CH437 CLASS 7
... being random, gradually diminishes, whereas signals become more intense. Fourier transform can then be carried out on the final FID data to produce the familiar frequency spectrum. The most common representation of an NMR experiment, in terms of pulse and acquisition times (etc), are as in the figur ...
... being random, gradually diminishes, whereas signals become more intense. Fourier transform can then be carried out on the final FID data to produce the familiar frequency spectrum. The most common representation of an NMR experiment, in terms of pulse and acquisition times (etc), are as in the figur ...
Chapter 30: Quantum Physics
... Calculate the energy of a single photon from its wavelength using equations 30-4 and 14-1. Divide the total energy by the energy of the single photon to calculate the number of photons. 1. (a) Use equations 30-4 and 14-1 to write the energy of a single photon: 2. Divide the total energy by the energ ...
... Calculate the energy of a single photon from its wavelength using equations 30-4 and 14-1. Divide the total energy by the energy of the single photon to calculate the number of photons. 1. (a) Use equations 30-4 and 14-1 to write the energy of a single photon: 2. Divide the total energy by the energ ...
Preview of Period 3: Electromagnetic Waves – Radiant Energy II
... R.5 How does an AM radio signal differ from an FM signal? Does an AM or FM signal contain photons with greater energy per photon? Which signal uses radio waves with a higher frequency? ...
... R.5 How does an AM radio signal differ from an FM signal? Does an AM or FM signal contain photons with greater energy per photon? Which signal uses radio waves with a higher frequency? ...
Lecture 13: Heisenberg and Uncertainty
... TOTAL MOMENTUM IS ALWAYS CONSERVED Photons have energy and a finite velocity so there must be some momentum associated with photons ! ...
... TOTAL MOMENTUM IS ALWAYS CONSERVED Photons have energy and a finite velocity so there must be some momentum associated with photons ! ...
1H-NMR and 13C-NMR Spectra - Royal Society of Chemistry
... the FAB-MS spectrum of 5, some fragment peaks are located at m/z 1944 [M+– (p-TMP) – 2 CH3], 1848 [M+– (p-TMP) – 2 tBu – CH3], 1720, 996.5 [tBu4PcIn(p-TMP)+], and 851.5 [tBu4PcIn+]. The main fragment peaks of 4 appear at m/z 1854 (M+ – 3 CH3), 1737 [M+– 3 tBu], 1556[M+–6 tBu], 1365, 1206, 1016, 885. ...
... the FAB-MS spectrum of 5, some fragment peaks are located at m/z 1944 [M+– (p-TMP) – 2 CH3], 1848 [M+– (p-TMP) – 2 tBu – CH3], 1720, 996.5 [tBu4PcIn(p-TMP)+], and 851.5 [tBu4PcIn+]. The main fragment peaks of 4 appear at m/z 1854 (M+ – 3 CH3), 1737 [M+– 3 tBu], 1556[M+–6 tBu], 1365, 1206, 1016, 885. ...
Section 5-1
... • Contrast continuous electromagnetic spectra and atomic emission spectra. radiation: the rays and particles —alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays—that are emitted by radioactive material ...
... • Contrast continuous electromagnetic spectra and atomic emission spectra. radiation: the rays and particles —alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays—that are emitted by radioactive material ...
MLSystems Lab 1 - Fourier v4 - RIT
... These discrete coefficients are the diffraction orders of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern that are produced when a diffraction grating is illuminated by coherent illumination. These coefficients, represented as terms in the harmonic decomposition of m(x) correspond to the discrete orders seen in ...
... These discrete coefficients are the diffraction orders of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern that are produced when a diffraction grating is illuminated by coherent illumination. These coefficients, represented as terms in the harmonic decomposition of m(x) correspond to the discrete orders seen in ...
Quantum Readiness
... Using good instrumentation, the researcher makes a careful study of the location of the particle in this well. The position is measured many times, and after each measurement the particle is once again allowed to reach thermal equilibrium near absolute zero, that is return to its ground state. Based ...
... Using good instrumentation, the researcher makes a careful study of the location of the particle in this well. The position is measured many times, and after each measurement the particle is once again allowed to reach thermal equilibrium near absolute zero, that is return to its ground state. Based ...
..............................................................
... The above data show that we have succeeded with the conditional gate operation. However, to understand our results more quantitatively, we compare the data with simulation data obtained by numerically calculating the time evolution of the density matrix. The results of the simulation are shown as bl ...
... The above data show that we have succeeded with the conditional gate operation. However, to understand our results more quantitatively, we compare the data with simulation data obtained by numerically calculating the time evolution of the density matrix. The results of the simulation are shown as bl ...
Mathematical Methods of Physics – Fall 2010 – Dr
... photons have energy E = h = hc/ and momentum p = h/ can be created or destroyed when radiation (e.g. particles) are emitted or absorbed can have particle-like collisions with other particles such as electrons Light also exhibits wave-like properties such as interference and diffraction. QM: ...
... photons have energy E = h = hc/ and momentum p = h/ can be created or destroyed when radiation (e.g. particles) are emitted or absorbed can have particle-like collisions with other particles such as electrons Light also exhibits wave-like properties such as interference and diffraction. QM: ...
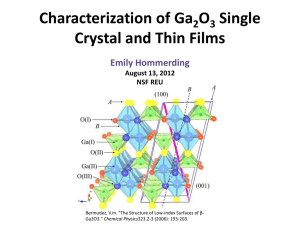
Characterization of Ga 2 0 3 Single Crystal and Thin Films
... Fadley, Charles S. "X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: From Origins to Future Directions." Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 601.1-2 (2009): ...
... Fadley, Charles S. "X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: From Origins to Future Directions." Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 601.1-2 (2009): ...
Chapter 27 Powerpoint
... The photon’s energy would be E = hƒ Each photon can give all its energy to an electron in the metal The maximum kinetic energy of the liberated photoelectron is KEmax = hƒ – Φ Φ is called the work function of the metal ...
... The photon’s energy would be E = hƒ Each photon can give all its energy to an electron in the metal The maximum kinetic energy of the liberated photoelectron is KEmax = hƒ – Φ Φ is called the work function of the metal ...
may11-95 as a Word 6.0 doc - Lyle School of Engineering
... Note #1: each question is worth 3 points except #23, which is worth 1 point. Note #2: ...
... Note #1: each question is worth 3 points except #23, which is worth 1 point. Note #2: ...