Basic Visual Processes
... photoreceptor array using laser interferometry •It is also possible to visualize the cone mosaic directly using various staining techniques or, in vivo, using adaptive optics •All of these measurements suggest ultimately that the receptor array is a very good optimized match for the eye’s optics. In ...
... photoreceptor array using laser interferometry •It is also possible to visualize the cone mosaic directly using various staining techniques or, in vivo, using adaptive optics •All of these measurements suggest ultimately that the receptor array is a very good optimized match for the eye’s optics. In ...
Paper Report on “Optical Computing: Need and Challenge”
... computational systems, how an optical switching circuit functions, and the challenges faced by optical computing in the current generation and how long before the advent of a prototype optical computer. The first point the authors make in their paper is the need for optics in computing. The reliabil ...
... computational systems, how an optical switching circuit functions, and the challenges faced by optical computing in the current generation and how long before the advent of a prototype optical computer. The first point the authors make in their paper is the need for optics in computing. The reliabil ...
Comparison of laser scanning methods
... Ref. Dholakia and Gabriel C. Spalding, 2004 SPIE course on Optical Tweeezers ...
... Ref. Dholakia and Gabriel C. Spalding, 2004 SPIE course on Optical Tweeezers ...
Advanced Capabilities of the Multimodal
... wavefront to dynamically compensate for those aberrations. AO research in the last few years has gradually shifted from instrument development to exploitation for a wide variety of clinical and vision research applications [9-12]. We have developed a multimodal retinal imager with significant functi ...
... wavefront to dynamically compensate for those aberrations. AO research in the last few years has gradually shifted from instrument development to exploitation for a wide variety of clinical and vision research applications [9-12]. We have developed a multimodal retinal imager with significant functi ...
PDF
... 2sbd shows a dramatic intensity degradation of the same-area F-CARS image at n p − ns = 2252 cm−1, away from the CN resonance. Image quality depends on the powers of pump and Stokes beams and on the signal integration time. Images could be acquired by raster sample scanning as fast as 500 000 pixels ...
... 2sbd shows a dramatic intensity degradation of the same-area F-CARS image at n p − ns = 2252 cm−1, away from the CN resonance. Image quality depends on the powers of pump and Stokes beams and on the signal integration time. Images could be acquired by raster sample scanning as fast as 500 000 pixels ...
Wavelength swept amplified spontaneous emission source
... http://www.opticsinfobase.org/oe/abstract.cfm?URI=oe-17-12-9947. 31. C. M. Eigenwillig, B. R. Biedermann, G. Palte, and R. Huber, “K-space linear Fourier domain mode locked laser and applications for optical coherence tomography,” Opt. Express 16(12), 8916–8937 (2008), http://www.opticsinfobase.org/ ...
... http://www.opticsinfobase.org/oe/abstract.cfm?URI=oe-17-12-9947. 31. C. M. Eigenwillig, B. R. Biedermann, G. Palte, and R. Huber, “K-space linear Fourier domain mode locked laser and applications for optical coherence tomography,” Opt. Express 16(12), 8916–8937 (2008), http://www.opticsinfobase.org/ ...
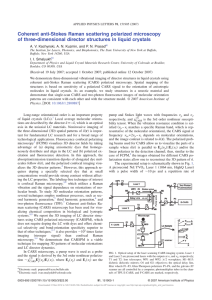
a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and
... Please use your drawing to illustrate how PMT and APD work and compare the mechanisms which enable them to achieve signal amplification. Also, explain why is it hard to make a detector that has high detectivity while also preserves a high detection speed? ...
... Please use your drawing to illustrate how PMT and APD work and compare the mechanisms which enable them to achieve signal amplification. Also, explain why is it hard to make a detector that has high detectivity while also preserves a high detection speed? ...
light microscopy
... intensities in the three-dimensional diffraction pattern, are calculated for incoherently illuminated (or emitting) point sources (i.e., NAcond NAobj ) . In general , the depth of focus increases, up to a factor of two, as the coherence of NAcond 0 illumination increases (i.e., as ...
... intensities in the three-dimensional diffraction pattern, are calculated for incoherently illuminated (or emitting) point sources (i.e., NAcond NAobj ) . In general , the depth of focus increases, up to a factor of two, as the coherence of NAcond 0 illumination increases (i.e., as ...
optical fiber communication - GTU e
... A semiconductor laser emits light through stimulated emission rather than spontaneous emission, which results in high output power (~100 mW) as well as other benefits related to the nature of coherent light. ...
... A semiconductor laser emits light through stimulated emission rather than spontaneous emission, which results in high output power (~100 mW) as well as other benefits related to the nature of coherent light. ...
Lecture_Feb18_2015
... incidence θi govern both the direction of reflected (R) and transmitted (T) radiation at a boundary (Snell’s Law), as well as the fraction of light transmitted versus reflected (Fresnel Equations). • By conservation of energy, R + T = 1 • The index of refraction has a real and imaginary part, and is ...
... incidence θi govern both the direction of reflected (R) and transmitted (T) radiation at a boundary (Snell’s Law), as well as the fraction of light transmitted versus reflected (Fresnel Equations). • By conservation of energy, R + T = 1 • The index of refraction has a real and imaginary part, and is ...
Space-Time-Wavelength Mapping Based
... 2. Modeling setup and theory The proposed setup is shown in Fig. 1. The optical tweezer is driven by a modelocked laser with broad bandwidth and high peak power. Here we assume 150 fs pulses with ~20 kW peak power at 50 MHz repetition rate. The laser beam propagates through a dispersive medium with ...
... 2. Modeling setup and theory The proposed setup is shown in Fig. 1. The optical tweezer is driven by a modelocked laser with broad bandwidth and high peak power. Here we assume 150 fs pulses with ~20 kW peak power at 50 MHz repetition rate. The laser beam propagates through a dispersive medium with ...
refl and refr, mirrors
... we see images where light appears to come from Consider how light from your eye reflects from a mirror to get to ...
... we see images where light appears to come from Consider how light from your eye reflects from a mirror to get to ...
Interference
... extravagant colours of many butterflies and moths arise - not from chemistry (pigments) but from physics (interference effects)!! ...
... extravagant colours of many butterflies and moths arise - not from chemistry (pigments) but from physics (interference effects)!! ...
Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... ﹡ fiber are usually coated with a thin transparent layer of glass or material of lower refractive index. Total reflection will still take place between the two. ﹡ producing of coated fibers: ① One method is to insert a thick high-refractive index glass rod in tubing of lower index. ② In a special fu ...
... ﹡ fiber are usually coated with a thin transparent layer of glass or material of lower refractive index. Total reflection will still take place between the two. ﹡ producing of coated fibers: ① One method is to insert a thick high-refractive index glass rod in tubing of lower index. ② In a special fu ...
ECEN 4616/5616 “Optoelectronic System Design” MWF 1:00 → 1:50
... Communication Systems: Using light to transport information. Computational Optics Systems: Using computer processing to supplement (or replace) some of the tasks of the optics. There is leading-edge research at CU on various aspects of this: ...
... Communication Systems: Using light to transport information. Computational Optics Systems: Using computer processing to supplement (or replace) some of the tasks of the optics. There is leading-edge research at CU on various aspects of this: ...
Lecture 1. Introduction. Nature of light, geometric optics.
... Newer: CF lens – meaning Chromatic aberration Free. ...
... Newer: CF lens – meaning Chromatic aberration Free. ...
Reflection-mode scanning near-field optical microscopy: Influence
... is observed here. The primary origin of the imaging mechanism therefore is point 1, as illustrated in Fig. 5. Light is not completely confined in the vicinity of the SNOM aperture. There are propagating waves transmitted through the aperture which are not confined below l/2. The overall confinement ...
... is observed here. The primary origin of the imaging mechanism therefore is point 1, as illustrated in Fig. 5. Light is not completely confined in the vicinity of the SNOM aperture. There are propagating waves transmitted through the aperture which are not confined below l/2. The overall confinement ...
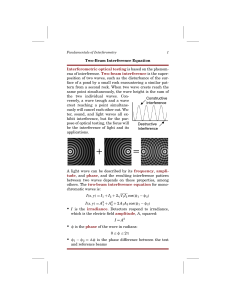
Two-Beam Interference Equation Interferometric optical testing is
... thicknesses, surface roughness, optical power, material homogeneity, distances; the list goes on. The resolution of an interferometer is governed by the wavelength of light used and is on the order of a few nanometers. In order to determine the properties of the sample under test, an interferogram i ...
... thicknesses, surface roughness, optical power, material homogeneity, distances; the list goes on. The resolution of an interferometer is governed by the wavelength of light used and is on the order of a few nanometers. In order to determine the properties of the sample under test, an interferogram i ...
Gaurav Chetna Josan - Department of Electrical Engineering
... correction using a PCM(Phase conjugate mirror). ...
... correction using a PCM(Phase conjugate mirror). ...
FTIR Instrumentation
... For example, if both interferometer mirrors are equidistant from the beamsplitter, the two light beams travel equal distances. As each beam returns to the beamsplitter, each is again split and then recombined with half of the light from the other interferometer arm. The two component beams that make ...
... For example, if both interferometer mirrors are equidistant from the beamsplitter, the two light beams travel equal distances. As each beam returns to the beamsplitter, each is again split and then recombined with half of the light from the other interferometer arm. The two component beams that make ...
REFRACTION AND REFLECTION POLARIZATION OF LIGHT
... air. As the light enters the glass of water it slows down(changes direction) and as it leaves the glass it speeds up again – therefore making the pencil look as though it is bent ...
... air. As the light enters the glass of water it slows down(changes direction) and as it leaves the glass it speeds up again – therefore making the pencil look as though it is bent ...
Imaging
... The readout register now begins to deliver the electrons to the detection device by the same process of varying the voltage applied to the electrodes, but now across the bottom row. The detection device counts the number of electrons by applying a known voltage across the final electrode. (The fina ...
... The readout register now begins to deliver the electrons to the detection device by the same process of varying the voltage applied to the electrodes, but now across the bottom row. The detection device counts the number of electrons by applying a known voltage across the final electrode. (The fina ...
SY1. CT Laser Light Accuracy Laser light accuracy must be
... which indicate the location of the radiation beam relative to the external anatomical structures of the patient, and the sagittal and coronal scan localization lights, which centre the anatomic structure of interest in the scan field of view. This can be tested in several ways as shown below: 1. Axi ...
... which indicate the location of the radiation beam relative to the external anatomical structures of the patient, and the sagittal and coronal scan localization lights, which centre the anatomic structure of interest in the scan field of view. This can be tested in several ways as shown below: 1. Axi ...
Fan, Shanhui - Quantum Electronics Group
... • Enhance light absorption at the DA interface. • Efficiently extract carriers once they are generated. ...
... • Enhance light absorption at the DA interface. • Efficiently extract carriers once they are generated. ...
Optical coherence tomography

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an established medical imaging technique that uses light to capture micrometer-resolution, three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution.Depending on the properties of the light source (superluminescent diodes, ultrashort pulsed lasers, and supercontinuum lasers have been employed), optical coherence tomography has achieved sub- micrometer resolution (with very wide-spectrum sources emitting over a ~100 nm wavelength range).Optical coherence tomography is one of a class of optical tomographic techniques. A relatively recent implementation of optical coherence tomography, frequency-domain optical coherence tomography, provides advantages in signal-to-noise ratio, permitting faster signal acquisition. Commercially available optical coherence tomography systems are employed in diverse applications, including art conservation and diagnostic medicine, notably in ophthalmology and optometry where it can be used to obtain detailed images from within the retina. Recently it has also begun to be used in interventional cardiology to help diagnose coronary artery disease. It has also shown promise in dermatology to improve the diagnostic process.