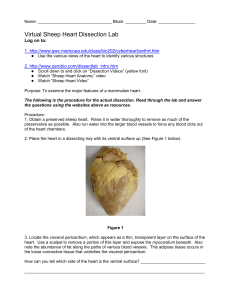
Virtual Sheep Heart Dissection Lab Student Worksheet
... 4. The line running diagonally down from the right side (facing you) of the heart to the bottom left side is the coronary artery. The coronary artery supplies blood to the heart muscle tissue. The pointed bottom of the heart is called the apex. What do you think is the purpose of the coronary artery ...
... 4. The line running diagonally down from the right side (facing you) of the heart to the bottom left side is the coronary artery. The coronary artery supplies blood to the heart muscle tissue. The pointed bottom of the heart is called the apex. What do you think is the purpose of the coronary artery ...
Cardiovascular disease in Pregnancy
... Physiologic change in Pregnancy • Cardiac output increases 30-35% during pregnancy • HR rises steadily throughout pregnancy • Although elevated in pregnancy, SV ...
... Physiologic change in Pregnancy • Cardiac output increases 30-35% during pregnancy • HR rises steadily throughout pregnancy • Although elevated in pregnancy, SV ...
The clinical challenge of concomitant aortic and mitral valve stenosis
... concomitant MS. Rapid relief of the mitral obstacle following balloon dilatation or surgery will abruptly increase preload which may eventually lead to acute left ventricular failure and “flash” pulmonary oedema. Left ventricular abnormal relaxation resulting from AS can increase mitral E wave half- ...
... concomitant MS. Rapid relief of the mitral obstacle following balloon dilatation or surgery will abruptly increase preload which may eventually lead to acute left ventricular failure and “flash” pulmonary oedema. Left ventricular abnormal relaxation resulting from AS can increase mitral E wave half- ...
Heart sounds and murmurs
... essential during diastole. Therefore in aortic regurgitation blood backflow in the ventricles causing diastolic murmurs (after the 2nd heart sound). ...
... essential during diastole. Therefore in aortic regurgitation blood backflow in the ventricles causing diastolic murmurs (after the 2nd heart sound). ...
Sheep Heart Dissection Lab
... Can blood go backwards from the right ventricle to the right atrium? ___________________ 2. Find the superior vena cava on the back side of the heart. 3. Peek into the right atrium and notice the tricuspid valve (from the other side). Stick your finger into the superior vena cava and through the tri ...
... Can blood go backwards from the right ventricle to the right atrium? ___________________ 2. Find the superior vena cava on the back side of the heart. 3. Peek into the right atrium and notice the tricuspid valve (from the other side). Stick your finger into the superior vena cava and through the tri ...
Pulmonic Stenosis Explained - New
... pumped into the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps blood into the lungs, where it receives oxygen. It flows from the lungs into the left atrium; it is held here briefly before going into the left ventricle. The left ventricle contains the largest muscle of the heart so the blood can be pumpe ...
... pumped into the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps blood into the lungs, where it receives oxygen. It flows from the lungs into the left atrium; it is held here briefly before going into the left ventricle. The left ventricle contains the largest muscle of the heart so the blood can be pumpe ...
ANEURYSMS AND DISSECTIONS
... early recognition and treatment of syphilis Tertiary stage of syphilis can cause obliterative endarteritis of the involve small vessels in any part of the body, including the vasa vasorum of the aorta this results in ischemic medial injury, leading to aneurysmal dilation of the aorta and aortic annu ...
... early recognition and treatment of syphilis Tertiary stage of syphilis can cause obliterative endarteritis of the involve small vessels in any part of the body, including the vasa vasorum of the aorta this results in ischemic medial injury, leading to aneurysmal dilation of the aorta and aortic annu ...
AORTIC ANEURYSMS AND DISSECTION Aorta is about 1 inch or 2
... Pericardial Tamponade A. Patho/Causes a. Rate of fluid accumulation, not the amount i. 200 mL of fluid develops rapidly = tamponade ii. 2 L can accum slowly – heart can adapt and stretch b. Pericardial effusion that impairs diastolic filling of the heart c. Pressures of RV, LV, RA, LA, pulm art and ...
... Pericardial Tamponade A. Patho/Causes a. Rate of fluid accumulation, not the amount i. 200 mL of fluid develops rapidly = tamponade ii. 2 L can accum slowly – heart can adapt and stretch b. Pericardial effusion that impairs diastolic filling of the heart c. Pressures of RV, LV, RA, LA, pulm art and ...
Valvular Heart Disease
... Efforts should be made to preserve the posterior, and in some cases the anterior leaflets and chordae tendineae; studies have shown an advantage to left ventricular function with preservation. Operative mortality is 2-10%. Five year survival rate is 70-90%. ...
... Efforts should be made to preserve the posterior, and in some cases the anterior leaflets and chordae tendineae; studies have shown an advantage to left ventricular function with preservation. Operative mortality is 2-10%. Five year survival rate is 70-90%. ...
human anatomy and physiology name - H
... 4) Locate the anterior interventricular groove and locate the left coronary (4,6)artery within the groove. Using the next page as a guide, try to find the right coronary artery (3), the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery(5), and the coronary sinus(9). Fat may obscure these structures but ...
... 4) Locate the anterior interventricular groove and locate the left coronary (4,6)artery within the groove. Using the next page as a guide, try to find the right coronary artery (3), the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery(5), and the coronary sinus(9). Fat may obscure these structures but ...
Chapter 5: Blood and Circulation
... • The semi-lunar valves close. • The cycle starts again as the atria start filling with blood. ...
... • The semi-lunar valves close. • The cycle starts again as the atria start filling with blood. ...
Valvular heart disease
... of virtually all cases of mitral stenosis in adults, its natural course in the U.S. and Canada is now less virulent than it was in the early decades of this century; it is now milder and more delayed (5). It is not uncommon for symptoms of mitral stenosis to first present in middle age, and up to on ...
... of virtually all cases of mitral stenosis in adults, its natural course in the U.S. and Canada is now less virulent than it was in the early decades of this century; it is now milder and more delayed (5). It is not uncommon for symptoms of mitral stenosis to first present in middle age, and up to on ...
Measuring Blood Pressure
... Force exerted against walls of a blood vessel when the heart contracts (systole) ...
... Force exerted against walls of a blood vessel when the heart contracts (systole) ...
Muscularisation of the chordae tendineae: an
... by delamination of the primitive endocardium (3). Transesophageal echocardiography, which provides detailed information both for the mitral valve anatomy and the papillary muscles, is a useful laboratory tool regarding with the diagnosis of muscularisation of the chordae tendineae. All examination p ...
... by delamination of the primitive endocardium (3). Transesophageal echocardiography, which provides detailed information both for the mitral valve anatomy and the papillary muscles, is a useful laboratory tool regarding with the diagnosis of muscularisation of the chordae tendineae. All examination p ...
Bicuspid Aortic Valve Disease Beyond the Aortic Root
... From the Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, Connecticut. ...
... From the Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, Connecticut. ...
Structure of the Heart
... The average (normal) blood pressure for an adult is 120/80. This number varies by person and it is best if you know what is normal for you, so that you (or your doctor) recognize when something is not. We will be doing a lab where you will learn to use a this device and check your own blood pressur ...
... The average (normal) blood pressure for an adult is 120/80. This number varies by person and it is best if you know what is normal for you, so that you (or your doctor) recognize when something is not. We will be doing a lab where you will learn to use a this device and check your own blood pressur ...
Valvular heart diseases Acute rheumatic fever Infective endocarditis
... • Clinical features – Concentric left ventricular (pressure overload) hypertrophy – The hypertrophied myocardium tends to be ischemic – Angina pectoris – Cardiac decompensation and heart failure – Systolic ejection murmur ...
... • Clinical features – Concentric left ventricular (pressure overload) hypertrophy – The hypertrophied myocardium tends to be ischemic – Angina pectoris – Cardiac decompensation and heart failure – Systolic ejection murmur ...
Tetralogy of Fallot
... Free breathing coronary MRA for retrosternal anatomy. Note the rotated aortic root, typical in TOF, and RCA coursing immediately behind the sternotomy wire. ...
... Free breathing coronary MRA for retrosternal anatomy. Note the rotated aortic root, typical in TOF, and RCA coursing immediately behind the sternotomy wire. ...
Bottle feeding
... between a wide range of abnormal heart sounds -- split sounds, ejection sounds, gallop rhythms, and clicks, for example. He or she also must differentiate between abnormal lung and heart sounds, and listen to see if timing of abnormal sound is correlated with respiration or heartbeat. The location a ...
... between a wide range of abnormal heart sounds -- split sounds, ejection sounds, gallop rhythms, and clicks, for example. He or she also must differentiate between abnormal lung and heart sounds, and listen to see if timing of abnormal sound is correlated with respiration or heartbeat. The location a ...
Influence of prosthetic mitral valve orientation on left ventricular flow
... The valves of the heart direct the blood pumped by the cardiac muscle from venous to arterial side. Due to pathological changes, the function of a valve may be compromised to the extent that it needs to be replaced. In many cases a mechanical prosthesis will be chosen due to its high Figure 1: Prosd ...
... The valves of the heart direct the blood pumped by the cardiac muscle from venous to arterial side. Due to pathological changes, the function of a valve may be compromised to the extent that it needs to be replaced. In many cases a mechanical prosthesis will be chosen due to its high Figure 1: Prosd ...
Cardiac Surgery: Aortic Aneurysms
... An aneurysm occurs when the wall of the aorta weakens. The pressure of the blood flowing through the vessel creates a bulge at the weak spot. This is similar to the way an overinflated inner tube can cause a bulge in a tire. The bulge usually starts small. Over time, as the pressure continues, it ca ...
... An aneurysm occurs when the wall of the aorta weakens. The pressure of the blood flowing through the vessel creates a bulge at the weak spot. This is similar to the way an overinflated inner tube can cause a bulge in a tire. The bulge usually starts small. Over time, as the pressure continues, it ca ...
first heart sound - Easymed.club
... Transmitted throughout the superior thoracic aorta and even into the large arteries of the neck ...
... Transmitted throughout the superior thoracic aorta and even into the large arteries of the neck ...
Congenital Diseases
... Hypoplastic left ventricle1-3 Hypoplastic right ventricle1-3 Truncus arteriosus1-2 Total anomalous pulmonary venous return1-2 ...
... Hypoplastic left ventricle1-3 Hypoplastic right ventricle1-3 Truncus arteriosus1-2 Total anomalous pulmonary venous return1-2 ...
Aortic stenosis

Aortic stenosis (AS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occurs due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercise. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially with lying down, at night, and with exercise as well as swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis.Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve and rheumatic fever. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population while rheumatic heart disease mostly occurring in the developing world. A normal valve, however, may also harden over the decades. Risk factors are similar to those of coronary artery disease and include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and being male. The aortic valve usually has three leaflets and is located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta. AS typically results in a heart murmur. Its severity can be divided into mild, moderate, severe, and very severe based on ultrasound of the heart findings.Aortic stenosis is typically followed using repeated ultrasounds. Once it has become severe treatment primarily involves valve replacement surgery with transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) being an option in some who are at high risk from surgery. Valves may either be mechanical or bioprosthetic with each having risks and benefits. Another less invasive procedure, balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) may result in benefit but this is for only for a few months. Complications like heart failure may be treated as per normal in those with mild to moderate AS. In those with severe disease a number of medications should be avoided including ACE inhibitors, nitroglycerin, and some beta blockers. Nitroprusside or phenylephrine may be used in those with decompensated heart failure depending on the blood pressure.Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease in the developed world. It affects about 2% of people who are over 65 years of age. Estimated rates are not known in most of the developing world as of 2014. In those who have symptoms, without repair, the chance of death at five years is about 50% and at 10 years is about 90%. Aortic stenosis was first described by French physician Lazare Rivière in 1663.























