Chemical Reactions
... Numbers and letters • The letters are the chemical symbols – N for nitrogen, C for carbon, etc. They always start with a CAPITAL letter. • If there is a capital next to another capital, it is two different elements. – NaOH is sodium, oxygen and hydrogen – KCl is Potassium and chlorine ...
... Numbers and letters • The letters are the chemical symbols – N for nitrogen, C for carbon, etc. They always start with a CAPITAL letter. • If there is a capital next to another capital, it is two different elements. – NaOH is sodium, oxygen and hydrogen – KCl is Potassium and chlorine ...
doc 3.5.1 photosynthesis revision Student notes for section
... These are converted into ………………………… …………………………… using the energy from ATP and using the hydrogen from reduced NADP. Most of this ………………………. ……………………………… is used to regenerate ……………………………………, but some is used to produce 6-carbon sugars from which complex carbohydrates, amino acids and other substance ...
... These are converted into ………………………… …………………………… using the energy from ATP and using the hydrogen from reduced NADP. Most of this ………………………. ……………………………… is used to regenerate ……………………………………, but some is used to produce 6-carbon sugars from which complex carbohydrates, amino acids and other substance ...
Photosynthesis in Bacteria By Emmy Muscan
... -light reactions- light energy absorbed & converted to chemical energy (ATP, NADPH) -dark reactions-carbohydrates made from CO2 using energy stored in ATP & NADPH ...
... -light reactions- light energy absorbed & converted to chemical energy (ATP, NADPH) -dark reactions-carbohydrates made from CO2 using energy stored in ATP & NADPH ...
Biology Fall Semester Test 1 Study Guide
... All living things are ________________, meaning they can’t survive on their own. The study of living things is called: A series of changes an organism undergoes in reaching its final adult form is called: Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are responsible for recycling which two nutrients? A we ...
... All living things are ________________, meaning they can’t survive on their own. The study of living things is called: A series of changes an organism undergoes in reaching its final adult form is called: Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are responsible for recycling which two nutrients? A we ...
7th Grade
... surroundings. This is an endothermic reaction. The temperature of the solution falls to about 35 F for 10 to 15 minutes. ...
... surroundings. This is an endothermic reaction. The temperature of the solution falls to about 35 F for 10 to 15 minutes. ...
1 Types of Chemical Reactions
... Sudden dramatic changes in temperature occur. A new solid suddenly appears. ...
... Sudden dramatic changes in temperature occur. A new solid suddenly appears. ...
biol 1406 chapter 3: water
... Determine if the statement is true. If it is not, rewrite the italicized part to make it true. 1. An element is a substance that can be broken down into simpler substances. ______________________ 2. On Earth, 90 elements occur naturally. ________________________________________ 3. Only four elements ...
... Determine if the statement is true. If it is not, rewrite the italicized part to make it true. 1. An element is a substance that can be broken down into simpler substances. ______________________ 2. On Earth, 90 elements occur naturally. ________________________________________ 3. Only four elements ...
Standard B-2
... Enzymatic proteins accelerate the speed of chemical reactions such as digestive enzymes Carbohydrates: sugars and starches; composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; main source of energy for the cell and used to store energy for short periods of time; caloric value of carbs depend on the number o ...
... Enzymatic proteins accelerate the speed of chemical reactions such as digestive enzymes Carbohydrates: sugars and starches; composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; main source of energy for the cell and used to store energy for short periods of time; caloric value of carbs depend on the number o ...
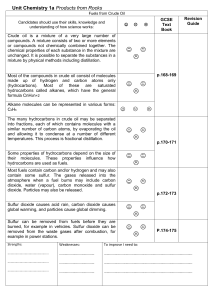
Unit_Chemistry_1a_Oil
... into fractions, each of which contains molecules with a similar number of carbon atoms, by evaporating the oil and allowing it to condense at a number of different temperatures. This process is fractional distillation. Some properties of hydrocarbons depend on the size of their molecules. These prop ...
... into fractions, each of which contains molecules with a similar number of carbon atoms, by evaporating the oil and allowing it to condense at a number of different temperatures. This process is fractional distillation. Some properties of hydrocarbons depend on the size of their molecules. These prop ...
Practical, Asymmetric Redox-Neutral Chemical Synthesis via Borrowing Hydrogen
... interest, but rather on how to prepare them in a highly efficient and economical manner. The concept of “redox economy” which focuses on minimizing synthetic steps that only adjust the oxidation state of the intermediates without generating structural complexity is an important consideration at the ...
... interest, but rather on how to prepare them in a highly efficient and economical manner. The concept of “redox economy” which focuses on minimizing synthetic steps that only adjust the oxidation state of the intermediates without generating structural complexity is an important consideration at the ...
NOTES - Ch. 8 - Photosynthesis
... Even though ATP is very efficient at transferring energy, it is not very good for storing large amounts of energy over the long term. In fact, a single molecule of the sugar glucose stores more than 90 times the chemical energy of a molecule of ATP. Therefore, it is more efficient for cells to keep ...
... Even though ATP is very efficient at transferring energy, it is not very good for storing large amounts of energy over the long term. In fact, a single molecule of the sugar glucose stores more than 90 times the chemical energy of a molecule of ATP. Therefore, it is more efficient for cells to keep ...
Modeling Photosynthesis: The Fruit-Loop Lab
... Modeling Photosynthesis: The Fruit-Loop Lab You may be familiar with the law of physics that states that matter and energy cannot be created or destroyed – they merely change from one form to another. This law also applies to the process of photosynthesis. You have learned that plants are called pro ...
... Modeling Photosynthesis: The Fruit-Loop Lab You may be familiar with the law of physics that states that matter and energy cannot be created or destroyed – they merely change from one form to another. This law also applies to the process of photosynthesis. You have learned that plants are called pro ...
BIOLOGY 1 TEST REVIEW SHEET
... 10. What is a photosystem? How many photosystems does a thylakoid have? Molecule that contains chlorophyll that absorb light; there are 2 of them and light actually strikes Photosystem II first, then strikes Photosystem I 11. Stage 1 of photosynthesis is called the __________light dependent_________ ...
... 10. What is a photosystem? How many photosystems does a thylakoid have? Molecule that contains chlorophyll that absorb light; there are 2 of them and light actually strikes Photosystem II first, then strikes Photosystem I 11. Stage 1 of photosynthesis is called the __________light dependent_________ ...
File - Milton High School Science
... Photosynthesis: Calvin cycle • CO2 gas fixed into sugars already there • ATP and NADPH spent to convert into other sugars • Some sugar can leave the cycle, others stay to fix more CO2 ...
... Photosynthesis: Calvin cycle • CO2 gas fixed into sugars already there • ATP and NADPH spent to convert into other sugars • Some sugar can leave the cycle, others stay to fix more CO2 ...
Document
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
•What makes up an atom? Draw an atom
... the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
... the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
4.4 Tissues Working Together
... 4.4 Tissues Working Together The leaves of most plants are highly specialized structures with one primary function, what is it? ...
... 4.4 Tissues Working Together The leaves of most plants are highly specialized structures with one primary function, what is it? ...
PowerPoint Overview for Introduction
... whereas those appearing only at the level of parts per million or less are referred to as micronutrients. These nutrients perform various functions, including the building of bones and cell structures, regulating the body's pH, carrying charge, and driving chemical reactions. ...
... whereas those appearing only at the level of parts per million or less are referred to as micronutrients. These nutrients perform various functions, including the building of bones and cell structures, regulating the body's pH, carrying charge, and driving chemical reactions. ...
Chapter 3
... hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Nothing is created nothing is destroyed All stable ecosystems recycle matter and get energy from the sun ...
... hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Nothing is created nothing is destroyed All stable ecosystems recycle matter and get energy from the sun ...
Photosynthesis
... contains the chlorophyll…and other pigments capable of absorbing solar energy. • The ________ contains an energy-rich solution where CO2 is first attached to an organic compound…then reduced to a carbohydrate. ...
... contains the chlorophyll…and other pigments capable of absorbing solar energy. • The ________ contains an energy-rich solution where CO2 is first attached to an organic compound…then reduced to a carbohydrate. ...
Intro Biochemistry/Ecology
... A water molecule is polar, because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. Acidic solutions contain higher concentrations of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values below 7. Basic, or alkaline, solutions contain lower concentrations of H+ ions than pure ...
... A water molecule is polar, because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. Acidic solutions contain higher concentrations of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values below 7. Basic, or alkaline, solutions contain lower concentrations of H+ ions than pure ...
Exam practice answers 5
... Therefore, more energy is available for photosynthesis. (d) They contain a number of different pigments, particularly those that can absorb the wavelengths of light that penetrates to greater depth in the water — that is blue light. Red pigments absorb blue light. A range of pigments including red a ...
... Therefore, more energy is available for photosynthesis. (d) They contain a number of different pigments, particularly those that can absorb the wavelengths of light that penetrates to greater depth in the water — that is blue light. Red pigments absorb blue light. A range of pigments including red a ...
3.8 – Photosynthesis
... 3.8.6 - State that ATP and hydrogen (derived from the photolysis of water) are used to fix carbon dioxide to make organic molecules Once the water molecules have undergone photolysis, their electrons combine with carbon dioxide to form organic compounds. This process is called fixing CO2. The energ ...
... 3.8.6 - State that ATP and hydrogen (derived from the photolysis of water) are used to fix carbon dioxide to make organic molecules Once the water molecules have undergone photolysis, their electrons combine with carbon dioxide to form organic compounds. This process is called fixing CO2. The energ ...
Artificial photosynthesis

Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that replicates the natural process of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into Hydrogen Ions and oxygen, and is a main research area in artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another studied process, replicating natural carbon fixation.Research developed in this field encompasses design and assembly of devices (and their components) for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Many, if not most, of the artificial approaches are bio-inspired, i.e., they rely on biomimetics.