Echocardiographic left ventricular dimensions
... pressure in I5 normal subjects, in I5 patients with left ventricular volume or pressure overload without aortic stenosis, and in 23 patients with aortic stenosis. All these patients had a mean rate of circumferential fibre shortening greater than I.O circumference per second and were regarded as hav ...
... pressure in I5 normal subjects, in I5 patients with left ventricular volume or pressure overload without aortic stenosis, and in 23 patients with aortic stenosis. All these patients had a mean rate of circumferential fibre shortening greater than I.O circumference per second and were regarded as hav ...
Chambers and Great Vessels of the Heart
... corresponding atrium. The left atrium pumps oxygen-rich blood to the left ventricle during diastole. The left ventricle then pumps the blood into the aorta, which then transports it via its branches to the systemic circulation. The right atrium pumps oxygen-poor blood into the right ventricle, which ...
... corresponding atrium. The left atrium pumps oxygen-rich blood to the left ventricle during diastole. The left ventricle then pumps the blood into the aorta, which then transports it via its branches to the systemic circulation. The right atrium pumps oxygen-poor blood into the right ventricle, which ...
17- interior of heart
... Impulses from the sinuatrial node have been shown to travel to the atrioventricular node more rapidly than they can travel by passing along the ordinary myocardium. The anterior internodal pathway leaves the anterior end of the sinuatrial node and passes anterior to the SVC opening. It descends on t ...
... Impulses from the sinuatrial node have been shown to travel to the atrioventricular node more rapidly than they can travel by passing along the ordinary myocardium. The anterior internodal pathway leaves the anterior end of the sinuatrial node and passes anterior to the SVC opening. It descends on t ...
the usefulness of the tdi tei index in left ventricular functional
... Objectives: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of a dialysis session diastolic function of the left ventricle using conventional sonographic markers (pulsed and tissue Doppler) and in particular the use of TDI TEI index in adults with end-stage renal disease. Background: 16 adults w ...
... Objectives: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of a dialysis session diastolic function of the left ventricle using conventional sonographic markers (pulsed and tissue Doppler) and in particular the use of TDI TEI index in adults with end-stage renal disease. Background: 16 adults w ...
Cardiac disorders of the newborn
... - two leaflets of the tricuspid valve are displaced downward into the pumping chamber - These abnormalities cause the tricuspid valve to leak blood back into the right atrium. As a result, the right atrium becomes enlarged. - If the leak is severe enough, it can lead to congestive heart failure - Th ...
... - two leaflets of the tricuspid valve are displaced downward into the pumping chamber - These abnormalities cause the tricuspid valve to leak blood back into the right atrium. As a result, the right atrium becomes enlarged. - If the leak is severe enough, it can lead to congestive heart failure - Th ...
with 1
... It is performed in patients with cyanotic lesions. They are defined as those operations which serve to either increase or decrease pulmonary blood flow while allowing a mixed circulation and cyanosis to persist. ...
... It is performed in patients with cyanotic lesions. They are defined as those operations which serve to either increase or decrease pulmonary blood flow while allowing a mixed circulation and cyanosis to persist. ...
Calculation Of Stenotic Valve Orifice Area
... aortic pressure of 120 mm Hg. Such a major increase in LV pressure obviously increases myocardial oxygen demand and limits ejection performance. These factors contribute to the symptoms of angina and congestive heart failure, respectively (6) , (7) . The limitations in cardiac output imposed by high ...
... aortic pressure of 120 mm Hg. Such a major increase in LV pressure obviously increases myocardial oxygen demand and limits ejection performance. These factors contribute to the symptoms of angina and congestive heart failure, respectively (6) , (7) . The limitations in cardiac output imposed by high ...
CV Exercises - Seattle Central College
... 1. What is the stroke volume if cardiac output is 10,000 ml/min (10 L/min) and heart rate is 50 beats per min (bpm)? Cardiac output = heart rate ...
... 1. What is the stroke volume if cardiac output is 10,000 ml/min (10 L/min) and heart rate is 50 beats per min (bpm)? Cardiac output = heart rate ...
aneurysms
... wall, and a dense surrounding rim of lymphocytes and plasma cells that may extend into the media With destruction of the media, the aorta loses its elastic recoil and may become dilated, producing an aneurysm. valvular insufficiency and massive volume overload lead to hypertrophy of the left ventric ...
... wall, and a dense surrounding rim of lymphocytes and plasma cells that may extend into the media With destruction of the media, the aorta loses its elastic recoil and may become dilated, producing an aneurysm. valvular insufficiency and massive volume overload lead to hypertrophy of the left ventric ...
Aortic stiffness as a predictor of coronary atherosclerosis
... patients than was previously possible. Assessment of arterial stiffness is of special interest for coronary heart disease because, when large artery distensibility is reduced, there is: (i) an increase in systolic blood pressure, arterial impedance and left ventricular load; (ii) a reduction in dias ...
... patients than was previously possible. Assessment of arterial stiffness is of special interest for coronary heart disease because, when large artery distensibility is reduced, there is: (i) an increase in systolic blood pressure, arterial impedance and left ventricular load; (ii) a reduction in dias ...
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Lange-pp. 362
... patients older thatn 60 Presenting signs and symptoms: Majority of patients are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms Dyspnea, angina, presyncope or syncope with symptoms worse with exertion. ...
... patients older thatn 60 Presenting signs and symptoms: Majority of patients are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms Dyspnea, angina, presyncope or syncope with symptoms worse with exertion. ...
The surgeon`s role in transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI)
... into a routine procedure for elderly high-risk patients with severe aortic stenosis in specialised centres. It can be performed via a transfemoral or a transapical approach. Both approaches are truly minimally invasive and avoid the use of cardio-pulmonary bypass and cardioplegic arrest. TAVI is ass ...
... into a routine procedure for elderly high-risk patients with severe aortic stenosis in specialised centres. It can be performed via a transfemoral or a transapical approach. Both approaches are truly minimally invasive and avoid the use of cardio-pulmonary bypass and cardioplegic arrest. TAVI is ass ...
An Electronic Stethoscope with Diagnosis Capability
... fully, leading to abnormally high pressure in the left ventricle. The time-frequency signature for AS, shown in Fig. 4a, exhibits a crescendo-decrescendo in magnitude at relatively uniform frequency across the systolic phase. In mitral regurgitation (MR), the mitral valve does not completely close d ...
... fully, leading to abnormally high pressure in the left ventricle. The time-frequency signature for AS, shown in Fig. 4a, exhibits a crescendo-decrescendo in magnitude at relatively uniform frequency across the systolic phase. In mitral regurgitation (MR), the mitral valve does not completely close d ...
Prosthesis-Patient Mismatch in Individuals Undergoing Aortic Valve
... Conclusions: The patients profile is similar to that described in the literature, the incidence of PPM is high, varying greatly between the prosthesis models. There was no difference in the reduction of postoperative gradients between the groups with or without PPM. Keywords: Aortic valve stenosis; ...
... Conclusions: The patients profile is similar to that described in the literature, the incidence of PPM is high, varying greatly between the prosthesis models. There was no difference in the reduction of postoperative gradients between the groups with or without PPM. Keywords: Aortic valve stenosis; ...
THE HEART
... – Get both LA LV and retrograde flow (LV to LA) • Blood simultaneously to aorta and back to LA • both LV and LA pump harder (move same blood twice) • LV hypertrophy and dilation as compensation • Compensation works awhile, then decr’d C.O. • heart failure ...
... – Get both LA LV and retrograde flow (LV to LA) • Blood simultaneously to aorta and back to LA • both LV and LA pump harder (move same blood twice) • LV hypertrophy and dilation as compensation • Compensation works awhile, then decr’d C.O. • heart failure ...
Simultaneous Coronary Artery Bypass and Carotid Endarterectomy
... indications for combined procedures intraoperative techniques for brain protection sequence of operation outcome of the surgical treatment. ...
... indications for combined procedures intraoperative techniques for brain protection sequence of operation outcome of the surgical treatment. ...
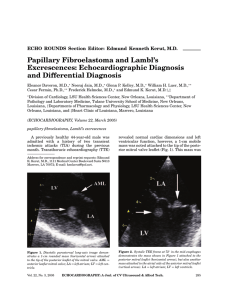
ECHO ROUNDS Section Editor: Edmund Kenneth Kerut
... 2. usually <1 cm in diameter, but may become 3–4 cm in size 3. the tumor usually arises from the midportion of valve leaflets (a fibrous strand usually arises from the line of closure) 4. often pedunculated (occasionally sessile) with high-frequency oscillations during the cardiac cycle 5. character ...
... 2. usually <1 cm in diameter, but may become 3–4 cm in size 3. the tumor usually arises from the midportion of valve leaflets (a fibrous strand usually arises from the line of closure) 4. often pedunculated (occasionally sessile) with high-frequency oscillations during the cardiac cycle 5. character ...
High implantation technique during CoreValve replacement in a
... a Medtronic CoreValve (MCV) is generally recommended. However, severe left ventricular hypertrophy and sigmoid septum are also risk factors for the development of conduction disturbances with the usage of MCV. The depth of implantation of MCV within the left ventricular outflow tract and larger or s ...
... a Medtronic CoreValve (MCV) is generally recommended. However, severe left ventricular hypertrophy and sigmoid septum are also risk factors for the development of conduction disturbances with the usage of MCV. The depth of implantation of MCV within the left ventricular outflow tract and larger or s ...
Hemodynamic Determinants of Prognosis of Aortic
... SUMMARY Fourteen patients with critical aortic stenosis (valve area 0.4 cm2/m2), a history of advanced congestive heart failure, left ventricular ejection fraction less than 0.45 (mean 0.28 d 0.03) and no other valvular lesions or obstructive coronary artery disease were studied to assess prognosis ...
... SUMMARY Fourteen patients with critical aortic stenosis (valve area 0.4 cm2/m2), a history of advanced congestive heart failure, left ventricular ejection fraction less than 0.45 (mean 0.28 d 0.03) and no other valvular lesions or obstructive coronary artery disease were studied to assess prognosis ...
Heart Failure
... costal cartilage 1 cm from the right sternal line (upper right side of heart) -4. The lower border of the second left costal cartilage 2.5 cm from the left lateral sternal line (upper left side of heart) ...
... costal cartilage 1 cm from the right sternal line (upper right side of heart) -4. The lower border of the second left costal cartilage 2.5 cm from the left lateral sternal line (upper left side of heart) ...
How should I treat a perimembranous
... PRESENTATION OF THE CASE A 73-year-old man was admitted to our Institute for repeated episodes of congestive heart failure. His past medical history included arterial hypertension, dyslipidaemia, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, prior episodes of lower intestinal bleeding, and recurrent ...
... PRESENTATION OF THE CASE A 73-year-old man was admitted to our Institute for repeated episodes of congestive heart failure. His past medical history included arterial hypertension, dyslipidaemia, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, prior episodes of lower intestinal bleeding, and recurrent ...
Right Atrium
... The heart is a muscular, hollow organ often called the “pump” of the body. The size of the heart is a little larger than the size of a fist. The heart is located between the lungs, behind the sternum and above the diaphragm. The heart are two separate pumps that continuously send blood throughout th ...
... The heart is a muscular, hollow organ often called the “pump” of the body. The size of the heart is a little larger than the size of a fist. The heart is located between the lungs, behind the sternum and above the diaphragm. The heart are two separate pumps that continuously send blood throughout th ...
HCM - cardiology zagazig university
... It has been identified in athletes, sexual differences, in relation to modifications in the heart's dimensions and left ventricular ...
... It has been identified in athletes, sexual differences, in relation to modifications in the heart's dimensions and left ventricular ...
Pulmonary semilunar valve
... • Artificial pacemaker needed if pace is too slow • Extra beats forming at other sites are called ectopic pacemakers – caffeine & nicotine increase activity ...
... • Artificial pacemaker needed if pace is too slow • Extra beats forming at other sites are called ectopic pacemakers – caffeine & nicotine increase activity ...
Sutureless aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic
... The valves require minimal sutures to remain in situ and reduce CPB and aortic crossclamp time as compared to traditional AVR, thus providing a treatment option for patients at a high operative risk. The results of studies included within this technology brief demonstrate low rates of adverse events ...
... The valves require minimal sutures to remain in situ and reduce CPB and aortic crossclamp time as compared to traditional AVR, thus providing a treatment option for patients at a high operative risk. The results of studies included within this technology brief demonstrate low rates of adverse events ...
Aortic stenosis

Aortic stenosis (AS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occurs due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercise. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially with lying down, at night, and with exercise as well as swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis.Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve and rheumatic fever. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population while rheumatic heart disease mostly occurring in the developing world. A normal valve, however, may also harden over the decades. Risk factors are similar to those of coronary artery disease and include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and being male. The aortic valve usually has three leaflets and is located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta. AS typically results in a heart murmur. Its severity can be divided into mild, moderate, severe, and very severe based on ultrasound of the heart findings.Aortic stenosis is typically followed using repeated ultrasounds. Once it has become severe treatment primarily involves valve replacement surgery with transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) being an option in some who are at high risk from surgery. Valves may either be mechanical or bioprosthetic with each having risks and benefits. Another less invasive procedure, balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) may result in benefit but this is for only for a few months. Complications like heart failure may be treated as per normal in those with mild to moderate AS. In those with severe disease a number of medications should be avoided including ACE inhibitors, nitroglycerin, and some beta blockers. Nitroprusside or phenylephrine may be used in those with decompensated heart failure depending on the blood pressure.Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease in the developed world. It affects about 2% of people who are over 65 years of age. Estimated rates are not known in most of the developing world as of 2014. In those who have symptoms, without repair, the chance of death at five years is about 50% and at 10 years is about 90%. Aortic stenosis was first described by French physician Lazare Rivière in 1663.