H2O - WCCUSD.net
... § Each pure substance has characteristic physical and chemical properties (for any bulk quantity under given conditions) that can be used to identify it. (MS-‐PS1-‐2) ...
... § Each pure substance has characteristic physical and chemical properties (for any bulk quantity under given conditions) that can be used to identify it. (MS-‐PS1-‐2) ...
Chemistry I – Fall 2004
... 13. Which compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds? (A) KCl (B) NH4Cl (C) CCl4 (D) CO2 14. Covalent bonds are most likely to be found in the compound represented by the formula (A) NaCl (B) KBr (C) CH4 (D) HI E) CaF2 15. A pure substance melts at 113 °C and does not conduct electricity in ei ...
... 13. Which compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds? (A) KCl (B) NH4Cl (C) CCl4 (D) CO2 14. Covalent bonds are most likely to be found in the compound represented by the formula (A) NaCl (B) KBr (C) CH4 (D) HI E) CaF2 15. A pure substance melts at 113 °C and does not conduct electricity in ei ...
01 Intro Chemistry
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
02Ch02chemistry2005
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
Standards Practice
... know chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as Hz , CH4, NH3, HzCCHz , Nz, Clz, and many large biological molecules are covalent. 5. Which do not form covalent bonds? A. diatomic molecules B. large biological molecules C. molecules containing carbon D. salts 6. The bonds found in C2H4 are A. ...
... know chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as Hz , CH4, NH3, HzCCHz , Nz, Clz, and many large biological molecules are covalent. 5. Which do not form covalent bonds? A. diatomic molecules B. large biological molecules C. molecules containing carbon D. salts 6. The bonds found in C2H4 are A. ...
Periodic Table, Bonding, Reactions, and Moles
... similar to the bonding in barium chloride, BaCl2. 9. Identify the type of bonding between the atoms in an oxygen molecule. ...
... similar to the bonding in barium chloride, BaCl2. 9. Identify the type of bonding between the atoms in an oxygen molecule. ...
CrystEngComm
... furan-2,5-dicarboxylate (Cu(FDC)(H2O)) crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/m (no. 12) with one Cu-center on a mirror plane and one Cu-center on a general position. The asymmetric unit contains 1.5 Cu2+ ions, 1.5 FDC ligands and 1.5 coordinated H2O molecules (Fig. 1). Cu1 and water oxygen O ...
... furan-2,5-dicarboxylate (Cu(FDC)(H2O)) crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/m (no. 12) with one Cu-center on a mirror plane and one Cu-center on a general position. The asymmetric unit contains 1.5 Cu2+ ions, 1.5 FDC ligands and 1.5 coordinated H2O molecules (Fig. 1). Cu1 and water oxygen O ...
∙ ∙B x
... 28. See the graph with the boiling points of hydrogen halides and state what is exceptional there: 3. Hydrogen bonding (hydrogen bridges) When a very electronegative element (F, O, N) is bonded to a hydrogen atom, the hydrogen electron is drawn to the more electronegative atom. A hydrogen atom has a ...
... 28. See the graph with the boiling points of hydrogen halides and state what is exceptional there: 3. Hydrogen bonding (hydrogen bridges) When a very electronegative element (F, O, N) is bonded to a hydrogen atom, the hydrogen electron is drawn to the more electronegative atom. A hydrogen atom has a ...
∙ ∙B x
... There are regularly arranged positive and negative ions. They hold together due strong electrostatic interactions (............. bond). Properties: hard/soft and rigid/brittle, involatile, with low/high melting and boiling point, good electric conductors when .................... or in a ........... ...
... There are regularly arranged positive and negative ions. They hold together due strong electrostatic interactions (............. bond). Properties: hard/soft and rigid/brittle, involatile, with low/high melting and boiling point, good electric conductors when .................... or in a ........... ...
Unit - III - E
... forms of bonding. This bonding supplies a basic molecular skeleton that is modified by repulsive forces. These repulsive forces include the steric interactions described above. Basic bonding and steric are at times insufficient to explain many structures, properties, and reactivity. Thus steric effe ...
... forms of bonding. This bonding supplies a basic molecular skeleton that is modified by repulsive forces. These repulsive forces include the steric interactions described above. Basic bonding and steric are at times insufficient to explain many structures, properties, and reactivity. Thus steric effe ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding
... Hence: atoms tend to be surrounded by 8 valence e- - this is the reason that group 1 atoms form +1 ions, group 6 atoms form -2 ions, etc ...
... Hence: atoms tend to be surrounded by 8 valence e- - this is the reason that group 1 atoms form +1 ions, group 6 atoms form -2 ions, etc ...
FREE Sample Here
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
Covalent Bonding
... Group 1 and 17 elements are always at ends Atoms that are less numerous are usually in the middle Hydrogen always forms one single bond Oxygen has two bonding electrons and two lone pairs Nitrogen has three bonding electron and one lone pair Group 13 elements have three bonding electrons and z ...
... Group 1 and 17 elements are always at ends Atoms that are less numerous are usually in the middle Hydrogen always forms one single bond Oxygen has two bonding electrons and two lone pairs Nitrogen has three bonding electron and one lone pair Group 13 elements have three bonding electrons and z ...
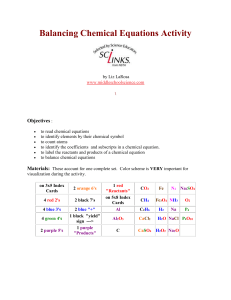
Balancing Chemical Equations Activity by Liz LaRosa www
... The index cards are a bit time consuming to create. I had some students help at lunch time for a few days. Once done, you can laminate them and have them forever! The materials account for one complete set which is good for 2-3 students to use. Print activity cards on card stock instead of making in ...
... The index cards are a bit time consuming to create. I had some students help at lunch time for a few days. Once done, you can laminate them and have them forever! The materials account for one complete set which is good for 2-3 students to use. Print activity cards on card stock instead of making in ...
Ch. 2 Chemistry
... Covalent Bonds A molecule • Consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds ...
... Covalent Bonds A molecule • Consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds ...
Chemical Bonding I
... 2) Calculate the total number of electrons by summing the valence electrons of each atom. (Be sure to take ions into account!) 3) Distribute the electrons among the atoms giving octets to all atoms ...
... 2) Calculate the total number of electrons by summing the valence electrons of each atom. (Be sure to take ions into account!) 3) Distribute the electrons among the atoms giving octets to all atoms ...
bonding and geometry
... the bonding pair is shared equallythis bond is called non polar covalent When atoms in a molecule are different, the bonding pair of electrons are not shared equallythis is called a polar covalent bond ...
... the bonding pair is shared equallythis bond is called non polar covalent When atoms in a molecule are different, the bonding pair of electrons are not shared equallythis is called a polar covalent bond ...
Covalent Bonding - Effingham County Schools
... •As independent particles, most atoms are at relatively high potential energy. •Nature, however, favors arrangements in which potential energy is minimized. •This means that most atoms are less stable existing by themselves than when they are combined. •By bonding with each other, atoms decrease in ...
... •As independent particles, most atoms are at relatively high potential energy. •Nature, however, favors arrangements in which potential energy is minimized. •This means that most atoms are less stable existing by themselves than when they are combined. •By bonding with each other, atoms decrease in ...
Covalent Bonding - Effingham County Schools
... •As independent particles, most atoms are at relatively high potential energy. •Nature, however, favors arrangements in which potential energy is minimized. •This means that most atoms are less stable existing by themselves than when they are combined. •By bonding with each other, atoms decrease in ...
... •As independent particles, most atoms are at relatively high potential energy. •Nature, however, favors arrangements in which potential energy is minimized. •This means that most atoms are less stable existing by themselves than when they are combined. •By bonding with each other, atoms decrease in ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
... Bonds are forces that hold groups of atoms together and ...
... Bonds are forces that hold groups of atoms together and ...
Chemical Bonds - coellochemistry
... Naming Covalent Compounds For covalent compounds both of the nonmetals must have prefixes assigned to represent the number of atoms The second element has a prefix and has the ending changed to -ide ...
... Naming Covalent Compounds For covalent compounds both of the nonmetals must have prefixes assigned to represent the number of atoms The second element has a prefix and has the ending changed to -ide ...
Thermochimica Acta Thermodynamics of hydrogen bonding and van
... [1,2], wood [3,4], organic polymers [5], but to name a few. Their wide range in polarity allows them to be fully miscible with polar substances (water, amides, alcohols, etc.) [6–8], as well as able to dissolve non-polar compounds (aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons) [9]. This fact makes them usefu ...
... [1,2], wood [3,4], organic polymers [5], but to name a few. Their wide range in polarity allows them to be fully miscible with polar substances (water, amides, alcohols, etc.) [6–8], as well as able to dissolve non-polar compounds (aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons) [9]. This fact makes them usefu ...
synoptic - chemnotes.org.uk
... A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons Covalent bonds hold atoms together because both nuclei are attracted to the shared pair of electrons The strength of the bond depends on the strength of attraction between the nuclei and the shared pair Down a group attraction for the shared pair will de ...
... A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons Covalent bonds hold atoms together because both nuclei are attracted to the shared pair of electrons The strength of the bond depends on the strength of attraction between the nuclei and the shared pair Down a group attraction for the shared pair will de ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.