Name: Notes – 18.7 Conductors and Electric Fields in Static
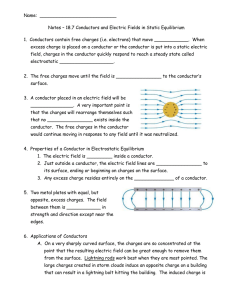
... C. Another device that makes use of some of these principles is a Faraday cage. This is a metal shield that encloses a volume. All electrical charges will reside on the outside surface of this shield, and there will be no electrical field inside. A Faraday cage is used to prohibit stray electrical f ...
... C. Another device that makes use of some of these principles is a Faraday cage. This is a metal shield that encloses a volume. All electrical charges will reside on the outside surface of this shield, and there will be no electrical field inside. A Faraday cage is used to prohibit stray electrical f ...
ASSIGNMENT ON PHYSICS CLASS:12 DATE:18-O4
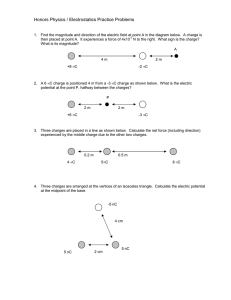
... 2. A charge of 10 μc is brought from point A (0,4 cm,0) to C (3 cm,0,0) via point B (0,0,6 cm) in vacuum. Calculate the work done if the charge at origin is 20 μc. niformly char. Where the energy of capacitor does resides? ...
... 2. A charge of 10 μc is brought from point A (0,4 cm,0) to C (3 cm,0,0) via point B (0,0,6 cm) in vacuum. Calculate the work done if the charge at origin is 20 μc. niformly char. Where the energy of capacitor does resides? ...
Unit 14: Electric Charge
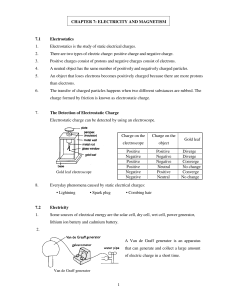
... o Conductors are materials that permit charge to move easily and insulators so not allow charge to move easily o Coulomb’s law is the basic law of interaction for point electric charges. o Electric field is the force per unit charge exerted on a test charge at any point. o Field lines provide a grap ...
... o Conductors are materials that permit charge to move easily and insulators so not allow charge to move easily o Coulomb’s law is the basic law of interaction for point electric charges. o Electric field is the force per unit charge exerted on a test charge at any point. o Field lines provide a grap ...
40679_2014_2_MOESM1_ESM - Springer Static Content Server
... In order to accurately simulate interface structure with shifted-force electrostatics, it is necessary to include a correction, along the interface normal, to the force calculation. This is needed due to the anisotropic charge distribution that results at the interface. Corrective procedure is based ...
... In order to accurately simulate interface structure with shifted-force electrostatics, it is necessary to include a correction, along the interface normal, to the force calculation. This is needed due to the anisotropic charge distribution that results at the interface. Corrective procedure is based ...
AP Physics Chp 18
... • How large is the electric field that levitates a proton in the air? m = 1.67 x 10-19 kg and q = 1.6 x 10-19 C ...
... • How large is the electric field that levitates a proton in the air? m = 1.67 x 10-19 kg and q = 1.6 x 10-19 C ...
Chapter 4
... RAD 350 Chapter 4 Electricity, Magnetism and Electromagnetism I. The primary purpose of an x-ray tube is to convert electric energy into electromagnetic energy or x-rays -energy conversion is around us everywhere -electricity created the heat in a hair dryer or toaster -chemical energy cranks the st ...
... RAD 350 Chapter 4 Electricity, Magnetism and Electromagnetism I. The primary purpose of an x-ray tube is to convert electric energy into electromagnetic energy or x-rays -energy conversion is around us everywhere -electricity created the heat in a hair dryer or toaster -chemical energy cranks the st ...
Electricity - WordPress.com
... electric field : an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving . The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. Moving charges additionally produce a magnetic field. electric potential: the capacity of an electric ...
... electric field : an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving . The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. Moving charges additionally produce a magnetic field. electric potential: the capacity of an electric ...
1 CHAPTER 7: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 7.1
... Electrostatics is the study of static electrical charges. ...
... Electrostatics is the study of static electrical charges. ...
EXAM A
... (20) 8. Consider two concentric hollow sphere as shown below. Use Gauss’s Law to find the equation for the electric field in the region where c < r < d. There is charge +Q on the inner sphere and —Q on the outer sphere. (You must start with Gauss’s Law and show each step clearly to obtain the answe ...
... (20) 8. Consider two concentric hollow sphere as shown below. Use Gauss’s Law to find the equation for the electric field in the region where c < r < d. There is charge +Q on the inner sphere and —Q on the outer sphere. (You must start with Gauss’s Law and show each step clearly to obtain the answe ...
Michael Faraday
... Developed an interest in science Saved money to buy some apparatus for his first experiment Began to attend some lectures on science Decided to quit trade and pursue science at the end of his apprenticeship ...
... Developed an interest in science Saved money to buy some apparatus for his first experiment Began to attend some lectures on science Decided to quit trade and pursue science at the end of his apprenticeship ...
Physics in the Enlightenment
... "I am going to tell you about a new but terrible experiment which I advise you not to try yourself, nor would I, who have experienced it and survived by the grace of God, do it again for all the kingdom of France. I was making some investigations on the force of electricity; for this purpose I had ...
... "I am going to tell you about a new but terrible experiment which I advise you not to try yourself, nor would I, who have experienced it and survived by the grace of God, do it again for all the kingdom of France. I was making some investigations on the force of electricity; for this purpose I had ...
Electricity
... fire thus obtained spirits may be kindled, and all other electric experiments [may be] performed which are usually done by the help of a rubber glass globe or tube; and therefore the sameness of the electrical matter with that of lightening completely demonstrated. • He did not wait, until struck by ...
... fire thus obtained spirits may be kindled, and all other electric experiments [may be] performed which are usually done by the help of a rubber glass globe or tube; and therefore the sameness of the electrical matter with that of lightening completely demonstrated. • He did not wait, until struck by ...
Electrostatic generator

An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is an electromechanical generator that produces static electricity, or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current. The knowledge of static electricity dates back to the earliest civilizations, but for millennia it remained merely an interesting and mystifying phenomenon, without a theory to explain its behavior and often confused with magnetism. By the end of the 17th Century, researchers had developed practical means of generating electricity by friction, but the development of electrostatic machines did not begin in earnest until the 18th century, when they became fundamental instruments in the studies about the new science of electricity. Electrostatic generators operate by using manual (or other) power to transform mechanical work into electric energy. Electrostatic generators develop electrostatic charges of opposite signs rendered to two conductors, using only electric forces, and work by using moving plates, drums, or belts to carry electric charge to a high potential electrode. The charge is generated by one of two methods: either the triboelectric effect (friction) or electrostatic induction.