04_HMDs
... concentric series of simple lens sections so that a thin lens with a short focal length and large diameter is possible More even resolution distribution Less distortion ...
... concentric series of simple lens sections so that a thin lens with a short focal length and large diameter is possible More even resolution distribution Less distortion ...
Guided Discovery and Lesson Notes on Mirrors and Applications
... 3. Point C is the center of curvature of the mirror (all points on the surface of the mirror are a distance r from this point). 4. The point F is the focal point of the mirror. Any ray traveling close to & parallel to the principal axis will be reflected through F. F is mid-way between C & A. 5. The ...
... 3. Point C is the center of curvature of the mirror (all points on the surface of the mirror are a distance r from this point). 4. The point F is the focal point of the mirror. Any ray traveling close to & parallel to the principal axis will be reflected through F. F is mid-way between C & A. 5. The ...
PH 481
... Experiment VIII.1: Birefringence and Optical Isolation In this experiment the birefringence of a material will be used to change the polarization of the laser beam. You will use a quarter-wave plate and a polarizer to build an optical isolator. This is a useful device that ensures that light is not ...
... Experiment VIII.1: Birefringence and Optical Isolation In this experiment the birefringence of a material will be used to change the polarization of the laser beam. You will use a quarter-wave plate and a polarizer to build an optical isolator. This is a useful device that ensures that light is not ...
Light book student use
... You need: A small toy motor A paper disk the size of a CD 9V battery and wires ...
... You need: A small toy motor A paper disk the size of a CD 9V battery and wires ...
2004 - thephysicsteacher.ie
... Optical fibres are made of very transparent glass or plastic. The fibres contain at least two layers. Guiding light in an optical fibre depends on how light travels through different media. Light waves are bent, or refracted, as they pass between materials of different refractive index. The amount o ...
... Optical fibres are made of very transparent glass or plastic. The fibres contain at least two layers. Guiding light in an optical fibre depends on how light travels through different media. Light waves are bent, or refracted, as they pass between materials of different refractive index. The amount o ...
Review ! a
... and part of the wave is reflected ! The transmitted light passes through the film completely ! The reflected light has no phase shift because n > nair and travels back to the front surface of the film Physics for Scientists&Engineers 2 ...
... and part of the wave is reflected ! The transmitted light passes through the film completely ! The reflected light has no phase shift because n > nair and travels back to the front surface of the film Physics for Scientists&Engineers 2 ...
Click To
... Background: A high-average-power solid-state laser is typically pumped by injecting light from high-power two-dimensional semiconductor laser arrays. The laser arrays are frequently fitted with lenses that separately collimate the output of the bars so that the pump light is collimated well enough f ...
... Background: A high-average-power solid-state laser is typically pumped by injecting light from high-power two-dimensional semiconductor laser arrays. The laser arrays are frequently fitted with lenses that separately collimate the output of the bars so that the pump light is collimated well enough f ...
10.2 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
... occurs at 4,400 cm-1. Although this transition is not infrared active (it is Raman active), ~4,000 cm-1 is usually taken to be the upper limit of the infrared. The lower limit is determined by instrumental considerations and is often near 50 cm-1. The mid infrared extends from 4,000 to 200 cm-1. Thi ...
... occurs at 4,400 cm-1. Although this transition is not infrared active (it is Raman active), ~4,000 cm-1 is usually taken to be the upper limit of the infrared. The lower limit is determined by instrumental considerations and is often near 50 cm-1. The mid infrared extends from 4,000 to 200 cm-1. Thi ...
Microbiology
... The electron microscope is capable of magnifying biological specimens up to one million times. These computer enhanced images of 1. smallpox, 2. herpes simplex, and 3. mumps are magnified, respectively, 150,000, 150,000 and 90,000 times. ...
... The electron microscope is capable of magnifying biological specimens up to one million times. These computer enhanced images of 1. smallpox, 2. herpes simplex, and 3. mumps are magnified, respectively, 150,000, 150,000 and 90,000 times. ...
Film Screen Q & A
... RAPHEX General Question 2003 D25: A radiograph with an optical density (OD) of 3.0. A. Transmits 1/3 times as much light as a film with an OD of 1.0. B. Has a combined OD of 6.0 when placed over another film of OD 2.0. C. Looks “light gray” on a standard view box. D. Transmits 0.1% of the light inc ...
... RAPHEX General Question 2003 D25: A radiograph with an optical density (OD) of 3.0. A. Transmits 1/3 times as much light as a film with an OD of 1.0. B. Has a combined OD of 6.0 when placed over another film of OD 2.0. C. Looks “light gray” on a standard view box. D. Transmits 0.1% of the light inc ...
Resolution and Sampling Considerations
... These defects result in a loss of image quality in the projected image onto the sensor. Many of these defects can be “corrected” by design and materials, and some can also be eliminated by postprocessing of the digital image. ...
... These defects result in a loss of image quality in the projected image onto the sensor. Many of these defects can be “corrected” by design and materials, and some can also be eliminated by postprocessing of the digital image. ...
Photoelectron imaging of modal interference in
... As nano-optical devices promise a large variety of applications and interesting questions for fundamental research, the investigation of plasmonic excitations in nanostructures has evolved into a very active research field. Plasmonic whispering gallery mode (WGM) cavities are highly interesting for ...
... As nano-optical devices promise a large variety of applications and interesting questions for fundamental research, the investigation of plasmonic excitations in nanostructures has evolved into a very active research field. Plasmonic whispering gallery mode (WGM) cavities are highly interesting for ...
Mirrors and Lenses
... The image in a plane mirror appears to be behind the mirror. The rays of light diverge at the location of the image. When the rays diverge, the image is called a virtual image. ...
... The image in a plane mirror appears to be behind the mirror. The rays of light diverge at the location of the image. When the rays diverge, the image is called a virtual image. ...
6th grade reflection lab final
... 1. Turn the lights off in the classroom. Take each of the 10 filters and the microscope slide from the filter envelope. Hold each filter separately between a flashlight and another white sheet of paper. Decide if the filters are transparent (nearly all light passes through easily onto the white pape ...
... 1. Turn the lights off in the classroom. Take each of the 10 filters and the microscope slide from the filter envelope. Hold each filter separately between a flashlight and another white sheet of paper. Decide if the filters are transparent (nearly all light passes through easily onto the white pape ...
Ultrafast Optics: Tools and Techniques
... harnessed to produce to ultrashort pulses. The titanium in the sapphire is needed to create an energy level of the crystal that is quantum mechanically suitable to emit laser light when stimulated by the pump laser. The light emitted from the crystal is reflected back and forth between the mirrors i ...
... harnessed to produce to ultrashort pulses. The titanium in the sapphire is needed to create an energy level of the crystal that is quantum mechanically suitable to emit laser light when stimulated by the pump laser. The light emitted from the crystal is reflected back and forth between the mirrors i ...
Optical Instruments - Dr. Dr. Bill`s Page
... a lens and an erecting pentaprism. When the shutter is triggered the mirror flips out of the way and the shutter opens permitting light to go to the film. In most modern cameras, focusing is done with the aperture stop wide open to give maximum illuminance of the image on the focusing screen along w ...
... a lens and an erecting pentaprism. When the shutter is triggered the mirror flips out of the way and the shutter opens permitting light to go to the film. In most modern cameras, focusing is done with the aperture stop wide open to give maximum illuminance of the image on the focusing screen along w ...
The Fresnel Biprism
... that enters the biprism does so at a more acute angle than when the biprism is closer. This produces a more tightly packed interference pattern and as a result, there are more fringes spaced closer together. There was some potential error in setting up the system in that the rib of the prism was mea ...
... that enters the biprism does so at a more acute angle than when the biprism is closer. This produces a more tightly packed interference pattern and as a result, there are more fringes spaced closer together. There was some potential error in setting up the system in that the rib of the prism was mea ...
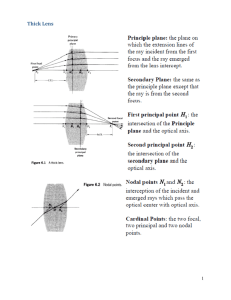
Thick Lens 1
... All modern astronomical telescopes have this basic configuration because it is much more practical to fabricate large mirrors than lenses. The size of the large main mirror (the entrance pupil) sets the diffraction limit. Also, a larger entrance pupil gathers more light, so that faint objects can be ...
... All modern astronomical telescopes have this basic configuration because it is much more practical to fabricate large mirrors than lenses. The size of the large main mirror (the entrance pupil) sets the diffraction limit. Also, a larger entrance pupil gathers more light, so that faint objects can be ...
Optics Ic
... objective, that is, the objective will be focusing on an image made by a lens system, as shown in the sketches above. For this test of lenses, you will use 4 different lens arrangements, all with nominal 50 mm distance from the object to the first lens, and 50 mm from the last lens to the microscope ...
... objective, that is, the objective will be focusing on an image made by a lens system, as shown in the sketches above. For this test of lenses, you will use 4 different lens arrangements, all with nominal 50 mm distance from the object to the first lens, and 50 mm from the last lens to the microscope ...
Limits of Resolution: The Rayleigh Criterion
... Draw two lines on a white sheet of paper (several mm apart). How far away can you be and still distinguish the two lines? What does this tell you about the size of the eye's pupil? Can you be quantitative? (The size of an adult's pupil is discussed in Physics of the Eye .) Just what is the limit? To ...
... Draw two lines on a white sheet of paper (several mm apart). How far away can you be and still distinguish the two lines? What does this tell you about the size of the eye's pupil? Can you be quantitative? (The size of an adult's pupil is discussed in Physics of the Eye .) Just what is the limit? To ...
Fibre Optics - Westmount High School
... index of refraction (n2), it bends or refracts away from an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface (normal line). As the angle of the beam through n1 becomes greater with respect to the normal line, the refracted light through n2 bends further away from the line. ...
... index of refraction (n2), it bends or refracts away from an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface (normal line). As the angle of the beam through n1 becomes greater with respect to the normal line, the refracted light through n2 bends further away from the line. ...
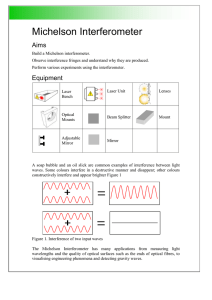
Michelson Interferometer - Research School of Physics and
... The circular pattern occurs when the mirrors are perfectly aligned. As the light comes from a small source the rays travel out at an angle, so travel slightly different distances to and from the mirrors. The interferometer can be used to measure optical surfaces or structures. Keep the circular frin ...
... The circular pattern occurs when the mirrors are perfectly aligned. As the light comes from a small source the rays travel out at an angle, so travel slightly different distances to and from the mirrors. The interferometer can be used to measure optical surfaces or structures. Keep the circular frin ...
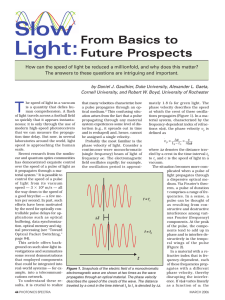
Slow Light - Duke Physics
... Figure 2. Sinusoidal component waves interfere to create a pulse of light. atoms with a strong absorption resonance is an interesting candidate. The refractive index for such a sample is typically small (n21 ≈ 1023), but it varies rapidly in the region of the resonance so that dn/dω and, hence, ng c ...
... Figure 2. Sinusoidal component waves interfere to create a pulse of light. atoms with a strong absorption resonance is an interesting candidate. The refractive index for such a sample is typically small (n21 ≈ 1023), but it varies rapidly in the region of the resonance so that dn/dω and, hence, ng c ...
Coherence and Combining Filters
... camera, and therefore exceptional blocking by emission filters is critical ...
... camera, and therefore exceptional blocking by emission filters is critical ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.