AP PHYSICS 2- Electricity and Magnetism
... • Inductors • Solenoid and Toroid Inductance • Self -Induction • Series RL Circuits • Storage of Energy by an Inductor • Magnetic Field Energy • Mutual Induction ...
... • Inductors • Solenoid and Toroid Inductance • Self -Induction • Series RL Circuits • Storage of Energy by an Inductor • Magnetic Field Energy • Mutual Induction ...
Lecture
... Gauss’ Law relates the net flux of an electric field through a closed surface to the net charge qenc that is enclosed by that surface ...
... Gauss’ Law relates the net flux of an electric field through a closed surface to the net charge qenc that is enclosed by that surface ...
Electricity
... eighteenth centuries. It would remain however until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put electricity to industrial and residential use, a time which witnessed a rapid expansion in the development of electrical technology. ...
... eighteenth centuries. It would remain however until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put electricity to industrial and residential use, a time which witnessed a rapid expansion in the development of electrical technology. ...
P6F
... The slip rings are connected to the coil. The brushes are connected to the external circuit. The brushes touch the spinning slip rings, which maintain electrical contact between the coil and the external circuit. At the power station Electricity is a useful form of energy. It allows energy to be tra ...
... The slip rings are connected to the coil. The brushes are connected to the external circuit. The brushes touch the spinning slip rings, which maintain electrical contact between the coil and the external circuit. At the power station Electricity is a useful form of energy. It allows energy to be tra ...
Electric potential
... The concept of electric potential is closely linked to that of the electric field. A small charge placed within an electric field experiences a force, and to have brought that charge to that point against the force requires work. The electric potential at any point is defined as the energy required ...
... The concept of electric potential is closely linked to that of the electric field. A small charge placed within an electric field experiences a force, and to have brought that charge to that point against the force requires work. The electric potential at any point is defined as the energy required ...
Name___________________________________ February 15
... tells how to produce a static charge on a rubber balloon? a) Stick the balloon to a wall. b) Touch the balloon to a magnet. c) Blow up the balloon. d) Rub the balloon with a wool cloth. ...
... tells how to produce a static charge on a rubber balloon? a) Stick the balloon to a wall. b) Touch the balloon to a magnet. c) Blow up the balloon. d) Rub the balloon with a wool cloth. ...
Chapter 2. Electrostatics
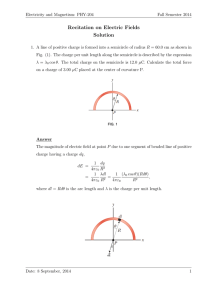
... To solve the force on Q using the superposition principle sounds very easy, BUT, the force on Q depends not only on the separation distance r between the charges, it also depends on both their velocities and on the acceleration of q. Moreover, electromagnetic fields travels at the speed of lig ...
... To solve the force on Q using the superposition principle sounds very easy, BUT, the force on Q depends not only on the separation distance r between the charges, it also depends on both their velocities and on the acceleration of q. Moreover, electromagnetic fields travels at the speed of lig ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.