses its magnetism if the electric current stops flowing. Generators A generator produces an electric current when a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core is rotated near a magnet. Generators at power plants produce electric energy for ou ...
... producing a magnetic field. The magnet that results loses its magnetism if the electric current stops flowing. Generators A generator produces an electric current when a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core is rotated near a magnet. Generators at power plants produce electric energy for ou ...
Section 20.1 Electric Charge and Static Electricity
... 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about electric force. a. Like charges attract and opposite charges repel. b. Electric force is the attraction or repulsion between electrically charged objects. c. Electric force is inversely proportional to the amount of charge. d. Electric force i ...
... 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about electric force. a. Like charges attract and opposite charges repel. b. Electric force is the attraction or repulsion between electrically charged objects. c. Electric force is inversely proportional to the amount of charge. d. Electric force i ...
Electric Fields and Potential
... The direction of the field is always determined, by convention, with a small, positive test charge. Electric Field strength can be calculated using: E = F/q and E = kq/d ...
... The direction of the field is always determined, by convention, with a small, positive test charge. Electric Field strength can be calculated using: E = F/q and E = kq/d ...
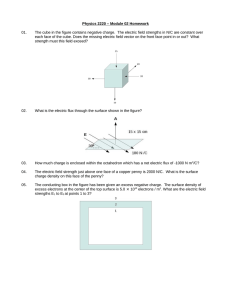
7. Two fixed charges +4q and +q are kept at
... 15. Electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume of the conductor and has the same value on its surface. Why ? 16. If the electric potential at a certain point is zero, does the electric field at that point have to be zero? 17. If the electric field at a certain point is zero, does the ...
... 15. Electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume of the conductor and has the same value on its surface. Why ? 16. If the electric potential at a certain point is zero, does the electric field at that point have to be zero? 17. If the electric field at a certain point is zero, does the ...
Gauss' Law Review & Summary
... Gauss' law and Coulomb's law are different ways of describing the relation between charge and electric field in static situations. Gauss' law is ...
... Gauss' law and Coulomb's law are different ways of describing the relation between charge and electric field in static situations. Gauss' law is ...
Practice Problems: Coulomb`s Law and Electric Field Strength
... F = ____________; unit is ____________ ...
... F = ____________; unit is ____________ ...
Electrostatics
... noticed would mysteriously attract small particles after it had been rubbed with fur. ...
... noticed would mysteriously attract small particles after it had been rubbed with fur. ...
Document
... a. Charge _______________ b. Electrical force _______________ c. Electric field _________ or ________________ d. Electric potential or potential difference ____________________ ...
... a. Charge _______________ b. Electrical force _______________ c. Electric field _________ or ________________ d. Electric potential or potential difference ____________________ ...
Fall 2006
... IMP 113: Final Exam Part I (Union College: Spring 2008) Instructions: 1. Read all directions. 2. In keeping with the Union College policy on academic honesty, you should neither accept nor provide unauthorized assistance in the completion of this work. Name:__________________________________ ...
... IMP 113: Final Exam Part I (Union College: Spring 2008) Instructions: 1. Read all directions. 2. In keeping with the Union College policy on academic honesty, you should neither accept nor provide unauthorized assistance in the completion of this work. Name:__________________________________ ...
PHYSICS 100 ELECTROSTATICS
... positive and negative charge. It was observed that rubbing two materials together sometimes resulted in both materials acquiring opposite net charges. In this process, the outermost or valence electrons in one material were transferred to the second material. The first material would be charged posi ...
... positive and negative charge. It was observed that rubbing two materials together sometimes resulted in both materials acquiring opposite net charges. In this process, the outermost or valence electrons in one material were transferred to the second material. The first material would be charged posi ...
1) Two charges of opposite sign are fixed in space forming and
... Use Gauss’ law to obtain expressions for the electric field in the three regions. In each case clearly define the Gaussian surface you are using and your assumptions about the electric field. ...
... Use Gauss’ law to obtain expressions for the electric field in the three regions. In each case clearly define the Gaussian surface you are using and your assumptions about the electric field. ...
Electrostatic generator

An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is an electromechanical generator that produces static electricity, or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current. The knowledge of static electricity dates back to the earliest civilizations, but for millennia it remained merely an interesting and mystifying phenomenon, without a theory to explain its behavior and often confused with magnetism. By the end of the 17th Century, researchers had developed practical means of generating electricity by friction, but the development of electrostatic machines did not begin in earnest until the 18th century, when they became fundamental instruments in the studies about the new science of electricity. Electrostatic generators operate by using manual (or other) power to transform mechanical work into electric energy. Electrostatic generators develop electrostatic charges of opposite signs rendered to two conductors, using only electric forces, and work by using moving plates, drums, or belts to carry electric charge to a high potential electrode. The charge is generated by one of two methods: either the triboelectric effect (friction) or electrostatic induction.